Yakov Lyubarsky
| |||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Buddhist temple in Tianjin, China This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Temple of Great Compassion – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Temple of Great Compassion大悲院Temple of Great CompassionReligionAffiliationBuddhi...

Simón Bolívar Youth Symphonic BandYouth orchestraNative nameBanda Sinfónica Juvenil Simón BolívarFormer nameBanda Sinfónica Juvenil de CaracasFounded2005Principal conductorSergio RosalesWebsiteFundamusical - SBYSB The Simón Bolívar Youth Symphonic Band (SBYSB) (Spanish: Banda Sinfónica Juvenil Simón Bolívar) is a wind band based in Caracas, Venezuela and the principal band of El Sistema.[1] Since 2008, its principal conductor has been Sergio Rosales. History The Simón Bol�...

إينياس-غاستون باردي (بالفرنسية: Ignace-Gaston Pardies) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 5 سبتمبر 1636 بو الوفاة 22 أبريل 1673 (36 سنة) باريس مواطنة فرنسا الحياة العملية المهنة فيزيائي، ورياضياتي، وكاهن كاثوليكي اللغات الفرنسية، واللاتينية مجال العمل رياضيات،

Вибухи в Багдаді у лютому 2017 рокуЧастина Громадянська війна в Іраку Місце атаки Ірак Багдад, ІракМета атаки шиїтські цивільні особиДата 11 лютого 2017 — 16 лютого 2017Спосіб атаки вибухи автомобілів та саморобних вибухових пристроївЗброя бомби в автомобіляхЗагиблі щ

العلاقات الصينية الكوستاريكية الصين كوستاريكا الصين كوستاريكا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الصينية الكوستاريكية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين الصين وكوستاريكا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه �...

Japanese animation studio Telecom Animation Film Co., Ltd.Native name株式会社テレコム・アニメーションフィルムRomanized nameKabushiki-gaisha Terekomu Animēshon FirumuTypeSubsidiary (Kabushiki gaisha)[1]FoundedMay 19, 1975; 48 years ago (1975-05-19)[1]HeadquartersNakano, Tokyo[1]ProductsAnimeOwnerSega Sammy HoldingsParentTMS Entertainment[1] Telecom Animation Film Co., Ltd. (株式会社テレコム・アニメーションフ

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of eroge – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Part of a series onAnime and manga Anime History Voice acting Companies Studios Original video animation Original net animation Fansub F...

Russian legislative constituency Krasnoyarsk single-member constituency Constituency of the Russian State DumaDeputyYury ShvytkinUnited RussiaFederal subjectKrasnoyarsk KraiDistrictsBeryozovsky (Magansky, Zykovsky), Borodino, Irbeysky, Kansk, Kansky, Krasnoyarsk (Kirovsky, Leninsky, Sverdlovsky), Mansky, Partizansky, Rybinsky, Sayansky, Uyarsky, ZATO Zelenogorsk[1]Voters514,693 (2021)[2] The Krasnoyarsk constituency (No.54[a]) is a Russian legislative constituency in K...
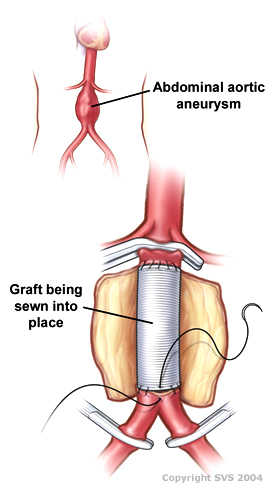
Surgical technique Open aortic surgeryDrawing of an open infrarenal aortic aneurysm repair using a tube graftOther namesOpen aortic repairSpecialtyVascular Surgery[edit on Wikidata] Open aortic surgery (OAS), also known as open aortic repair (OAR), describes a technique whereby an abdominal, thoracic or retroperitoneal surgical incision is used to visualize and control the aorta for purposes of treatment, usually by the replacement of the affected segment with a prosthetic graft. OAS is u...

2016 video game This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Dan The Man – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 2015 video gameDan The ManDeveloper(s)Halfbrick StudiosPublisher(s)Halfbrick StudiosPlatform(s)iOSAndroidReleaseNovember 26, 2015 (Android)[1]October 5, 2016 (...

First edition(publ. J. B. Lippincott & Co.) The Gadget Maker is a 1954 novel by Maxwell Griffith. It is notable for its vivid depiction of an otherwise-rarely-described milieu: campus life at MIT in the 1940s. It also presents a striking engineers-eye-view of guided missile development at a West Coast aerospace firm during the early days of the cold war. On its appearance, The New York Times described The Gadget Maker as the story of a misguided zealot devoted body and soul to the advance...

Hindu temple of Shiva and Parvati in Andhra Pradesh Sri Bhramarambika Mallikarjuna TempleGold plated Vimana of Mallikarjuna shrineReligionAffiliationHinduismDistrictNandyalaDeityShiva, ParvatiFestivalsMaha ShivaratriLocationLocationSrisailamStateAndhra PradeshCountryIndiaLocation in Andhra PradeshGeographic coordinates16°04′27″N 78°52′05″E / 16.07417°N 78.86806°E / 16.07417; 78.86806Temple(s)1WebsiteOfficial Website Sri Bhramaramba Mallikarjuna Temple (IAST...

Koilsagar Koilsagar Dam is located at Koilsagar Village of Deverakadra Mandal in Mahabubnagar District.[1][2] Koilsagar Dam is one of the famous tourist attractions of Mahabubnagar District. Beside Koilsagar there is Veerabadhra Temple called KoilKonda. Every year there is a celebration (Jathara) held by nearby villagers. This medium reservoir with live water storage capacity of 60 million cubic meters (2.1 tmc ft), was constructed on the peddavagu tributary of Krishna river&#...

Ethnic group New Zealand AmericansTotal population19,961 (2010 American Community Survey)[1]Regions with significant populationsIllinois, Wisconsin, California, and WashingtonLanguagesAmerican English, New Zealand English, Māori, SpanishRelated ethnic groupsAustralian Americans · Oceanian Americans Lists of Americans By US state By ethnicity or nationality Afghan African Americans African-American Jews Albanian Algerian Amish Angolan Antiguan and Barbudan Arab Argentine...

Baseball player Mitch SkupienAll-American Girls Professional Baseball League ManagerBats: n/aThrows: n/aCareer statisticsGames 415Wins 221Losses 194W-L%.533 Teams Grand Rapids Chicks (1951) Kalamazoo Lassies (1952–'54) Career highlights and awards Championship Title (1954) Three playoff appearances (1951, 1953-'54) Mitch Skupien was a manager and executive in the All-American Girls Professional Baseball League.[1] Very little is known about this man who worked hard fo...

Private university in Uttar Pradesh Monad UniversityTypePrivateEstablished2010Vice-ChancellorMuhammad JavedLocationHapur, Uttar Pradesh, India28°43′18″N 77°41′46″E / 28.7216°N 77.6962°E / 28.7216; 77.6962AffiliationsUGCWebsitewww.monad.edu.in Monad University is a state private university located in NCR region, Hapur, Uttar Pradesh.[1] It was established by UP State Govt. Act 23 of 2010 & U/S 2 (f) of 1956.University offers various courses in fi...

Carriles de peaje de alta ocupación (HOT) de FasTrak a lo largo de la Interestatal 15 en dirección sur en Escondido, California. Tenga en cuenta la tarifa variable. Un carril de peaje de alta ocupación (o carril HOT) es un tipo de carril de tráfico o carretera que está disponible para vehículos de alta ocupación y otros vehículos exentos sin cargo; otros vehículos deben pagar una tarifa variable que se ajusta en respuesta a la demanda. A diferencia de los peajes de carreteras, los co...

This article is about the local government area. For the suburb, see Ipswich (suburb), Queensland. For the metropolitan area, see Ipswich, Queensland. For the county town in Suffolk, England, see Ipswich. Ipswich City redirects here. For the Brisbane football club, see Ipswich City FC. Ipswich Council redirects here. For the council in England, see Ipswich Borough Council. Local government area in Queensland, AustraliaCity of IpswichQueenslandLocation within South East QueenslandCity of Ipswi...

Morticia Addams Sexo femininConjuge Gomez AddamsInfantes Pugsley Addams, Wednesday AddamsParentes matre Hester Frump[*]Fratres/sorores Ophelia Frump[*]IdentificatoresCommons Morticia Addams Morticia Addams es un personage fictional in le Familia Addams create per Charles Addams. Illa es le sposa de Gomez Addams, le matre de Wednesday Addams e Pugsley Addams, e le empleator del dispensero Lurch. Morticia Addams (Carolyn Jones) con Gomez (John Astin) e lor dispensero Lurch (Ted Cassidy) Le pers...

الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد للرجال الموسم 1998-1999 البلد تونس المنظم الجامعة التونسية لكرة اليد النسخة 44 عدد الفرق 12 الفائز النجم الرياضي الساحلي الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد 1997–98 الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد 1999–00 تعديل مصدري - تعديل الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد 1998-1999...

