Jugendstil
| |||||||||
Read other articles:
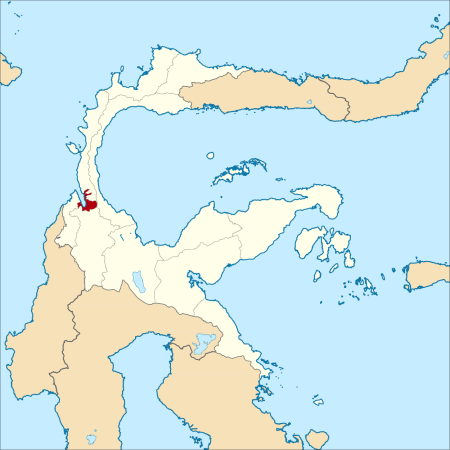
Peta Kota Palu di Sulawesi Tengah Berikut adalah daftar kecamatan dan kelurahan di Kota Palu, Provinsi Sulawesi Tengah, Indonesia. Kota Palu terdiri dari 8 Kecamatan dan 46 Kelurahan dengan luas wilayah 395,06 km² dan jumlah penduduk sebesar 363.867 jiwa dengan sebaran penduduk 921 jiwa/km².[1][2] Sebelumnya, Kota Palu terbagi atas 4 Kecamatan sesuai arah mata angin yaitu Kecamatan Palu Barat, Kecamatan Palu Timur, Kecamatan Palu Utara dan Kecamatan Palu Selatan. Empat kecam...

Francisco Ortiz de Ocampo 1.er Gobernador de la Provincia de La Rioja 1 de marzo-septiembre de 1820Predecesor Nuevo cargoSucesor Nicolás Dávila Gobernador Intendente de Córdoba 1 de febrero-4 de junio de 1814Predecesor Francisco Javier de VianaSucesor José Javier Díaz 10.o Gobernador intendente de Chuquisaca(y 2.o presidente de la Cámara de Apelaciones de Charcas) septiembre-noviembre de 1813Predecesor Dos sucesivos: Juan Ramírez Orozco Agustín Esteban Gascón (revolucionario)Sucesor ...

Veronika Vítková Verband Tschechien Tschechien Geburtstag 8. Dezember 1988 (34 Jahre) Geburtsort Vrchlabí, Tschechoslowakei Tschechoslowakei Karriere Beruf Sportlehrerin Verein SKP Kornspitz Jablonec Trainer Egil Gjelland Aufnahme in denNationalkader 2005 Debüt im Weltcup 2006 Weltcupsiege 7 (1 Einzelsieg) Status zurückgetreten Karriereende 23. April 2020 Medaillenspiegel Olympische Medaillen 0 × 1 × 2 × WM-Medaillen 1 × 0 × 1 × JWM-Medaillen 0 × 2 × 0 × SWM-Medai...

بن سليمان - مدينة - تقسيم إداري البلد المغرب[1] عاصمة لـ إقليم بنسليمان الجهة الإقتصادية الدار البيضاء - سطات المسؤولون الإقليم إقليم بن سليمان الدائرة الإدارية ؟؟؟ القيادة الإدارية ؟؟؟؟ خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 33°36′44″N 7°07′16″W / 33.61222222°N 7.12111111°W / 33.61222...

Naura & Genk JuaraPoster filmSutradara Eugene Panji Produser Handoko Hendroyono Pax Benedanto Amalia Prabowo Ditulis oleh Asaf Antariksa Bagus Bramanti PemeranAdyla Rafa Naura AyuJoshua Yorie RundenganVickram PriyonoAndryan BimaPenata musikAdyla Rafa Naura AyuAndi RiantoPerusahaanproduksiKompas Gramedia ProductionKonsorsium KreatifHOOQ OriginalDistributorMAXstream OriginalsTanggal rilis16 November 2017Durasi102 menitNegara IndonesiaBahasa Indonesia Naura & Genk Juara adalah...

Bus terminal in Japan You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (March 2023) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the Japanese article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text...

For other uses, see Roadkill (disambiguation). Traffic victims redirects here. For human casualties, see Epidemiology of motor vehicle collisions. Animals that have died due to vehicular incursions The battered remains of a roadkilled deer on Route 170/Okatie Highway by the Chechessee River in South Carolina, US Wide-ranging large carnivores like this bear are particularly vulnerable to becoming roadkill. Roadkill is an animal or animals that have been struck and killed by drivers of motor ve...

Brazilian accountability office Federal Court of AccountsTribunal de Contas da UniãoCourt headquarters in BrasíliaAgency overviewFormed7 November 1890; 133 years ago (1890-11-07)[1]Preceding agencyNational Public Treasury CourtTypeCourt of AuditHeadquartersSAFS Quadra 4, Lote 1Brasília, Federal District15°48′14″S 47°51′48″W / 15.8039°S 47.8633°W / -15.8039; -47.8633Agency executiveBruno Dantas, PresidentWebsiteportal.tcu.gov.br ...

قرية غربابة - قرية - تقسيم إداري البلد اليمن المحافظة محافظة صنعاء المديرية مديرية الحيمة الخارجية العزلة عزلة دروان السكان التعداد السكاني 2004 السكان 333 • الذكور 176 • الإناث 157 • عدد الأسر 41 • عدد المساكن 38 معلومات أخرى التوقيت توقيت اليمن (+3 غ...

American enterprise software company This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (June 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) BMC Software, Inc.TypePrivateIndustryInformation...

German economist (1906–1990) Ludwig LachmannBorn(1906-02-01)1 February 1906Berlin, German EmpireDied17 December 1990(1990-12-17) (aged 84)Johannesburg, South AfricaNationalityGermanSpouseMargot LachmannAcademic careerFieldEconomicsEconomic historySchool ortraditionAustrian SchoolInfluencesFriedrich HayekCarl MengerMax WeberLudwig von MisesG. L. S. ShackleAlfred Schütz[1] Ludwig Maurits Lachmann (/ˈlɑːxmən/; German: [ˈlaxman]; 1 February 1906 – 17 December 1...

American TV series or program Second Generation WayansGenreComedy dramaCreated by Craig Wayans Damien Dante Wayans Devon K. Shepard Starring Damien Dante Wayans Craig Wayans George O. Gore II Tatyana Ali Country of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons1No. of episodes10 (list of episodes)ProductionExecutive producers Craig Wayans Damien Dante Wayans Devon Shepard George O. Gore II Marlon Wayans Rick Alvarez Camera setupMultipleRunning time22 minutesProduction companyB...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилиями Райан и Циммерман. В статье не хватает ссылок на источники (см. рекомендации по поиску). Информация должна быть проверяема, иначе она может быть удалена. Вы можете отредактировать статью, добавив ссылки на авторитетные ис�...

German actor Max LandaLanda photographed in 1920 by Nicola PerscheidBorn24 April 1873Minsk, Russian EmpireDied8 November 1933Bled, Drava BanovinaKingdom of YugoslaviaOther namesMax LandauOccupationActorYears active1913–1928 (film)SpouseMargot Walter Max Landa (Belarusian: Макс Ландаў; 24 April 1873 – 8 November 1933;[1] born Max Landau) was a Russian Empire-born Austrian silent film and stage actor. Career Landa attended the Handelsakademie (commercial academy)...

2017 International Wrestling Revolution Group event 55th Anniversary of Lucha Libre in Estadio de MexicoOfficial poster for the eventPromotionInternational Wrestling Revolution GroupDateDecember 3, 2017[1]CityNaucalpan, State of Mexico[1]VenueArena Naucalpan[1]Event chronology ← PreviousEl Castillo del Terror Next →Arena Naucalpan 40th Anniversary Show Anniversary of Lucha Libre in Estado de México Shows chronology ← Previous54th Anniversary Next&...

Posthumous biography of L. Ron Hubbard Bare-faced Messiah Cover of UK paperback editionAuthorRussell MillerCountryUnited KingdomLanguageEnglishSubjectL. Ron HubbardGenreNon-fictionPublisherMichael JosephPublication date26 October 1987Media typePrint (Hardcover and Paperback)Pages380ISBN0-7181-2764-1OCLC20634668Dewey Decimal299/.936/092 B 20LC ClassBP605.S2 M55 1987 L. Ron Hubbard, the subject of Bare-faced Messiah Bare-faced Messiah: The True Story of L. Ron Hubbard is a posthumous ...

Francisco León de la Barra Presidente de los Estados Unidos MexicanosInterino 25 de mayo de 1911-6 de noviembre de 1911Gabinete Gabinete de Francisco León de la BarraVicepresidente Vacante[nota 1]Predecesor Porfirio DíazSucesor Francisco I. Madero Secretario de Relaciones Exteriores 1 de abril de 1911-25 de mayo de 1911Presidente Porfirio DíazVicepresidente Ramón CorralPredecesor Enrique C. CreelSucesor Victoriano Salado Álvarez 21 de febrero de 1913-6 de julio de 1913Presidente ...

Seks dan hukum Isu sosial Usia dewasa · Penyensoran Sunat · Pornografi Pelanggaran tertentu(Dapat bervariasi sesuai dengan yurisdiksi) Perselingkuhan · Pemikatan anak Pornografi anak-anak · Pelacuran anak Hubungan sedarah · Pelacuran Pedofilia · Pemerkosaan (Pemerkosaan statutori · Pemerkosaan dalam pernikahan) Sexting · Pelecehan seksual terhadap anak Perbudakan seksual · Pelecehan seksual Zoofili...

1948 film The Spice of LifeDirected byJean DrévilleWritten byNoël-NoëlProduced byAlain PoiréStarringNoël-Noël Bernard Blier Jean TissierCinematographyLéonce-Henri BurelEdited byJean FeyteMusic byRené CloërecProductioncompanyCinéphonicDistributed byGaumont Film CompanyRelease date26 October 1948Running time75 minutesCountryFranceLanguageFrenchBox office4,328,290 admissions (France)[1] The Spice of Life (French: Les Casse Pieds) is a 1948 French comedy film directed by Jean Dr...

'n Gedenkplaat op 'n sypaadjie voor 'n Berlynse woonhuis herinner aan 'n Sjoa-slagoffer wat hier gewoon het, gedeporteer en in Riga, Letland vermoor is Die Auschwitz-konsentrasiekamp vanaf sy binnekant gesien kort nadat dit in Januarie 1945 deur die Rooi Leër bevry is Kaart van die Sjoa in Europa Die Holocaust (oftewel Sjoa, Volkslagting, Uitwissing, Jodeslagting, of Joodse Volksmoord), ook bekend as die HaShoah (Hebreeus: השואה, HaShoah, die katastrofe letterlik die ongeluk, die ramp o...
































