Michael J. S. Dewar
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Astral LimitedJenisPublikKode emitenBSE: 532830NSE: ASTRALISININE006I01046Didirikan1996; 26 tahun lalu (1996)PendiriSandeep EngineerKantorpusatAhmedabad, Gujarat, IndiaWilayah operasiSeluruh duniaPeringkatCRISIL AAA / Stabil / CRISIL A1+Situs w…

Сії-ан-СольнуаSilly-en-Saulnois Країна Франція Регіон Гранд-Ест Департамент Мозель Округ Мец Кантон Верні Код INSEE 57653 Поштові індекси 57420 Координати 48°59′30″ пн. ш. 6°16′38″ сх. д.H G O Висота 250 - 303 м.н.р.м. Площа 2,35 км² Населення 33 (01-2020[1]) Густота 14,89 ос./км² Розм…

此條目疑似由大量爱好者内容组成。維基百科不是不經篩選的資訊收集處。請幫助改進這個條目,使用中立的語氣(而不是愛好者或媒體報道的語氣),移除瑣碎的軼事與未經證實的評論、不合適的列表和链接收集等。如條目內有愛好者可能感興趣而不符維基百科收錄標準的內容,可考慮將該等內容移至其他專門描寫魔法少女小圓的百科或網站,或在不存在相關主題的其他愛

2004 studio album by the ZutonsWho Killed...... The Zutons?Studio album by the ZutonsReleased19 April 2004Recorded2003Studio RAK, London Parr Street, Liverpool Toe Rag, London GenreFolkgarage rockindie popLength45:57LabelDeltasonicProducerIan Broudie, Liam WatsonThe Zutons chronology Who Killed...... The Zutons?(2004) Tired of Hanging Around(2006) Singles from Who Killed...... The Zutons? Pressure PointReleased: 19 January 2004 You Will You Won'tReleased: 5 April 2004 Remember MeReleased…

Hungarian politician and jurist András Tasnádi NagyMinister of Justice of HungaryIn office15 November 1938 – 9 November 1939Preceded byÖdön MikeczSucceeded byLászló Radocsay Personal detailsBorn(1882-01-29)29 January 1882Budapest, Austria-HungaryDied1 July 1956(1956-07-01) (aged 74)Budapest, People's Republic of HungaryPolitical partyUnity Party, Party of National Unity, Party of Hungarian LifeProfessionpolitician, jurist The native form of this personal name is Tasnádi Na…

Ferrocarriles de montaña de la India Patrimonio de la Humanidad de la Unesco El viaje en el ferrocarril de las montañas Nilgiri proporciona espectaculares vistas de las montañas Nilgiri. Ferrocarril de las montañas NilgiriLocalizaciónPaís IndiaCoordenadas 11°20′40″N 76°47′31″E / 11.344316666667, 76.791944444444Datos generalesTipo CulturalCriterios ii, ivIdentificación 944Región Asia y OceaníaInscripción 1999 (XXIII sesión)Extensiones 2005; 2008 Sitio we…

Polish mathematician (1884-1972) Władysław ŚlebodzińskiŚlebodziński in 1938Born(1884-02-06)6 February 1884Pysznica in PolandDied3 January 1972(1972-01-03) (aged 87)Wrocław, PolandAlma materWrocław UniversityKnown forDifferential GeometryScientific careerFieldsMathematicsInstitutionsWrocław University, Wrocław University of TechnologyThesisO pewnej klasie powierzchni Riemanna (1929)Doctoral advisorKazimierz Żorawski[1]Doctoral studentsStefan Drobot (1947); A…

Former theater in Manhattan, New York Mark Hellinger Theatre(Times Square Church)Warner Bros. Hollywood Theatre (1930–1948)51st St. Theatre (1936–1937, 1940–1941)Mark Hellinger Theatre (after 1948)Times Square Church (1989–present)Times Square Church, June 2007Address237 West 51st StreetManhattan, New York CityUnited StatesCoordinates40°45′45″N 73°59′03″W / 40.76250°N 73.98417°W / 40.76250; -73.98417TypeChurchFormer Broadway and cinemaCapacity1,603Curr…

Danish politician (1941–2022) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Uffe Ellemann-Jensen – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Uffe Ellemann-JensenMinister of Foreign AffairsIn office10 September 1982 – 25 January 19…

Der Titel dieses Artikels ist mehrdeutig. Weitere Bedeutungen sind unter Gravelotte (Begriffsklärung) aufgeführt. Gravelotte Gravelotte (Frankreich) Staat Frankreich Region Grand Est Département (Nr.) Moselle (57) Arrondissement Metz Kanton Les Coteaux de Moselle Gemeindeverband Metz Métropole Koordinaten 49° 7′ N, 6° 2′ O49.1102777777786.0297222222222Koordinaten: 49° 7′ N, 6° 2′ O Höhe 221–325 m Fläche 5,66 km² Einwohner 821…

City in Alaska, United States City in Alaska, United StatesWainwright UlġuniqCityWainwright during the summer months with the Arctic Ocean in the backgroundWainwrightLocation in AlaskaCoordinates: 70°38′50″N 160°00′58″W / 70.64722°N 160.01611°W / 70.64722; -160.01611CountryUnited StatesStateAlaskaBoroughNorth SlopeIncorporatedDecember 31, 1962[1]Government • MayorRaymond Henry Savik Nashookpuk.[2] • State senatorDonny O…

This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Denis Mercier – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Denis MercierGeneral Deni…

2016 novel written by Neal Shusterman This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Scythe novel – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Scythe AuthorNeal ShustermanCover artistKevin TongCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishSer…

Опис Емблема ФК Нафтовик Долина Джерело http://naftovyk.if.ua/ Час створення 2018 Автор зображення невідомо Ліцензія Відповідно до статті 8 Закону України про авторське право і суміжні права, наступні об'єкти не охороняються авторським правом: 1) повідомлення про новини або інші факти…

Este artigo ou secção necessita de referências de fontes secundárias fiáveis e independentes. Fontes primárias, ou com conflitos de interesse, não são adequadas para verbetes enciclopédicos. Ajude a incluir referências.—Encontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Abril de 2020) Este artigo ou secção contém uma lista de referências no fim do texto, mas as suas fontes não são claras porque não são citadas no…

Funerary figurines of Tang dynasty officials The administration of territory in dynastic China is the history of practices involved in governing the land from the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) to the Qing dynasty (1636–1912). Administrative divisions in imperial China Song dynasty officials See also: List of current and former capitals of subnational entities of China County The only level at which state officials actually governed the common people was the county level. Counties were coordinated…

Hotel in Wan Chai, Hong Kong Novotel Century Hong KongGeneral informationLocation238 Jaffe Road, Wan Chai, Hong KongCoordinates22°16′44.43″N 114°10′36.13″E / 22.2790083°N 114.1767028°E / 22.2790083; 114.1767028Opening1991; 32 years ago (1991)Technical detailsFloor count23Other informationNumber of rooms511Number of restaurants3Websitehttp://www.novotel.com/3562 Novotel Century Hong KongTraditional Chinese世紀香港酒店Simplified Chin…
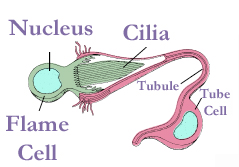
Perform excretion and maintain osmotic pressure in Platyhelminthes A flame cell is a specialized excretory cell found in the simplest freshwater invertebrates , including flatworms(Platyhelminthes), rotifers and nemerteans; these are the simplest animals to have a dedicated excretory system. Flame cells function like a kidney, removing waste materials. Bundles of flame cells are called protonephridia.[1] The flame cell has a nucleated cell body, with a cup-shaped projection, with flagell…

Targeting & night vision system M-TADS / PNVS on a Boeing AH-64 Apache helicopter The Apache Arrowhead (also Modernized Target Acquisition and Designation Sight/Pilot Night Vision Sensor or M-TADS/PNVS), is an integrated targeting and night vision system developed by Lockheed Martin for the Boeing AH-64 Apache attack helicopter. It uses second-generation long-wave Forward looking infrared (FLIR) sensors with three fields of view, a charge-coupled device TV camera, dual field of view pilotage…

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Glossary of graffiti – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) A number of words and phrases that have come to describe different styles and aspects of graffiti and its subculture. Like other ja…

