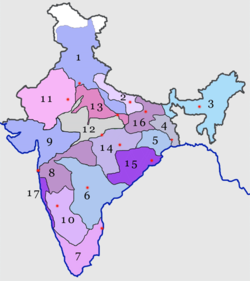
North Western Railway zone
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Ця стаття має кілька недоліків. Будь ласка, допоможіть удосконалити її або обговоріть ці проблеми на сторінці обговорення. Ця стаття потребує упорядкування для відповідності стандартам якості Вікіпедії. Будь ласка, допоможіть поліпшити цю статтю. Можливо, сторінка обгов

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Nikolay Ivanovich ShchetininNama asliНиколай Иванович ЩетининLahir21 Maret 1921Desa Mikhayevsky, Vologda Governorate, RSFS RusiaMeninggal3 Oktober 1968Vologda, Uni SovietPengabdian Soviet UnionDinas/cabangTentara MerahLama&#...

Guo Guangchang 郭广昌LahirFebruari 1967 (umur 56)Dongyang, Zhejiang, TiongkokPendidikanUniversitas FudanPekerjaanPengusahaDikenal atasPendiri dan ketua Fosun International LimitedKekayaan bersihUS$6.3 miliar (November 2019)Suami/istriWang JinyuanAnak3 Guo Guangchang (Hanzi sederhana: 郭广昌; Hanzi tradisional: 郭廣昌, kelahiran Februari 1967) adalah seorang pengusaha dan investor Tiongkok. Ia adalah ketua dan pendiri Fosun International Limited, dan perwakilan ...

For other uses, see Huanggang (disambiguation). Prefecture-level city in Hubei, People's Republic of ChinaHuanggang 黄冈市HwangkangPrefecture-level cityClockwise: Huanggang skyline, Li Siguang Memorial Museum, Shopping street in Huangzhou, Mount Tashan near Fengshan.Location of Huanggang City jurisdiction in HubeiHuanggangLocation of downtown Huanggang in HubeiCoordinates (Huanggang municipal government): 30°27′13″N 114°52′21″E / 30.4537°N 114.8724°E...

2019 Indian Tamil-language action drama film Namma Veettu PillaiTheatrical release posterDirected byPandirajWritten byPandirajProduced byKalanithi MaranStarringSivakarthikeyanAishwarya RajeshAnu EmmanuelCinematographyNirav ShahEdited byRubenMusic byD. ImmanProductioncompanySun PicturesDistributed byRed Giant MoviesRelease date September 27, 2019 (2019-09-27) Running time152 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageTamilBudget₹40 crore[1]Box office₹70 crore[1] Na...

UK and Canada bowling and minigolf centre operator This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Hollywood Bowl Group – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Hollywood Bowl Group PLCTypePublic companyTraded asLSE: BOWLHeadquartersH...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع دار السلام (توضيح). هذه المقالة عن دار السلام في تنزانيا. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع دار السلام. دار السلام (تنزانيا) تاريخ التأسيس 1862 تقسيم إداري البلد تنزانيا [1][2] عاصمة لـ تنزانيا (–1996)إقليم تنجانيقا [لغات أخرى]تنجانيقاإق�...

Koordinat: 0°34′01″S 117°06′35″E / 0.56697°S 117.10986°E / -0.56697; 117.10986 Universitas Islam Negeri Sultan Aji Muhammad Idris SamarindaMotoMencetak Generasi yang Memiliki Kecerdasan Intelektual, spiritual, dan ProfesionalJenisPerguruan tinggi Islam negeri di IndonesiaDidirikan12 Dzulqaidah 1417 H / 21 Maret 1997 M(SK Presiden RI No. 11, tahun 1997)Lembaga indukKementerian Agama Republik IndonesiaAfiliasiIslamRektorProf. Dr. Zurqoni, M.AgLokasiSamarinda,...

Street in Portland, Oregon, U.S. Stark StreetStreet signage, 2011LocationPortland, Oregon, U.S. Stark Street is an east-west-running street in Portland, Oregon, in the United States. The street is named after Benjamin Stark, and Southeast Stark Street and Southwest Stark Street are divided by the Willamette River. In late 2017, activists proposed renaming Southwest Stark Street for gay rights activist Harvey Milk, noting that Stark was an unapologetic racist who advocated for slavery.[1&#...

American soccer player and general manager Yael Averbuch West Averbuch in 2015Personal informationFull name Yael Averbuch WestBirth name Yael Friedman Averbuch[1]Date of birth (1986-11-03) November 3, 1986 (age 37)Place of birth New York, New York, United StatesHeight 5 ft 10 in (1.78 m)Position(s) DefenderTeam informationCurrent team NJ/NY Gotham FC (general manager)Youth career Monclair Kangaroos Montclair Mavericks Ramapo WildcatsCollege careerYears Team Apps (G...

Highway in Maryland This article is about the highway currently numbered Interstate 895. For other uses, see Interstate 895 (disambiguation). Interstate 895Harbor Tunnel ThruwayI-895 and spurs highlighted in redRoute informationAuxiliary route of I-95Maintained by MDTALength11.44 mi[1] (18.41 km)NHSEntire routeRestrictionsNo hazardous goods allowed in the Baltimore Harbor TunnelMajor junctionsSouth end I-95 in ElkridgeMajor intersections US 1 in Elkridge I-695...

Human settlement in EnglandShipleyChurch of St. Mary the Virgin,viewed from the windmillShipleyLocation within West SussexArea31.26 km2 (12.07 sq mi) [1]Population1,075 [1] 2001 Census 1,147 (Census 2011)[2]• Density34/km2 (88/sq mi)OS grid referenceTQ144219• London37 mi (60 km) NNECivil parishShipleyDistrictHorshamShire countyWest SussexRegionSouth EastCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited Kingdom...

Bagian dari seri mengenai Sejarah Mesir Mesir Prasejarahpra–3100 SM Mesir Kuno Periode Dinasti Awal3100–2686 SM Kerajaan Lama2686–2181 SM Periode Menengah ke-12181–2055 SM Kerajaan Pertengahan2055–1650 SM Periode Menengah ke-21650–1550 SM Kerajaan Baru1550–1069 SM Periode Menengah ke-31069–664 SM Periode Akhir664–332 SM Mesir Akhemeniyah525–332 SM Zaman Klasik Mesir Makedonia dan Ptolemaik332–30 SM Mesir Romawi dan Bizantium30 SM–641 M Mesir Sasaniyah619–629 Timur Te...

النشيد الملكي (Marcha Real) (Marcha Granadera) البلد إسبانيا تأليف بارطولومي بيريث كاساس (1908 كأول توزيع موسيقي معاصر) نوبة الإستهلال لابن باجة (محتمل) (القرن 12) تلحين فرانثيسكو غراو حسب الصيغة التي أقرها المرسوم الملكي 1560/1997 (1997) اللغة الإسبانية استمع للنشيد تعديل مصدري - تعديل &#...

American animated television series Donald Duck PresentsTitle screenGenreAnthologyStarringDonald Duck (voiced by Clarence Nash)Theme music composerPhil BaronWill RyanOpening themeDonald Duck PresentsEnding themeDonald Duck PresentsCountry of originUnited StatesNo. of seasons2ProductionRunning time28 minutesProduction companyWalt Disney ProductionsOriginal releaseNetworkThe Disney ChannelReleaseSeptember 1, 1983 (1983-09-01) –November 1, 1992 (1992-11-01)RelatedGood Morning, M...

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: International Road Assessment Programme – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The International Road Assessment Programme or iRAP assesses roads all over the world and aims to significantly reduce road ...

Island in North Maluku, Indonesia MangoliMangoliLocation of Mangole Island on a topographic map of the Maluku IslandsGeographyLocationSouth East AsiaCoordinates1°48′S 125°48′E / 1.8°S 125.8°E / -1.8; 125.8ArchipelagoMaluku IslandsArea2,142.48 km2 (827.22 sq mi)AdministrationIndonesiaProvinceNorth MalukuDemographicsPopulation39,736 (2020 Census)Pop. density18.55/km2 (48.04/sq mi) The Sula Islands, showing Mangole Mangoli or Mangole (Xulla Man...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Луизиана (значения). Штат США Луизиана англ. State of Louisiana Флаг Луизианы Печать Луизианы Девиз штата «Союз, справедливость и уверенность» Прозвище штата «Штат пеликанов» Столица Батон-Руж Крупнейший город Новый Орлеан Кру�...

Cocktail traditionally made with cognac, orange liqueur and lemon For other uses, see Sidecar (disambiguation). SidecarIBA official cocktailTypeCocktailBase spirit Cognac ServedStraight up: chilled, without iceStandard drinkware Cocktail glassIBA specifiedingredients† 50 ml cognac 20 ml triple sec 20 ml fresh lemon juice PreparationPour all ingredients into a cocktail shaker, shake well with ice, strain into a chilled cocktail glass.Commonly servedAll Day† Sidecar recipe at...

Spanish cardinal This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: John de Lugo – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) His EminenceJohn de LugoJohn de LugoDioceseDiocese of RomeAppointed17 October 1644Term ended20 August 1660Order...