STS-63
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Spanish statesman In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Echegaray and the second or maternal family name is Eizaguirre. The Most ExcellentJosé EchegarayBornJosé Echegaray y Eizaguirre(1832-04-19)19 April 1832Madrid, SpainDied14 September 1916(1916-09-14) (aged 84)Madrid, SpainResting placeSaint Isidore CemeteryOccupationDramatist, civil engineer and mathematicianNationalitySpanishGenreDramaNotable awardsNobel Prize in Literature 1904 Seat e of the Real Academia...

United States historic placeMasonic Temple BuildingU.S. National Register of Historic Places Show map of MichiganShow map of the United StatesLocation122--126 N. Mitchell St., Cadillac, MichiganCoordinates44°15′5″N 85°24′0″W / 44.25139°N 85.40000°W / 44.25139; -85.40000Arealess than one acreBuilt1889Built byJohn Mosser and Charles DuttonArchitectSidney OsgoodArchitectural styleRomanesqueNRHP reference No.94000747[1]Added to NRHPJuly 2...

Provincial electoral district in Nova Scotia, CanadaFairview-Clayton Park Nova Scotia electoral districtProvincial electoral districtLegislatureNova Scotia House of AssemblyMLA Patricia ArabLiberalDistrict created2012First contested2013Last contested2021DemographicsElectors17,380Area (km²)6Census division(s)Halifax Regional Municipality Fairview-Clayton Park is a provincial electoral district in Nova Scotia, Canada, that elects one member of the Nova Scotia House of Assembl...
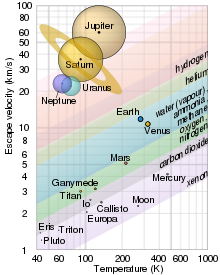
Đồ thị vận tốc thoát ly và nhiệt độ của một số hành tinh tại Hệ Mặt Trời vẫn có khí. Các hành tinh được vẽ theo tỷ lệ và các điểm giá trị là chấm den ở giữa. Thoát ly khí quyển là sự mất các khí trong khí quyển hành tinh ra không gian ngoài thiên thể. Một số cơ chế khác nhau có thể gây ra thoát ly khí quyển, hoạt động theo các quy mô thời gian khác nhau; nổi bật nhất là Thoát ly...

Tan Hiong LiongBiografiKelahiran20 Agustus 1938 KematianSeptember 2009 (71 tahun)KegiatanPekerjaanPecatur Membela negara (untuk olahraga)Indonesia Olahragacatur Igo Hoan Liong Tan,A.k.a Hoan Liang Tan or H.L Tan (Hanzi: 陈香良; Pinyin: Chén Xiāngliáng; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Tân Hoan-liang; lahir di Buitenzorg, 20 Agustus 1938 - meninggal di Bogor, September 2009)[1] adalah seorang pemain catur Indonesia-Belanda. Ia adalah pecatur Indonesia pertama dan salah satu pecatur As...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) ريج كينت معلومات شخصية الميلاد 24 أكتوبر 1944 (79 سنة) ويلينغدون مواطنة كندا الوزن 190 رطل الحياة العملية المهنة لاعب هوكي الجليد الرياضة هوكي الج�...

Skymark AirlinesスカイマークSukai Māku IATA ICAO Kode panggil BC SKY SKYMARK Didirikan12 November 1996Mulai beroperasi19 September 1998PenghubungBandar Udara HanedaKota fokusBandar Udara KobeBandar Udara NahaBandar Udara Chitose BaruBandar Udara FukuokaArmada27[1]Tujuan11[2]Kantor pusatBandar Udara Haneda, Ōta, Tokyo, JepangTokoh utamaMasakazu Arimori (Presiden dan CEO)David Pflieger (Ketua dari Januari 2016)Pendapatan ¥86.0 miliar (FY Maret 2014)[3]Laba opera...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع البيت المسكون (توضيح). البيت المسكونThe Haunted House (بالإنجليزية) معلومات عامةالتصنيف فيلم قصير الصنف الفني فيلم كوميدي — فيلم رعب — سينما صامتة تاريخ الصدور 1921 30 يناير 1921[1] (بوسطن)21 فبراير 1921[1] (الولايات المتحدة) مدة العرض 23 دقيقة العرض أبيض وأسود

الفرع الظاهر للشريان المنعطف الفخذي الإنسي الاسم العلميramus superficialis arteriae circumflexae femoris medialis تفاصيل ترمينولوجيا أناتوميكا 12.2.16.022 FMA 20810 [عدل في ويكي بيانات ] تعديل مصدري - تعديل الفرع الظاهر للشريان المنعطف الفخذي الإنسي (بالإنجليزية: Superficial branch of medial circumflex femoral arte...

Sanskrit loanwords in modern Indic languages This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (June 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This article is missing information abou...

Archeological museum, open-air museum in Batman, TurkeyBatman MuseumBatman MüzesiLocation within TurkeyEstablishedMarch 12, 2010 (2010-03-12)LocationBatman, TurkeyCoordinates37°53′55″N 41°08′28″E / 37.8986°N 41.1411°E / 37.8986; 41.1411Typearcheological museumopen-air museumKey holdingsBaşur Höyük gaming piecesCollection size450 items on displayWebsitehttps://www.muze.gov.tr/tr/muzeler/batman-muzesi Batman Museum is an archaeological muse...

Highest honorary title of Russia AwardHonorary titleHero of the Russian FederationObverse of the Gold Hero of the Russian FederationTypeHonorary titleAwarded forExtraordinary service to the statePresented bythe Russian FederationEligibilityRussian citizens and foreign nationalsStatusActiveEstablished20 March 1992[1]PrecedenceNext (lower)Order of St AndrewRelatedHero of the Soviet UnionHero of Labour of the Russian FederationHero of UkraineHero of BelarusHero of Kazakhstan Hero of...

American rapper (1983–2015) ChinxBackground informationBirth nameLionel Du Fon PickensAlso known asChinx DrugzBorn(1983-12-04)December 4, 1983[1]Far Rockaway, Queens, New York, U.S.DiedMay 17, 2015(2015-05-17) (aged 31)Jamaica, Queens, New York, U.S.GenresHip hopOccupation(s)RappersongwriterInstrumentsVocalsYears active1999–2015LabelsE1Coke BoysRiot SquadNuSenseMusical artist Lionel Du Fon Pickens (December 4, 1983 – May 17, 2015),[2] better known by his stage name ...

8ft 10in Pearson 4-2-4T no. 2002 (previously no. 40) at Exeter in 1876 The Bristol and Exeter Railway locomotives worked trains on the Bristol and Exeter Railway from 1 May 1849 until the railway was amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1876. The Great Western Railway had leased the Bristol and Exeter Railway from its opening and provided the locomotives up until 1849. The Bristol and Exeter Railway in turn provided the broad gauge locomotive power on most of the railways w...
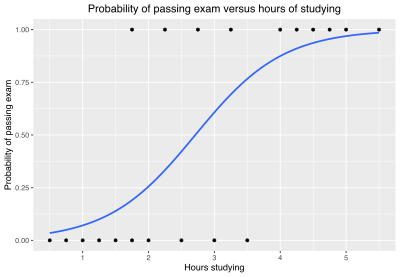
Statistical model for a binary dependent variable Logit model redirects here. Not to be confused with Logit function. Example graph of a logistic regression curve fitted to data. The curve shows the probability of passing an exam (binary dependent variable) versus hours studying (scalar independent variable). See § Example for worked details. In statistics, the logistic model (or logit model) is a statistical model that models the probability of an event taking place by having the log-o...

Schematic illustrating diffusiophoretic motion of a colloidal particle (blue) in a concentration gradient of a solute (red). Note that there is also a concentration gradient of the solvent (green). The particle is moving a diffusiophoretic velocity v d p {\displaystyle {\bf {v}}_{dp}} , in a fluid that is stationary far from the particle. The fluid velocity decays from v d p {\displaystyle {\bf {v}}_{dp}} for fluid in contact with the surface of the particle, to near zero, within the interfac...

1975 studio album by Mahavishnu OrchestraVisions of The Emerald BeyondStudio album by Mahavishnu OrchestraReleasedFebruary 1975 (1975-02)RecordedDecember 1974StudioElectric Lady Studios, New York City; mixed at Trident Studios, London[1]GenreJazz fusionLength40:23LabelColumbiaProducerKen Scott, Mahavishnu John McLaughlinMahavishnu Orchestra chronology Apocalypse(1974) Visions of The Emerald Beyond(1975) Inner Worlds(1976) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRating...

A number of medieval inscriptions written in Tamil language and script that have been found in Southeast Asia and China, mainly in Sumatra and peninsular Thailand. These texts arose directly from trade links between south India and certain parts of Southeast Asia and China, which involved the residence in those regions of Tamil-speaking Indians. Several of these overseas Tamil inscriptions mention well-known medieval Indian merchant associations.[1] A good number of Tamil inscriptions...

2007 single by PrinceGuitarSingle by Princefrom the album Planet Earth B-sideSomewhere Here On EarthReleasedJuly 9, 2007RecordedEarly 2007[1]StudioPaisley ParkGenre Rock[2] funk rock[3] post-punk revival[4] Length3:45Label NPG Columbia Songwriter(s)PrinceProducer(s)PrincePrince singles chronology Fury (2006) Guitar (2007) F.U.N.K. (2007) Guitar is the first single from Prince's 2007 album Planet Earth. This song was number 39 on Rolling Stone's list of the ...

1934 film by Mervyn LeRoy Hi, Nellie!Lobby cardDirected byMervyn LeRoyWritten byAbem FinkelSidney SutherlandStory byRoy ChanslorProduced byRobert Presnell Sr.StarringPaul MuniGlenda FarrellCinematographySol PolitoEdited byWilliam HolmesMusic byBernhard KaunProductioncompanyWarner Bros. PicturesDistributed byWarner Bros. PicturesRelease date January 20, 1934 (1934-01-20) Running time75 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishBudget$223,000[1]Box office$647,000[1 ...