Antidepressants and suicide risk
|
Read other articles:

آنا كومنينا معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1 ديسمبر 1083(1083-12-01)القسطنطينية الوفاة 1153القسطنطينية مواطنة الإمبراطورية البيزنطية الأب ألكسيوس الأول كومنينوس[1][2] الأم ايرنا دوكاينا إخوة وأخوات يوحنا الثاني كومنين، وإسحاق كومنينوس عائلة كومنينيون الحياة الع

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang gunung di Papua Tengah. Untuk kabupaten, lihat Kabupaten Puncak Jaya. Untuk kabupaten, lihat Kabupaten Puncak. Puncak JayaGunung Puncak JayaTitik tertinggiKetinggian4.884 m (16.024 ft)[1]Masuk dalam daftarTujuh PuncakKoordinat04°04′44″N 137°09′31″E / 4.07889°N 137.15861°E / 4.07889; 137.15861Koordinat: 04°04′44″N 137°09′31″E / 4.07889°N 137.15861°E / 4.07889; 137.15861&...

Dieser Artikel beschreibt die französische Gemeinde Lechâtelet. Eine gleichlautende Gemeinde hat die Schreibweise Le Châtelet. Lechâtelet Lechâtelet (Frankreich) Staat Frankreich Region Bourgogne-Franche-Comté Département (Nr.) Côte-d’Or (21) Arrondissement Beaune Kanton Brazey-en-Plaine Gemeindeverband Communauté de communes Rives de Saône Koordinaten 47° 4′ N, 5° 9′ O47.0613888888895.145Koordinaten: 47° 4′ N, 5° 9′ O Höhe 176�...

Beebe Entidad subnacional Bandera Localización en el condado de White y en el estado de ArkansasCoordenadas 35°04′17″N 91°53′31″O / 35.0714, -91.8919Entidad Ciudad de Estados Unidos • País Estados UnidosSuperficie • Total 26,47 km² Altitud • Media 75 m s. n. m.Población (1 de abril de 2010) • Total 7315 hab. • Densidad 276,34 hab/km²Código ZIP 72012[1]Código de área 501 Sitio ...

Кудояров Габдулла Хабіровичбашк. Ҡоҙаяров Ғабдулла Хәбир улыНародився 7 червня 1899(1899-06-07)Аблаєво, Q43425723?, Белебейський повітd, Уфимська губернія, Російська імперіяПомер 14 вересня 1984(1984-09-14) (85 років)Уфа, РРФСР, СРСРКраїна Російська імперія СРСРДіяльність офтальмологAl...

Ponte viva de raíz dupla no leste de Khasi Hills Ponte viva de raíz perto do vilarejo de Kongthong sob reparos. Os War Khasis locais estão usando as jovens raízes aéreas flexíveis, de uma figueira para criar novos corrimões para a ponte. Pontes de raízes vivas são uma forma de arborescultura comum no estado indiano de Meghalaya. São feitos das raízes aéreas de árvores-de-borracha ( Ficus elastica[1][2] ) pelos povos Khasi e Jaintia. Se faz com que as raízes flexíveis cresçam e...

Ця стаття є частиною Проєкту:Населені пункти України (рівень: невідомий) Портал «Україна»Мета проєкту — покращувати усі статті, присвячені населеним пунктам та адміністративно-територіальним одиницям України. Ви можете покращити цю статтю, відредагувавши її, а на стор�...

Morihei Ueshiba(植芝 盛平 Ueshiba Morihei)Morihei UeshibaLahir(1883-12-14)14 Desember 1883Tanabe, Prefektur Wakayama, JepangMeninggal26 April 1969(1969-04-26) (umur 85)Iwama, Ibaraki, Jepangkarena karsinoma hepatoselulerGayaPendiri Aikido Morihei Ueshiba (植芝 盛平code: ja is deprecated , Ueshiba Morihei, 14 Desember 1883 – 26 April 1969) adalah pendiri seni bela diri Jepang Aikido. Di kalangan murid aikido (aikidoka), ia dipanggil Kaiso (Pendiri), atau Osensei (G...

1997 greatest hits album by Billy JoelGreatest Hits Volume IIIGreatest hits album by Billy JoelReleasedAugust 19, 1997Recorded1983–1997GenreRockLength76:08LabelColumbiaProducerPhil Ramone, Mick Jones, Billy Joel, Danny Kortchmar, Joe Nicolo, David ThoenerBilly Joel chronology River of Dreams(1993) Greatest Hits Volume III(1997) The Complete Hits Collection: 1973–1997(1997) Singles from Greatest Hits Volume III To Make You Feel My LoveReleased: August 13, 1997 Hey GirlReleased: Oct...

River in Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir, tributary of the Jhelum River This article is about the river in Jammu and Kashmir. For the river in Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, see Sindh River. This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: Unencyclopedic language. Please help improve this article if you can. (March 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Sind RiverSind RiverLocationCountryIndiaUnion territoryJammu and...

United States historic placeOld U.S. Post Office and CourthouseU.S. National Register of Historic Places Show map of MiamiShow map of FloridaShow map of the United StatesLocationMiami, FloridaCoordinates25°46′31.3854″N 80°11′31.8402″W / 25.775384833°N 80.192177833°W / 25.775384833; -80.192177833NRHP reference No.88002962[1]Added to NRHPJanuary 4, 1989 The Old U.S. Post Office and Courthouse is a historic courthouse in Miami, Florida. It is...

1999 film directed by K. S. Ravikumar Sneham KosamTheatrical posterDirected byK. S. RavikumarScreenplay byK. S. Ravikumar Dialogues byParuchuri Brothers Story byJyothi KrishnaBased onNatpukkagaProduced byA. M. RathnamStarringChiranjeeviMeenaCinematographyK. DatthuEdited byKola BhaskarMusic byS. A. RajkumarProductioncompanySri Surya MoviesRelease date1 January 1999CountryIndiaLanguageTelugu Sneham Kosam (transl. For friendship) is a 1999 Indian Telugu-language drama film produced by A. M...

Village outside Uppsala in Sweden Gamla Uppsala is an area rich in archaeological remains: seen from the grave field whose larger mounds (left part) are close to the royal mounds. The building beyond the mounds is the church and to its right is the low Ting-mound and then Gamla Uppsala museum. Gamla Uppsala (Swedish: [ˈɡâmːla ˈɵ̂pːˌsɑːla], Old Uppsala) is a parish and a village outside Uppsala in Sweden. It had 17,973 inhabitants in 2016.[1] As early as the 3rd cent...

トヨタ・ハリアー 4代目 G 4WD概要製造国 日本販売期間 1997年 -ボディボディタイプ 5ドア クロスオーバーSUV駆動方式 FF / 4WDテンプレートを表示 ハリアー(HARRIER)は、トヨタ自動車が製造・販売している高級中型クロスオーバーSUVである。 概要 「高級サルーンの乗り心地と快適性を兼ね備えたクロスオーバーSUV」として開発され、1997年に初代モデルが発売された。「高�...

Count of Luxemburg and Arlon Henry VICount of Luxemburg and ArlonReign24 December 1281 – 5 June 1288PredecessorHenry VSuccessorHenry VIIBornc. 1240Died5 June 1288 (aged 48)WorringenSpouseBeatrice d'AvesnesIssuemore...Henry VII, Holy Roman EmperorBaldwin, Archbishop of TrierHouseLuxembourgFatherHenry V, Count of LuxembourgMotherMargaret of Bar Henry VI (c. 1240 – 5 June 1288) was Count of Luxembourg and Arlon from the death of his father, Henry V the Blond, in 1281 until h...

1922 film EnvironmentDirected byIrving CummingsWritten byHarvey GatesProduced byIrving Cummings Sol LesserStarringMilton Sills Alice Lake Gertrude ClaireProductioncompanyIrving Cummings ProductionsDistributed byPrincipal DistributingRelease dateDecember 1, 1922Running time60 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguagesSilent English intertitles Environment is a 1922 American silent crime film directed by Irving Cummings and starring Milton Sills, Alice Lake and Gertrude Claire.[1] Synopsis As...

Hereford Nomenclatura biológica Bos taurusRegión de origen Herefordshire, InglaterraCaracterísticasTipo BovinoPelaje rojo cereza al rojo abayadoCabeza blancaOtros datosUtilización Producción de carne[editar datos en Wikidata] Hereford es una raza bovina originaria de Inglaterra[1][2] , productora de carne Los animales de esta raza se identifican por ser colorados desde bayo a cereza con manchas blanco puro en la cabeza, parte posterior de las orejas, pecho, vientr...

UzbekistanJulukanOq boʻrilar/(White Wolves)AsosiasiFederasi Sepak Bola UzbekistanKonfederasiAFC (Asia)Sub-konfederasiCAFA (Asia Tengah)Stadion kandangStadion Pakhtakor MarkaziyKode FIFAUZB Warna pertama Warna kedua Piala Dunia U-20 FIFAPenampilan4 (Pertama kali pada 2003)Hasil terbaikQuarterfinals: 2013, 2015Kejuaraan U-19 AFCPenampilan7 (Pertama kali pada 2002)Hasil terbaik Runners-up, 2008 Tim nasional sepak bola U-20 Uzbekistan mewakili Uzbekistan dalam kompetisi sepak bola internasional ...
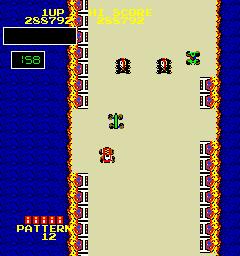
Bump 'n' JumpvideogiocoSchermata di Burnin' Rubber col livello 12PiattaformaArcade, Atari 2600, Intellivision, Commodore 64, ColecoVision, NES, Sharp MZ, Sharp X1 Data di pubblicazioneArcade: 1982Conversioni: 1983-1986 GenereSimulatore di guida OrigineGiappone SviluppoData East PubblicazioneData East, Bally Midway Modalità di giocoGiocatore singolo o 2 alternati Periferiche di inputJoystick SupportoCartuccia, cassetta Specifiche arcadeCPUM6502 a 750 kHz Proces...

Development of Mother 3 The development of Mother 3, a role-playing video game from Nintendo, spanned a total of twelve years between 1994 and 2006 with a three year gap in between, and spanned four consoles and multiple delays. Following the commercial success of its predecessor, Mother 2 (EarthBound outside Japan), Mother series creator Shigesato Itoi was given the previous game's development team. Inspired by Super Mario 64, the team set out to create a 3D game that ultimately exceeded the...

