FS Class E.332
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

ولادة النجوم وسط بين نجمي غيمة جزيئية كرة بوك سديم مظلم جرم نجمي فتي نجم أولي نجم تي الثور نجم قبل النسق الأساسي هيربيغ أي/ نجم بي سديم شمسي أصناف الأجرام الفلكية جرم هيربج هارو المفاهيم النظرية دالة الكتلة الأولية كتلة جينس آلية كلفن هلمهولتز فرضية السديم هجرة الكواكب هذا ا

Giuseppe Canepa Deputato dell'Assemblea CostituenteGruppoparlamentarePartito Socialista Italiano, Partito Socialista Lavoratori Italiani CollegioGenova Sito istituzionale Senatore della Repubblica ItalianaLegislaturaI GruppoparlamentareUnità Socialista Sito istituzionale Deputato del Regno d'ItaliaLegislaturaXXIII, XXIV, XXVI, XXVII Sito istituzionale Dati generaliPartito politicoPartito Socialista Italiano di Unità Proletaria Titolo di studiolaurea in giurisprudenza Professi...
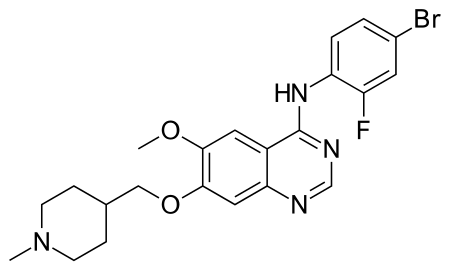
Chemical compound VandetanibClinical dataTrade namesCaprelsaOther namesZD6474AHFS/Drugs.comMonographMedlinePlusa611037License data EU EMA: by INN US DailyMed: Vandetanib US FDA: Vandetanib Pregnancycategory AU: D Routes ofadministrationBy mouthATC codeL01EX04 (WHO) Legal statusLegal status AU: S4 (Prescription only) CA: ℞-only UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only[1] EU: Rx-only Pharmacokinetic dataProtein bin...
Den här artikeln har skapats av Lsjbot, ett program (en robot) för automatisk redigering. (2016-05)Artikeln kan innehålla fakta- eller språkfel, eller ett märkligt urval av fakta, källor eller bilder. Mallen kan avlägsnas efter en kontroll av innehållet (vidare information) För andra betydelser, se Stora Högholmen. Stora Högholmen Ö Land Finland Landskap Nyland Ekonomisk region Borgå ekonomiska region Kommun Borgå Havsområde Finska viken Koordinater 60°16′09″N 25°51...

696 Shackleton Avro Shackleton AEW2 del 8º Sqd. de la RAF. 26 de junio de 1982. Tipo Avión de patrulla marítimaFabricante AvroDiseñado por Roy ChadwickPrimer vuelo Marzo de 1949Introducido Abril de 1951Retirado 1990Estado RetiradoUsuario principal Royal Air ForceOtros usuariosdestacados Fuerza Aérea SudafricanaProducción 1951 - 1958N.º construidos 185Desarrollo del Avro Lincoln[editar datos en Wikidata] El Avro 696 Shackleton era un avión de patrulla marítima de la Royal Ai...

Prupuk SelatanDesaNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenTegalKecamatanMargasariKode pos52463Kode Kemendagri33.28.01.2001 Rumah pegawai perkebunan di Prupuk pada masa Hindia Belanda. Prupuk Selatan (Jawa: ꦥꦿꦸꦥꦸꦏ꧀ꦏꦶꦢꦸꦭ꧀, translit. Prupuk Kidul; Sunda: ᮕᮁᮥᮕᮥᮊ᮪ ᮊᮤᮓᮥᮜ᮪ , translit. Prupuk Kidul) merupakan salah satu desa yang berada di kecamatan Margasari, Kabupaten Tegal, provinsi Jawa Tengah, Indonesia Bahasa Artikel...

Artikel ini sudah memiliki daftar referensi, bacaan terkait, atau pranala luar, tetapi sumbernya belum jelas karena belum menyertakan kutipan pada kalimat. Mohon tingkatkan kualitas artikel ini dengan memasukkan rujukan yang lebih mendetail bila perlu. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) SMK Negeri 1 BanyuwangiInformasiDidirikan1 Juni 1968JenisNegeriAkreditasiANomor Pokok Sekolah Nasional20525590Kepala SekolahDrs. Mulyadi, M.PdJurusan atau peminatanManajem...

米勒斯吉拿斯號米勒斯吉拿斯號航空母艦概觀艦種航空母舰擁有國 巴西結局退役技术数据標準排水量15,890噸滿載排水量19,890噸全長211.8米全寬24.4米吃水6.6米鍋爐2部總馬力40,000匹馬力蒸汽鍋爐最高速度25節乘員約1,300人武器裝備10座40毫米口徑防空高射機炮艦載機6架艦載S-2反潛機 11架SH-3海王直昇機 米勒斯吉拿斯號航空母艦(葡萄牙語:Minas Gerais)是巴西海軍一艘已退役航空

Gerbang Wrocław Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Oleśnica. Oleśnica (bahasa Jerman: Oels, nama lama Olesznica) ialah sebuah kota di Polandia selatan. Kota ini berpenduduk 37.000 jiwa (2007), dan terletak di Provinsi Dolnośląskie (bahasa Polandia: Województwo dolnośląskie). Sejarah Antara tahun 1312-1884, Oleśnica adalah ibu kota Kadipaten Oels. Setelah kematian Konrad Biały Młodszy, Kadipaten Oleśnica tak pernah lagi merdeka. Antara tahun 1792-1884, Oleśnica membentuk persatuan peroran...

El capitalismo de Estado es una denominación utilizada para referirse a los sistemas económicos en los que el Estado realiza actividades económicas mediante empresas estatales (incluidos los procesos de acumulación de capital, gestión centralizada y trabajo asalariado), o cuando existen agencias gubernamentales corporativas (organizadas según las prácticas de gestión empresarial) o de empresas públicas, como las empresas que cotizan en bolsa en las que el Estado tiene acciones de con...

This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Andrew Barton journalist – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) An...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's notability guidelines for products and services. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is l...

Indian film director A. JagannathanBorn(1935-11-26)26 November 1935Tiruppur, Coimbatore District, Madras Presidency, British India[1]Died7 October 2012(2012-10-07) (aged 76)[1]Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, IndiaOccupationfilm directorYears active1973-2012SpouseRajamaniChildrenUsha DeviPavithra DeviArun Kumar A. Jagannathan (26 November 1935 – 7 October 2012) was an Indian film director who worked in the Tamil, Telugu, Kannada and Hindi film industries and he...

الألعاب الإفريقية 2003 البلد نيجيريا المدينة المضيفة أبوجا الدول المشاركة 53 التاريخ 2003 المكان أبوجا الرياضة رياضات أولمبية الأحداث رياضة حفل الافتتاح 5 أكتوبر حفل الاختتام 17 أكتوبر المفتتح الرسمي أولوسيجون أوباسانجو الملعب الرئيسي ملعب أبوجا الألعاب الإفريق�...

Ketam kenari Periode Neogen-Sekarang, 23–00 jtyl PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N Birgus latro Status konservasiRentanIUCN2811 TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumArthropodaKelasMalacostracaOrdoDecapodaFamiliCoenobitidaeGenusBirgusSpesiesBirgus latro (Linnaeus, 1767) Tata namaSinonim takson Cancer crumenatus Rumphius, 1705 (pre-Linnean) Cancer crumenatus orientalis Seba, 1759 Cancer latro Linnaeus, 1767 Birgus laticauda Latreille, 1829[1] ProtonimCancer latro DistribusiKetam kenari terd...

A set of symptoms relating to excessive academic or intellectual pressure in the young Not to be confused with Brain fog. Brain fag syndrome (BFS) describes a set of symptoms; somatic, sleep-related and cognitive complaints, difficulty in concentrating and retaining information, head and or neck pains, and eye pain.[1] Brain fag is very common in adolescents and young adults. It is believed to be the most common in these age ranges due to the immense amount of pressure occurring in li...

American architect William B. IttnerWilliam B. Ittner, circa 1921Born(1864-09-04)September 4, 1864St. LouisDied1936St. LouisNationalityAmericanOccupationArchitect Art Deco style of the Continental Life Building in St. Louis William Butts Ittner (September 4, 1864 – 1936) was an American architect in St. Louis, Missouri. He designed over 430 school buildings in Missouri and other areas, was president of the St. Louis Chapter of the American Institute of Architects from 1893 to 1895,[1 ...

1985 film by Arne Mattsson This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Mask of Murder – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2017) Mask of MurderDirected byArne MattssonWritten byVolodja SemitjovProduced byTommy IweringStarringRod TaylorChristopher LeeValerie PerrineMusic byBjö...

Google Web Toolkit 開発元 Google 最新版 2.10.0 / 2022年6月9日 (17か月前) (2022-06-09)[1]リポジトリ github.com/gwtproject/gwt 対応OS Windows, macOS, Linux種別 Ajaxフレームワークライセンス Apache License 2.0公式サイト www.gwtproject.org テンプレートを表示 Google Web Toolkit (GWT) は、Javaを使ってウェブ用Ajaxアプリケーションを開発できるオープンソースのJavaソフトウェア開発フレームワーク�...

Valdefresno municipio de España Escudo Villavente de la Sobarriba ValdefresnoUbicación de Valdefresno en España. ValdefresnoUbicación de Valdefresno en la provincia de León. Mapa interactivo — ValdefresnoPaís España• Com. autónoma Castilla y León• Provincia León• Comarca La Sobarriba[1]• Partido judicial León• Mancomunidad Lancia y SobarribaUbicación 42°35′37″N 5°29′31″O /...

