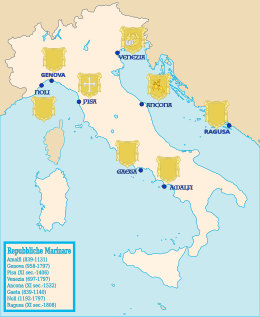
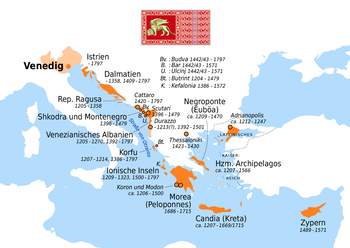
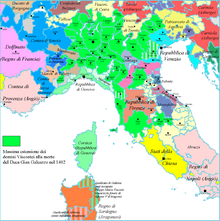
Italian city-states
|
Read other articles:

Minor league baseball teamEl Paso ChihuahuasFounded in 2014 El Paso, Texas Team logo Cap insignia Minor league affiliationsClassTriple-A (2014–present)LeaguePacific Coast League (2022–present)DivisionEast DivisionPrevious leagues Triple-A West (2021) Pacific Coast League (2014–2020) Major league affiliationsTeamSan Diego Padres (2014–present)Minor league titlesLeague titles (1)2016Conference titles (2)20162017Division titles (5)20152016201720182022Team dataNameEl Paso Chihuahuas (2014...

районное самоуправлениеРасейнское районное самоуправлениелит. Raseinių rajono savivaldybė[1] Герб 55°23′00″ с. ш. 23°09′00″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Литва[1] Входит в Каунасский уезд Включает 12 староств Адм. центр Расейняй[1] Глава Андрюс Баутронис[d][1] История и геогр�...

Stoffelskuppe (Stopfelskuppe) Hochsitz auf einem Stoppelfeld südlich der Stoffelskuppe Höhe 620,1 m ü. NHN [1] Lage bei Roßdorf; Landkreis Schmalkalden-Meiningen, Thüringen (Deutschland) Gebirge Salzunger Werrabergland bzw. Vordere Rhön Dominanz 2,2 km → Pleß Schartenhöhe 97 m Koordinaten 50° 43′ 39″ N, 10° 13′ 5″ O50.727510.218055555556620.1Koordinaten: 50° 43′ 39″ N, 10° 13′&#...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (نوفمبر 2019) عبد الواحد الأنصاري معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1978 (العمر 45 سنة) السعودية الإقامة السعودية الجنسية السعودية الديانة مسلم الحياة العملية التعلّم بكالوريوس أ

Dieser Artikel behandelt die Datenrate multimedialer Inhalte. Allgemeiner wird die Datenrate von Übertragungen als Datenübertragungsrate bezeichnet. Die Bitrate ist eine Datenübertragungsrate und bezeichnet die Ausgabemenge von Informationseinheiten bei digitalen Multimediaformaten im Verhältnis einer Datenmenge zu einer Zeitspanne, typischerweise gemessen in Bit pro Sekunde, abgekürzt als Bit/s oder (angelsächsisch) bps. Mit fortschreitender Technik sind je nach Themengebiet immer mehr...

Géraldine PailhasGéraldine Pailhas, 2014Lahir8 Januari 1971 (umur 52)Marseille, PrancisPekerjaanAktrisSuami/istriChristopher ThompsonAnak2 Géraldine Pailhas (lahir 8 Januari 1971) adalah seorang pemeran perempuan asal Prancis[1] Dia meraih kesuksesan internasional pertamanya pada tahun 1995 sebagai Doña Anna, cinta yang tak terpenuhi dari Johnny Depp dalam komedi Don Juan DeMarco. Dia menikah dengan aktor Christopher Thompson dan memiliki dua anak.[2] Pada tahun 2003,...

محطة حرارية بقرب صوفيا - بلغاريا محطة الطاقة موهاف تولد ما يقرب 1580 ميجا وات مشغلة بواسطة الفحم محطة طاقة حرارية في ايلاندا مشغلة بالطاقة الحرارية الأرضية (جيوثيرمال) المحطة الحرارية هي محطة توليد طاقة كهربائية تعمل باندفاع البخار، فالمحطة الحرارية تعمل على تسخين المياه وتح

SAMPSON adalah sebuah radar multi-fungsi AESA yang diproduksi oleh BAE Systems Maritime Services. Ini adalah komponen radar pengendalian tembak sistem pertahanan udara angkatan laut Sea Viper, yang sebelumnya PAAMS untuk membedakannya dari sistem PAAMS pada Franco-Italia Horizon Class. Sampson multi fungsi bisa mendeteksi semua jenis target untuk jarak 400 km, dan mampu melacak ratusan target pada satu waktu. Sea Viper menggunakan informasi ini untuk menilai dan perintah prioritas sasara...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Marie dari Prusia (disambiguasi). Marie dari PrusiaRatu BayernPotret Joseph Karl Stieler, minyak diatas kanvas, 1843, Gallery of Beauties, Istana NymphenburgPermaisuri BayernTenure28 Maret 1848 – 10 Maret 1864Informasi pribadiKelahiran(1825-10-15)15 Oktober 1825Istana Kota BerlinKematian17 Mei 1889(1889-05-17) (umur 63)Puri Hohenschwangau, BayernPemakamanGereja TheatineWangsaWangsa HohenzollernWangsa WittelsbachAyahPangeran Wilhelm dari PrusiaIbuPuteri Marie ...

Child often left at home with no supervision A child with keys to her home hanging from her neck A latchkey kid, or latchkey child, is a child who returns to an empty home after school (or other activities) or a child who is often left at home with no supervision because their parents are away at work. Such a child can be any age, alone or with siblings who are also under the age of majority for their community.[1] History of the term The term refers to the latchkey of a door to a hou...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Lampung (disambiguasi). Kabupaten Lampung TimurKabupatenTranskripsi bahasa daerah • Aksara LampungDari atas, kiri ke kanan; Kantor Bupati Lampung Timur, Islamic Centre Sukadana, Gajah Sumatra di Taman Nasional Way Kambas LambangMotto: Bumei tuwah pepadan(Lampung Pepadun) Daerah yang memberikan kemakmuranPetaKabupaten Lampung TimurPetaTampilkan peta SumatraKabupaten Lampung TimurKabupaten Lampung Timur (Indonesia)Tampilkan peta IndonesiaKoordina...

CloverfieldPoster rilis teaterSutradara Matt Reeves Produser J. J. Abrams Bryan Burk Ditulis oleh Drew Goddard PemeranMichael Stahl-DavidT. J. MillerJessica LucasOdette YustmanLizzy CaplanMike VogelDistributorParamount PicturesTanggal rilis18 Januari 2008[1]Durasi85 min.NegaraBahasa Inggris Rusia Anggaran$30 juta[2]PendapatankotorDomestic$78,778,933Foreign$74,180,860Worldwide$152,959,793[3]SekuelCloverfield 2IMDbInformasi di IMDbAMGProfil All Movie GuideSitus webhttp:/...

2006 film MajajanTheatrical release posterDirected bySyed Noor[1]Written byRukhsana Noor[1]Produced bySaimaSyed NoorStarring Shaan Shahid Saima Madiha Shah Saud Shafqat Cheema Iftikhar Thakur CinematographyWaqar BokhariEdited byAqeel Ali AsgharMusic byZulfiqar AliRelease date24 March 2006Running time2 hours 36 minCountryPakistanLanguagePunjabi Majajan is a 2006 Pakistani Punjabi drama film directed by Syed Noor[2][3] which was released across theaters in Pakist...

フィンランドの政党スウェーデン人民党Svenska folkpartiet i FinlandSuomen ruotsalainen kansanpuolue 党首 アンナ=マヤ・ヘンリクソン創立 1906年本部所在地 ヘルシンキ党員・党友数 28,000人[1](2011年)政治的思想 スウェーデン語少数言語話者の利益擁護[2]「自由主義」[2]国際連携 自由主義インターナショナル欧州連携 欧州自由民主改革党欧州議会会派 欧州刷�...

Shaw Millennium ParkShaw Millennium ParkTypeSkateparkLocationCalgary, Alberta, CanadaCoordinates51°02′46″N 114°05′31″W / 51.04611°N 114.09194°W / 51.04611; -114.09194Area17.3 acres (0.070 km2)Created2000Operated byCity of CalgaryStatusOpen year round Shaw Millennium Park is a skatepark in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, on the western end of downtown Calgary, on the site of the former Mewata Stadium adjacent to Mewata Armouries. The 75,000 square feet (...

In Passau gibt es folgende aktive Studentenverbindungen, die unterschiedlichen Korporationsverbänden angehören. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Aktive Verbindungen 2 Inaktive und erloschene Verbindungen 3 Weblinks 4 Einzelnachweise Aktive Verbindungen Name der Verbindung Gründung Farben Fuxenfarben Wappen Zirkel Verband Fechtfrage Mitglieder Verbindungshaus Corps Budissa-Leipzig 1859 blau-gold-weiß blau-weiß-blau KSCV pflicht Männerbund Gasthaus zur Blauen Taube, Schmiedgasse 4, 94032 Passau Bursc...

Olimpiade Musim Dingin IVTuan rumahGarmisch, JermanJumlah negara28Jumlah atlet646 (566 putra, 80 putri)Jumlah disiplin17 dalam 4 cabangPembukaan6 Februari 1936Penutupan16 Februari 1936Dibuka olehAdolf HitlerStadionStadion OlimpiaMusim Dingin ← Lake Placid 1932 St. Moritz 1948 → Musim Panas ← Los Angeles 1932 Berlin 1936 → Olimpiade Musim Dingin ke-4 diadakan di Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Jerman. Olimpiade ini dibuka oleh presiden Adolf Hitler. Jumlah atletnya ialah 646 (5...

Historic district in Maryland, United States United States historic placeRodgers Forge Historic DistrictU.S. National Register of Historic PlacesU.S. Historic district Brick rowhouses in Rodgers ForgeShow map of MarylandShow map of the United StatesLocationRoughly bounded by Stanmore Road, Stevenson Lane, York Road (Md. Route 45), Overbrook Road, and Bellona Avenue, north of Baltimore, MarylandCoordinates39°22′52″N 76°37′02″W / 39.38111°N 76.61722°W / 39.38...

Yang Berbahagia DatukDinsmanPMWDinsman. University of Malaya, 29.4.2009BornChe Shamsudin Osman (1949-05-20) May 20, 1949 (age 74)Kampung Raja, Jitra, Kedah, MalaysiaPen nameDinsmanOccupationpoet, dramatist, theatre practitionerLanguageMalayNationalityMalaysianCitizenshipMalaysiaAlma materUniversity of MalayaLiterary movementArtists with the People (Paksi)Notable awardsMalaysia Premier's Literary Award (1976, 1983) Dinsman ((1949-05-20)May 20, 1949, Kampung Raja, Jitra, Kedah) is a M...

1996 soundtrack album by Whitney HoustonThe Preacher's Wife: Original Soundtrack AlbumSoundtrack album by Whitney HoustonReleasedNovember 26, 1996RecordedJanuary – February 1996GenreGospelsoulR&B[1]Length62:20LabelAristaBMG EntertainmentProducerWhitney HoustonMervyn WarrenRicky MinorSteve LipsonBabyfaceDavid FosterWhitney Houston chronology The Bodyguard: Original Soundtrack Album(1992) The Preacher's Wife: Original Soundtrack Album(1996) My Love Is Your Love(1998) Singl...