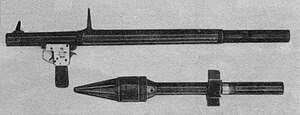
RPG-2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع مارك سوليفان (توضيح). هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (فبراير 2019) مارك سوليفان معلومات شخصية الميلاد 20 أكتوبر 1964 (59 سنة) الجنسية جنوب إفريقيا الحياة العملية المهنة لاعب كر

Prairie Condado Ubicación del condado en Arkansas Ubicación de Arkansas en EE.UU.Coordenadas 34°49′41″N 91°32′12″O / 34.828055555556, -91.536666666667Capital Des Arc y De Valls BluffEntidad Condado • País Estados Unidos • Estado Arkansas • Sede Des Arc y De Valls BluffFundación 25 de octubre 1846Superficie • Total 1750 km² • Tierra 1673 km² • Agua (4.43%) 78 km²Población (2000)

Derde Coalitieoorlog Onderdeel van de napoleontische oorlogen Napoleon tijdens de Slag bij Austerlitz, geschilderd door François Gérard Datum 1805–1806 Locatie Centraal-Europa, Italië en Atlantische Oceaan Resultaat Franse overwinning Oprichting van het Eerste Franse Keizerrijk Oprichting van de Confederatie van de Rijn Ontbinding van het Heilige Roomse Rijk Vierde Coalitieoorlog enkele maanden later Strijdende partijen Derde Coalitie: Keizerrijk Oostenrijk Russische Rijk Verenigd Konink...

Este artículo o sección necesita referencias que aparezcan en una publicación acreditada.Este aviso fue puesto el 30 de junio de 2015. Jean Bourgain Información personalNacimiento 28 de febrero de 1954 Ostende (Bélgica) Fallecimiento 22 de diciembre de 2018 (64 años)Bonheiden (Bélgica) Nacionalidad BelgaLengua materna Francés EducaciónEducado en Universidad Libre de Bruselas (flamenca) (Doctorate)Universidad Libre de BruselasUniversidad libre de Bruselas Supervisor doctoral Fred...

Der Titel dieses Artikels ist mehrdeutig. Weitere Bedeutungen sind unter Fritz Lang (Begriffsklärung) aufgeführt. Fritz Lang mit dem Kameramann Curt Courant (Mitte) bei den Dreharbeiten zum Stummfilm Frau im Mond (1929) Die Familie Lang wohnte seit 1900 nachweislich im Haus Zeltgasse 1 (zugleich Piaristengasse 28 und Neudeggergasse 23), womit die Gedenktafel fehlerhaft ist.[1] Friedrich „Fritz“ Christian Anton Lang (* 5. Dezember 1890 in Wien; † 2. August 1976 i...

Portrait of Gioachino Rossini by Vincenzo Camuccini, Museo Teatrale alla Scala in Milan. This is a list of the works of the Italian composer Gioachino Rossini (1792–1868). Operas See List of operas by Gioachino Rossini. Incidental music Edipo a Colono (1817) Cantatas Il pianto d'armonia sulla morte di Orfeo (1808) La morte di Didone (1811) Dalle quete e pallid'ombre (1812) Egle ed Irene (1814) L'aurora (1815) Le nozze di Teti e di Peleo (1816) Omaggio umiliato (1819) Cantata... 9 maggio 181...

Naval warfare branch of Bahrain's military Royal Bahrain Naval Forceسلاح البحرية الملكية البحرينيةFounded1979Country BahrainBranchNaval ForceSize1770 (Navy and Coastguard)Part ofMinistry of DefenseBahrain Defense ForceNickname(s)RBNFEquipment58 shipsEngagementsInvasion of KuwaitGulf WarCommandersCommander of the NavyRear Admiral Mohammed Yousif al-AsamInsigniaNaval EnsignNaval Flag and jackMilitary unit The Royal Bahrain Naval Force (RBNF) (previously know...
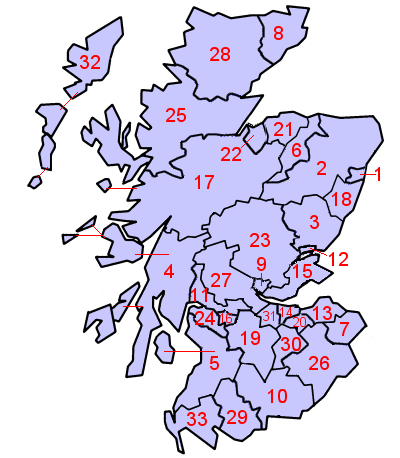
De Lieutenancy areas van Schotland zijn de gebieden waarin Schotland is verdeeld voor ceremoniële doeleinden. Zij stemmen ongeveer - maar niet helemaal - overeen met de historische graafschappen. Daarnaast is de naam nog in gebruik voor een gebiedscommissie van de Highland Council. De steden Aberdeen, Dundee, Edinburgh en Glasgow hebben een oud recht om zelf hun Lord Lieutenant te kiezen, die dan Lord Provost wordt genoemd en optreedt als burgemeester. Lieutenancy Areas van Schotland Aberdee...

1956 studio album by Buddy RichBuddy Rich Sings Johnny MercerStudio album by Buddy RichReleased1956RecordedJanuary 4–6, 1956GenreVocal jazzLength40:53LabelVerveProducerNorman GranzBuddy Rich chronology The Lionel Hampton Art Tatum Buddy Rich Trio(1956) Buddy Rich Sings Johnny Mercer(1956) This One's for Basie(1956) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmusic[1] Buddy Rich Sings Johnny Mercer is a 1956 studio album by Buddy Rich, of the lyrics of Johnny Mercer, arra...

2007 studio album by Kanye West This article is about the Kanye West album. For other albums, see Graduation (disambiguation) § Music. GraduationStudio album by Kanye WestReleasedSeptember 11, 2007 (2007-09-11)Recorded2005–2007StudioChung KingSony Music (New York City)ChaliceRecord Plant (Los Angeles)Genre Hip hop pop rap alternative rap progressive rap Length51:23Label Def Jam Roc-A-Fella Producer Kanye West Brian AllDay Miller DJ Toomp Eric Hudson Nottz Warryn Bab...

Artikel utama: Bus kota di Surabaya § Rute perjalanan Bus KotaPurabaya – Ngagel – SemutUnit bus kota trayek A2 milik PO Estraa Mandiri melintasi Jalan Ahmad Yani, Surabaya, 27 Oktober 2011. Salah satu trayek bus kota reguler di Surabaya adalah trayek A2 dengan relasi Terminal Purabaya – Ngagel – Semut. Jenis tingkatan layanan trayek ini tergolong dalam kelas ekonomi. Trayek ini memiliki rute lintasan sepanjang 16 km. Rute lintasan trayek ini melewati jalan arteri kawasan dalam k...

2017 single by Ruth BSuperficial LoveSingle by Ruth Bfrom the album The Intro and Safe Haven ReleasedFebruary 24, 2017 (2017-02-24)GenrePopLength3:27 (EP version)3:39 (single version)Label Columbia Sony Songwriter(s)Ruth BerheProducer(s)BerheRuth B singles chronology Lost Boy (2015) Superficial Love (2017) Rare (2018) Music videoSuperficial Love on YouTube Superficial Love is a single by Canadian singer Ruth B. It was originally released on November 27, 2015, alongside her debu...

Malaysian politician This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (February 2023) In this Malay name, there is no family name. The name Mahat is a patronymic, and the person should be referred to by the given name, Abu Samah. The Arabic-derived word bin or binti/binte, if used, means 'son of' or 'daughter of', respectively. Abu Samah bin Mahat is a Malaysian politician who served ...

13th season of FIA Formula One motor racing 1959 Formula One season Drivers' Champion: Jack BrabhamInternational Cup Champion: Cooper-Climax Previous 1958 Next 1960 Races by countryRaces by venue The 1959 Formula One season was the 13th season of FIA Formula One motor racing. It featured the 1959 World Championship of Drivers and the 1959 International Cup for F1 Manufacturers, contested concurrently over a nine-race series [1] which commenced on 10 May and ended on 12 December. The s...

TinorangsakTinorangsak babi, terong dan nasiNama lainTinoransakSajianHidangan utamaTempat asalIndonesiaDaerahSulawesi UtaraDibuat olehMasakan ManadoSuhu penyajianHangatBahan utamaDaging babi, daging lain, ayam, atau makanan laut hangat dalam campuran bumbu rempah-rempah Tinorangsak atau tinoransak adalah sebuah jenis hidangan daging hangat dan pedas yang memakai bumbu campuran rempah-rempah yang ditemukan dalam masakan Manado dari Sulawesi Utara, Indonesia.[1] Daging paling umum yang ...

Джамбия из Йемена Продавец кинжалов джамбия на улице Таиза (Йемен)Джамби́я (араб. جنۢبية) — восточный кинжал с широким загнутым клинком без гарды. Элемент национального мужского костюма йеменцев. В Йемене джамбию носят большинство лиц мужского пола.[1] Кинжал-д...

Cuban ballerina (1920–2019) For the Filipina actress, see Alicia Alonzo. Alicia AlonsoAlicia Alonso in 1955BornAlicia Ernestina de la Caridad del Cobre Martínez del Hoyo(1920-12-21)21 December 1920Havana, CubaDied17 October 2019(2019-10-17) (aged 98)Havana, CubaNationalityCubanOccupationBallet dancerSpouses Fernando Alonso (m. 1937; div. 1975) Pedro Simón Martínez (m. 1975) Children1 Alicia Al...

Historic seaport, now part of Elkridge, MD, US Elkridge LandingElkridge Main StreetLocationElkridge, MarylandCoordinates39°12′58.09″N 76°42′33.22″W / 39.2161361°N 76.7092278°W / 39.2161361; -76.7092278Area100 acresFounded1690 U.S. Historic districtOfficial nameElkridge Landing Historic DistrictDesignated2003Reference no.HO-784 Location of Elkridge Landing in Maryland Elkridge Landing was a Patapsco River seaport in Maryland, and is now part of Elkridge...

ACT III Theatres Act III Theatres was an American company that owned movie theater multiplexes and screens principally located in the U.S. states of Texas, Oregon and Washington. The company was in business from 1986 to 1997, when it was sold to Kohlberg Kravis Roberts (KKR). Television producer Norman Lear owned a controlling stake in Act III Theatres through his company Act III Communications.[1] At the time of sale in 1997, Act III Theaters consisted of 124 multiplex theaters opera...

Long-haul airline of French Polynesia For the domestic airline, see Air Tahiti. Air Tahiti Nui IATA ICAO Callsign TN THT TAHITI AIRLINES Founded31 October 1996; 27 years ago (1996-10-31)Commenced operations20 November 1998; 25 years ago (1998-11-20)HubsFaa'a International AirportFrequent-flyer programClub TiareFleet size4Destinations5HeadquartersPapeete, Tahiti, French Polynesia, FranceKey peopleMichel Monvoisin (CEO)Websitewww.airtahitinui.com Air Tahiti N...