Khanty
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1944 film by Mitchell Leisen Frenchman's CreekTheatrical posterDirected byMitchell LeisenScreenplay byTalbot JenningsBased onFrenchman's Creek1941 novelby Daphne Du MaurierProduced byBuddy G. DeSylvaStarringJoan FontaineArturo de C├│rdovaBasil RathboneCinematographyGeorge BarnesEdited byAlma MacrorieMusic byVictor YoungProductioncompanyParamount PicturesDistributed byParamount PicturesRelease date September 20, 1944 (1944-09-20) Running time113 minutesCountryUnited StatesLangua...
┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® ž¬žŁž¬ž¦ž¼ ┘ä┘ä┘ģž▓┘Ŗž» ┘ģ┘å ž¦┘ä┘łžĄ┘䞦ž¬ ┘ä┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘䞦ž¬ ž¦┘䞯ž«ž▒┘ē ┘ä┘ä┘ģž│ž¦ž╣ž»ž® ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¬ž▒ž¦ž©žĘ ┘ģ┘鞦┘䞦ž¬ ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘łž│┘łž╣ž®. ┘üžČ┘ä┘ŗž¦ ž│ž¦ž╣ž» ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¬žŁž│┘Ŗ┘å ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® ž©žźžČž¦┘üž® ┘łžĄ┘䞦ž¬ žź┘ä┘ē ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘䞦ž¬ ž¦┘ä┘ģž¬ž╣┘ä┘éž® ž©┘枦 ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘łž¼┘łž»ž® ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¦┘ä┘åžĄ ž¦┘䞣ž¦┘ä┘Ŗ. (┘Ŗ┘ł┘å┘Ŗ┘ł 2023) ┘Ŗ┘üž¬┘éž▒ ┘ģžŁž¬┘ł┘ē ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® žź┘ä┘ē ž¦┘䞦ž│ž¬ž┤┘枦ž» ž©┘ģžĄž¦ž»ž▒. ┘üžČ┘䞦┘ŗžī ž│ž¦┘ć┘ģ ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¬žĘ┘ł┘Ŗž▒ ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® ┘ģ

Yehezkiel 44Kitab Yehezkiel 30:13ŌĆō18 pada suatu naskah bahasa Inggris dari awal abad ke-13, MS. Bodl. Or. 62, fol. 59a. Teks bahasa Ibrani disalin sebagaimana dalam kodeks bahasa Latin. Terjemahan bahasa Latin ditulis di bagian marjin.KitabKitab YehezkielKategoriNevi'imBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen26← pasal 43 pasal 45 → Yehezkiel 44 (disingkat Yeh 44) adalah bagian dari Kitab Yehezkiel dalam Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama di Alkitab Kristen....

ąŻ ąÆč¢ą║č¢ą┐ąĄą┤č¢čŚ čö čüčéą░čéčéč¢ ą┐čĆąŠ č¢ąĮčłąĖčģ ą╗čÄą┤ąĄą╣ č¢ąĘ ą┐čĆč¢ąĘą▓ąĖčēąĄą╝ ąÜą░ą│ąĄąĮąĄą║. ąÜą╗ąĄą╝ąĄąĮčü-ąōąĄąĮčĆč¢čģ č乊ąĮ ąÜą░ą│ąĄąĮąĄą║ąĮč¢ą╝. Clemens-Heinrich Graf von KageneckąØą░čĆąŠą┤ąĖą▓čüčÅ 17 ąČąŠą▓čéąĮčÅ 1913(1913-10-17)[1]ąæąĄčĆą╗č¢ąĮ, ąØč¢ą╝ąĄčåčīą║ą░ č¢ą╝ą┐ąĄčĆč¢čÅą¤ąŠą╝ąĄčĆ 18 ą▒ąĄčĆąĄąĘąĮčÅ 2005(2005-03-18)[1] (91 čĆč¢ą║)ąæą░ą┤-ąōąŠą╝ą▒čāčĆęæ, ąöą░čĆą╝čłčéą░ą┤čé, ąōąĄčüčüąĄąĮ, ąØč¢ą╝ąĄčćčćąĖąĮą░ąÜčĆą░茹Įą░ ąØč¢ą╝ąĄčćčćąĖąĮą░ąŚąĮą░ąĮąĮčÅ...

Esta p├Īgina cita fontes, mas que n├Żo cobrem todo o conte├║do. Ajude a inserir refer├¬ncias. Conte├║do n├Żo verific├Īvel pode ser removido.ŌĆöEncontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Setembro de 2020) Negeri SembilanGeografiaPa├Łs Mal├ĪsiaSede Seremban (en)├ürea 6 686 km2Coordenadas 2┬░ 45ŌĆ▓ N, 102┬░ 15ŌĆ▓ LDemografiaPopula├¦├Żo 997 071 hab. (2010)Densidade 149,1 hab./km2 (2010)Funcionamen...

ActiveX [╦ī├”kt╔¬v╦ł╔øks] bezeichnet ein Softwarekomponenten-Modell von Microsoft f├╝r aktive Inhalte. ActiveX-Komponenten erweitern die Component-Object-Model-Standards (COM) von Microsoft. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Nutzbarkeit 2 Einsatzgebiete 3 Microsoft Update 4 Kritik 5 Einstellung des ActiveX-Support 6 Siehe auch 7 Weblinks 8 Einzelnachweise Nutzbarkeit ActiveX ist nur innerhalb der Betriebssystemfamilie Windows nutzbar und erfordert die Verwendung eines COM-f├żhigen Webbrowsers, da ActiveX-...

┘ģž¦┘Ŗ┘ā┘ä žŻ┘åž│ž¦ž▒ž¦ ┘ģž╣┘ä┘ł┘ģž¦ž¬ ž┤ž«žĄ┘Ŗž® ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘Ŗ┘䞦ž» 15 žŻž©ž▒┘Ŗ┘ä 1922(1922-04-15)ž│┘łž▒┘Ŗž¦ ž¦┘ä┘ł┘üž¦ž® 31 ┘Ŗ┘ł┘ä┘Ŗ┘ł 2013 (91 ž│┘åž®)┘āž¦┘䞦ž©ž¦ž│ž¦ž│žī ž¦┘ä┘ł┘䞦┘Ŗž¦ž¬ ž¦┘ä┘ģž¬žŁž»ž® ž│ž©ž© ž¦┘ä┘ł┘üž¦ž® ┘ģž▒žČ žó┘äž▓┘枦┘Ŗ┘ģž▒ ┘ģ┘āž¦┘å ž¦┘äž»┘ü┘å ┘ģ┘垬ž▓┘ć ┘ü┘łž▒ž│ž¬ ┘䞦┘ł┘å ž¦┘䞬ž░┘āž¦ž▒┘Ŗ ┘ģ┘łž¦žĘ┘åž® ž¦┘ä┘ł┘䞦┘Ŗž¦ž¬ ž¦┘ä┘ģž¬žŁž»ž® ž│┘łž▒┘Ŗž¦ ž¦┘äž▓┘łž¼ž® ž©ž¦ž▒ž©ž¦ž▒ž¦ žźž»┘Ŗ┘å (1958ŌĆō1974) ž╣ž»ž» ž¦┘䞯┘ł┘䞦ž» 1 ž¦┘䞣┘Ŗž¦ž® ž¦┘äž╣┘ģ┘ä

┘ä┘ģž╣ž¦┘å┘Ź žŻž«ž▒┘ēžī žĘž¦┘äž╣ ┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž¦┘äž┤┘łž▒┘ē ž¦┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘å┘Ŗ (ž¬┘łžČ┘ŖžŁ). ┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž¦┘äž┤┘łž▒┘ē (1971-1975) ┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž¦┘äž┤┘łž▒┘ē ž¦┘ä┘å┘łž╣ ž¦┘䞬žŻž│┘Ŗž│ 25 ┘üž©ž▒ž¦┘Ŗž▒ 1971 ž¬ž¦ž▒┘Ŗž« ž¦┘䞦┘äž║ž¦žĪ 29 žŻž©ž▒┘Ŗ┘ä 1975 ž¦┘ä┘å┘łž╣ ┘ģž¼┘äž│ ┘å┘łž¦ž© ┘ģ┘垬ž«ž© ž¦┘ä┘é┘Ŗž¦ž»ž® ž▒ž”┘Ŗž│ ┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž¦┘äž┤┘łž▒┘ē ž╣ž©ž» ž¦┘ä┘ä┘ć žŁž│┘Ŗ┘å ž¦┘䞯žŁ┘ģž▒žī ┘䞦 ┘Ŗ┘łž¼ž» žŁ┘Ŗ┘å┘枦 ž¬ž╣ž»ž»┘Ŗž® žŁž▓ž©┘Ŗž® ┘łž│┘Ŗž¦ž│┘Ŗž®┘ģ┘åž░ ┘üž©ž▒ž¦┘Ŗž▒ 1971 ┘垦ž”ž© ž▒ž”┘Ŗž│ ž¦┘ä┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž¦┘䞯┘ł┘ä...
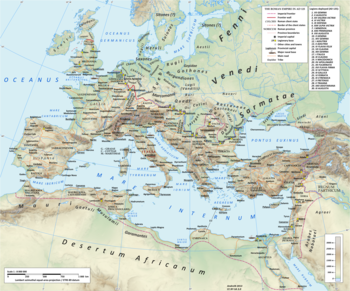
Early Germanic people Map of the Roman empire and contemporary indigenous Europe in AD 125, showing a proposed location of Heruli on the Danish islands. The Heruli (or Herules) were an early Germanic people. Possibly originating in Scandinavia, the Heruli are first mentioned by Roman authors as one of several Scythian groups raiding Roman provinces in the Balkans and the Aegean Sea, attacking by land, and notably also by sea. During this time they reportedly lived near the Sea of Azov. From t...
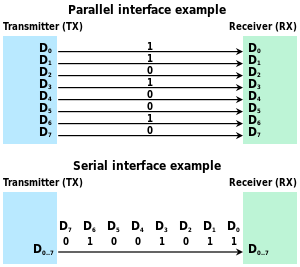
Type of data transfer This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Serial communication ŌĆō news ┬Ę newspapers ┬Ę books ┬Ę scholar ┬Ę JSTOR (August 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Serial and parallel data transmission of 010010112. Standard bit sequence is least-significant-bit-first ...

4th-century BCE Athenian politician and general For other people with similar names, see Chares (disambiguation). Coinage of Sigeion, Troas, Asia Minor, struck under Chares. Chares of Athens (Ancient Greek: ╬¦╬¼Žü╬ĘŽé ßĮü ß╝ł╬Ė╬Ę╬Į╬▒ß┐¢╬┐Žé) was a 4th-century BC Athenian military commander (Strategos), who for a number of years was one of Athens's foremost commanders. He was also a well connected politician enabling him to procure the commands he desired, commands he primarily used to enrich ...

2011 British filmOn the RopesOfficial cover (UK version)Directed byMark NoyceHamdy TahaWritten byMark NoyceStarringJoe EganMark NoyceBen ShockleyEdited byHamdy TahaMusic byGrange farm studioDistributed byCornerstone media internationalRelease date 6 December 2011 (2011-12-06) CountryUnited KingdomLanguageEnglish On the Ropes is a 2011 British mockumentary film written and directed by Mark Noyce.[1] It follows the fictional character of martial arts instructor Keith Kraf...

1993 novel by Ted Hughes For the 1916 silent film, see The Iron Woman (film). Not to be confused with The 'Iron Lady', Margaret Thatcher. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: The Iron Woman ŌĆō news ┬Ę newspapers ┬Ę books ┬Ę scholar ┬Ę JSTOR (February 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template me...

Personifications of chaos in mythology Set spearing the chaos snake Apep A chaos deity is a deity or more often a figure or spirit in mythology associated with or being a personification of primordial chaos. The following is a list of chaos deities in various mythologies. Africa and the Middle East Afroasiatic Middle East Arabian Falak Hinn and Binn Canaanite Yam, god of the sea and primordial chaos Tannin (monster)[1] Egyptian Apep the ultimate evil of Egyptian mythology in snake for...

Jos├®phine de Beauharnais 1763-1814 Keizerin der Fransen, koningin van Itali├½ Periode 1804-1814 Opvolger Marie Louise van Oostenrijk Vader Joseph Tascher de la Pagerie Moeder Rose-Claire des Vergers de Sanois Wapen als keizerin der Fransen Jos├®phine vicomtesse de Beauharnais, geboren Marie-Jos├©phe-Rose Tascher de la Pagerie, spreek uit Tasch├©r[1] (Les Trois-├Älets, Martinique, 23 juni 1763 ŌĆō Rueil-Malmaison, 29 mei 1814), kortweg Jos├®phine, was een West-Indische schoonheid, die...

Lukisan penduduk asli dari berbagai etnis di benua Amerika Wikisumber memiliki naskah asli yang berkaitan dengan artikel ini: Draft United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Deklarasi PBB tentang Hak-hak Masyarakat Adat (UNDRIP) adalah sebuah deklarasi yang disahkan oleh Majelis Umum Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa (MU PBB) dalam sesi ke-61-nya di Markas PBB di New York pada hari Kamis, 13 September 2007, oleh mayoritas 143 negara yang mendukung, 4 suara menentang (Australia, ...

Aksara Aborigin KanadaAksara Aborigin Cree Barat. Berikut adalah transilterasi teks tersebut: ├Ŗwako oma asiniwi m├¬nikan kiminawak ininiwak manitopa kaayacik. ├Ŗwakwanik oki kanocihtacik asiniwiatoskiininiw kakiminihcik om├¬niw. Akwani mitahtomitanaw askiy asay ├¬atosk├¬cik ota manitopa.Jenis aksara Abugida Bahasaalg: Cree, Naskapi, Ojibwe/Chippewa, Blackfoot (Siksika)esx: Inuktitut, Inuinnaqtunath: Dane-zaa, Slavey, Chipewyan (Denesuline)/Sayisi, Carrier (Dakelh), Sekani[1]Periode18...

Eilat MazarEilat Mazar berbicara pada kongres arkeologi Israel ke-34Lahir(1956-09-10)10 September 1956Meninggal25 Mei 2021(2021-05-25) (umur 64)[1]Tempat tinggalIsraelKebangsaanIsraelWarga negaraIsraelAlmamaterUniversitas Ibrani YerusalemDikenal atasPenemuan Struktur Batu BesarKarier ilmiahBidangArkeologiInstitusiShalem Center, Institute of Archaeology at the Universitas IbraniTerinspirasiBenjamin Mazar Eilat Mazar (Ibrani: ūÉūÖū£ū¬ ū×ū¢ū©code: he is deprecated ; 10 September 19...

ŃüōŃü«Ķ©śõ║ŗŃü½Ńü»ÕÅéĶĆāµ¢ćńī«ŃéäÕż¢ķā©Ńā¬Ńā│Ńé»Ńü«õĖĆĶ”¦ŃüīÕɽŃüŠŃéīŃü”ŃüäŃüŠŃüÖŃüīŃĆüĶäܵ│©Ńü½ŃéłŃéŗÕÅéńģ¦ŃüīõĖŹÕŹüÕłåŃü¦ŃüéŃéŗŃü¤ŃéüŃĆüµāģÕĀ▒µ║ÉŃüīõŠØńäČõĖŹµśÄńó║Ńü¦ŃüÖŃĆéķü®ÕłćŃü¬õĮŹńĮ«Ńü½Ķäܵ│©ŃéÆĶ┐ĮÕŖĀŃüŚŃü”ŃĆüĶ©śõ║ŗŃü«õ┐ĪķĀ╝µĆ¦ÕÉæõĖŖŃü½ŃüöÕŹöÕŖøŃüÅŃüĀŃüĢŃüäŃĆé’╝ł2017Õ╣┤2µ£ł’╝ē Õż¦µŚźµ£¼ÕĖØÕøĮµĄĘĶ╗Ź Õ«śĶĪÖ µĄĘĶ╗Źń£ü Ķ╗Źõ╗żķā© µĄĘĶ╗ŹĶē”µö┐µ£¼ķā© µĄĘĶ╗ŹĶł¬ń®║µ£¼ķā© Õż¢Õ▒ĆńŁēõĖĆĶ”¦ Õ£░µ¢╣ńĄäń╣ö ķÄ«Õ«łÕ║£ ĶŁ”ÕéÖÕ║£ Ķ”üµĖ»ķā© ķ¦Éµ║ƵĄĘĶ╗Źķā© Ķē”ķÜŖ ķĆŻÕÉłĶē”ķÜŖ ÕīŚµØ▒µ¢╣ķØóĶē”ķÜŖ õĖŁķā©Õż¬Õ╣...

Carolina Jaume Informaci├│n personalNombre de nacimiento Carolina Milena Jaume SaporitiNacimiento 18 de octubre de 1985 (38 a├▒os)Guayaquil, EcuadorNacionalidad EcuatorianaFamiliaC├│nyuge Xavier Pimentel (matr. 2007; div. 2010)Allan Zenck (matr. 2015; div. 2021)Hijos 2Familiares Dom├®nica Saporiti (prima)Educaci├│nEducada en Universidad Casa Grande Informaci├│n profesionalOcupaci├│n Actriz A├▒os activa 1993-presente[editar datos en Wikidat...