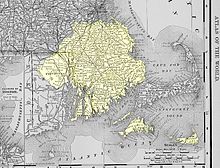
Pokanoket
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Pertemuan Abraham dan Melkisedek — oleh Dirk Bouts, 1464–67 Melkisedek dalam bahasa Ibrani Malki-tsedeq yang artinya rajaku atau raja kebenaran.[1] Melkisedek adalah seorang raja di negeri Salem (atau disebut juga Yerusalem).[1] Namanya disebut 12 kali dalam 12 ayat di Alkitab: 1 kali dalam Kejadian 14:17–24, 1 kali dalam Mazmur 110:4, dan 10 kali dalam surat Ibrani (pasal 5-7). Dalam kitab Kejadian 14:17-24, diceritakan bahwa Melkisedek adalah seorang imam Allah yang Ma...

Paços de Ferreira Freguesia de Portugal Iglesia parroquial de la freguesia Escudo Paços de FerreiraLocalización de Paços de Ferreira en PortugalCoordenadas 41°16′33″N 8°22′41″O / 41.27596, -8.37794Entidad Freguesia de Portugal • País Portugal • Distrito Oporto • Municipio Paços de FerreiraSuperficie • Total 6,08 km² Población (2021) • Total 9679 hab. • Densidad 1591,94 hab/km²[...

Prafulla Chandra GhoshPrafullachandra Ghosh di Writers' Building pada 1947Ketua Menteri Bengal Barat ke-1Masa jabatan2 November 1967 – 20 Februari 1968GubernurDharma ViraPendahuluAjoy Kumar MukherjeePenggantiPemerintahan presidenMasa jabatan15 Agustus 1947 – 22 Januari 1948GubernurC. RajagopalachariPendahuluJabatan didirikanPenggantiB. C. Roy Informasi pribadiLahir24 Desember 1891Maliakanda, Dohar, Dhaka, India Britania (kini Bangladesh)[1][2][3&#...

Токонаме 34°53′11″ пн. ш. 136°49′56″ сх. д.H G OРегіон Чюбу, Східномор'яПрефектура АйтіКод 23216-5Площа 55,63 км²[1]Населення 55 196 осіб(Станом на 1 серпня 2011)Густота 992 осіб/км²Зв'язок Офіційна сторінка Карти: Інститут географії Японії • Google • Bing • ...

Zhong NanshanFonctionsMembre du comité national de la conférence consultative politique du peuple chinois10e comité national de la conférence consultative politique du peuple chinois (d)9e comité national de la conférence consultative politique du peuple chinois (d)8e comité national de la conférence consultative du peuple chinois (d)Député12e Assemblée nationale populaire (en)11e Assemblée nationale populaire (en)BiographieNaissance 20 octobre 1936 (87 ans)Nankin (d)Nom dans...

White Supremacist Politician Alfred Moore WaddellAlfred M. Waddell between 1865 and 1880Mayor of Wilmington, North Carolinade facto, unlawful[a]In officeNovember 10, 1898 – 1906Preceded bySilas P. WrightSucceeded byWilliam E. SpringerMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom North Carolina's 3rd districtIn officeMarch 4, 1871 – March 3, 1879Preceded byOliver H. DockerySucceeded byDaniel L. Russell Personal detailsBornSeptember 16, 1834Hillsborou...

Cámara Venezolana de la Construcción Sede de la Cámara Venezolana de la Construcción en Caracas[editar datos en Wikidata] La Cámara Venezolana de la Construcción es una asociación civil de interés colectivo, sin fines de lucro, que tiene por objeto el fomento, desarrollo y protección de la Industria de la Construcción en Venezuela.[1] La Cámara esta afiliada a la Federación de Cámaras y Asociaciones de Comercio y Producción de Venezuela (Fedecámaras) y en la Fe...

American social scientist Donald T. CampbellBorn(1916-11-20)November 20, 1916Grass Lake, Michigan, U.S.DiedMay 6, 1996(1996-05-06) (aged 79)Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, U.S.NationalityAmericanAlma materUniversity of California, BerkeleyScientific careerFieldsPsychology, social scienceInstitutionsLehigh UniversityNorthwestern University Donald Thomas Campbell (November 20, 1916 – May 6, 1996) was an American social scientist. He is noted for his work in methodology. He coined the term ...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) برادلي دينتون معلومات شخصية الميلاد 7 يونيو 1958 (65 سنة)[1] تواندا[2] مواطنة الولايات المتحدة[3][4][5][2] الحياة العملية المدرسة الأ

Sexy Cat no Enzetsu / Mukidashi de Mukiatte / Sō ja NaiLagu oleh Morning MusumeDirilis23 November 2016 (2016-11-23) (Jepang)FormatCD single, DVDGenreJ-pop, electronica, diskoDurasi26:58LabelZetimaProduserTsunkuVideo musikSexy Cat no Enzetsu di YouTubeVideo musikMukidashi de MukiatteVideo musikSō ja Nai Sexy Cat no Enzetsu / Mukidashi de Mukiatte / Sō ja Nai (セクシーキャットの演説/ムキダシで向き合って/そうじゃないcode: ja is deprecated )[1] adala...

Sint-Remacluskerk De Sint-Remacluskerk (Frans: Église Saint-Remacle) is de parochiekerk van Cahottes, een kerkdorp in de Belgische gemeente Flémalle. Het betreft een eenbeukige bakstenen kerk in neoclassicistische stijl met een geveltorentje dat bekroond wordt door een ingesnoerde naaldspits. Het kerkje werd in 1846 gebouwd. Spoedig bleek het te klein te zijn en 1887 werd de kerk, naar ontwerp van Demany, vergroot met een transept en een koor met halfronde koorsluiting. De kerk bezit een ma...

Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Bahasa Isyarat Prancis – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Maret 2011) Bahasa Isyarat Prancis LSFLangue des Signes FrançaiseFranzösische GebärdenspracheLingua dei Segni FranceseSign Gallic...

Town in Victoria, AustraliaYarckVictoriaGeneral storeYarckCoordinates37°05′23″S 145°36′40″E / 37.08972°S 145.61111°E / -37.08972; 145.61111Population168 (2016 census)[1]Postcode(s)3719Location 166 km (103 mi) NE of Melbourne 55 km (34 mi) W of Mansfield 14 km (9 mi) NW of Alexandra LGA(s)Shire of MurrindindiState electorate(s)EildonFederal division(s)Indi Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yarck, Victoria. Yarc...

The Small Five Group or S-5 is a group of five small member states of the United Nations that works to improve the working methods of the Security Council. Its main goal is to increase transparency, accountability, and access for non-members. Members The S-5 Group is composed of five small states: Costa Rica Jordan Liechtenstein Singapore Switzerland Background Since the early 1990s, the working methods of the Security Council have been a source of concern to the wider membership of the Unite...

Hindu temple in Karnataka This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Kukke Subramanya Temple – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Kukke Subramanya TempleKukke Sri Subramanya TempleThe Gopura of the TempleReligionAffiliationHin...

غوريفسك شعار الاسم الرسمي (بالألمانية: Neuhausen)(بالروسية: Гурьевск) الإحداثيات 54°46′00″N 20°36′00″E / 54.766666666667°N 20.6°E / 54.766666666667; 20.6 تاريخ التأسيس 1262 تقسيم إداري البلد روسيا[2] الاتحاد السوفيتي (28 يناير 1945–26 ديسمبر 1991)[1] خصائص جغرافية &...

This article is about the 2012 browser game. For other meanings, see Clop. 2012 video gameCLOPDeveloper(s)Bennett FoddyRelease2012Genre(s)SportsMode(s)Single-player CLOP is a 2012 Flash game made by Australian game designer Bennett Foddy. It is considered a spiritual successor Foddy's previous game, QWOP, released four years prior which had gone on to become a viral sensation. Similarily to QWOP, the player is tasked with controlling a unicorn, rather than an athletic runner, and escort it to...

Salten Kraftsamband ASTypePrivateIndustryPowerFounded1956HeadquartersFauske, NorwayArea servedSaltenProductsHydroelectricityNumber of employees150 (2007)Websitewww.sks.no Salten Kraftsamband or SKS is a Norwegian power company that operates eight hydroelectric power stations with annual production of 1,770 GWh. Since 1997 the company has also sold power to end-users. Head offices are located in Fauske. Head office in Fauske The company is owned by the City of Bodø (47.72%), Troms Kraft (20.3...

Device or system that exhibits resonance For other uses, see Resonator (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Resonator – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) A resonator is a device or system that exhibits ...

Firearm created using 3D printing The Liberator, a 3D-printable single-shot handgun which was the first printable firearm design made widely available online in 2013 The Come and Take It (Folder) flag, a symbol used by Deterrence Dispersed (now Gatalog), as well as 3D-printed gun proponents and hobbyists[citation needed] A 3D printed firearm, is a firearm that is partially or primarily produced with a 3D printer . While plastic printed firearms are associated with improvised firearms,...