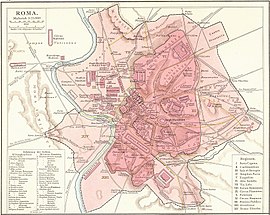
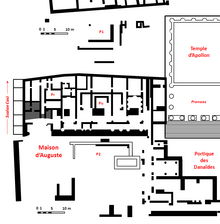
House of Augustus
| ||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

2 Samuel 8Kitab Samuel (Kitab 1 & 2 Samuel) lengkap pada Kodeks Leningrad, dibuat tahun 1008.KitabKitab 1 SamuelKategoriNevi'imBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen10← pasal 7 pasal 9 → 2 Samuel 8 (atau II Samuel 8, disingkat 2Sam 8) adalah bagian dari Kitab 2 Samuel dalam Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama di Alkitab Kristen. Dalam Alkitab Ibrani termasuk Nabi-nabi Awal atau Nevi'im Rishonim [נביאים ראשונים] dalam bagian Nevi'im (נביאי

Benedictus IXTựu nhiệmTháng 10 năm 1032 (lần đầu)Bãi nhiệmTháng 7 năm 1048 (Lần cuối)Tiền nhiệmGioan XIXSylvester IIIClêmentê IIKế nhiệmSylvester IIIGregory VIDamasus IIThông tin cá nhânTên khai sinhTheophylactusSinhkhoảng 1012Roma, Lãnh thổ Giáo hoàngMất18 tháng 9, 1055Grottaferrata, Lãnh thổ Giáo hoàngCác giáo hoàng khác lấy tông hiệu Benedict Biển Đức IX hoặc Bênêđictô IX (Latinh: Benedictus IX) là giáo hoàng được li

اضغط هنا للاطلاع على كيفية قراءة التصنيف سكلة زرقاء حالة الحفظ أنواع غير مهددة أو خطر انقراض ضعيف جدا[1] المرتبة التصنيفية نوع[2][3] التصنيف العلمي النطاق: حقيقيات النوى المملكة: الحيوانات الشعبة: الحبليات الطائفة: الطيور الرتبة: عصفوريات Passeriformes الفصيلة: صائد...

1850 painting by William-Adolphe Bouguereau Dante and Virgil in HellFrench: Dante et Virgille en EnferArtistWilliam-Adolphe BouguereauYear1850MediumOil on canvasSubjectThe Divine ComedyDimensions281 cm × 225 cm (111 in × 89 in)LocationMusée d'Orsay, Paris Dante and Virgil in Hell is an 1850 oil-on-canvas painting by the French academic painter William-Adolphe Bouguereau. It is in the Musée d'Orsay in Paris.[1] The painting depicts a scene ...

Esta página cita fontes, mas que não cobrem todo o conteúdo. Ajude a inserir referências. Conteúdo não verificável pode ser removido.—Encontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Julho de 2018) Coordenadas: 22° 23' 4 S 44° 41' 38 O Alto do Morro do Couto. O morro do Couto é a oitava maior elevação rochosa brasileira, com 2 680 metros de altitude. Fica no Parque Nacional do Itatiaia, no est...

Miguel Aldama Localidad Miguel AldamaLocalización de Miguel Aldama en México Miguel AldamaLocalización de Miguel Aldama en ChiapasCoordenadas 17°48′06″N 93°19′01″O / 17.80167, -93.31694Entidad Localidad • País México • Estado Chiapas • Municipio ReformaAltitud • Media 41 m s. n. m.Población (2020) • Total 86 hab.[1]Huso horario Tiempo del Centro (UTC -6) • en verano UTC -5Código pos...

أبراو-ديورسو الإحداثيات 44°42′10″N 37°36′06″E / 44.702777777778°N 37.601666666667°E / 44.702777777778; 37.601666666667 تاريخ التأسيس 1871 تقسيم إداري البلد روسيا[2] الإمبراطورية الروسية الاتحاد السوفيتي[1] التقسيم الأعلى كراسنودار كراي (13 سبتمبر 1937–2005) خصائص جغرافية ا�...

Not to be confused with St. Peter Port. ParishSaint Peter Saint Pierre du BoisParish FlagLocation of Saint Pierre Du Bois in GuernseyCoordinates: 49°26′28″N 2°38′28″W / 49.44111°N 2.64111°W / 49.44111; -2.64111Crown DependencyGuernsey, Channel IslandsGovernment • Electoral districtWestArea • Total6.2 km2 (2.4 sq mi)Population (2019) • Total2,036 • Density330/km2 (850/sq mi)Time zoneGMT...

Distilled beverage Himbeergeist made from wild raspberries in the Black Forest region of Germany Himbeergeist (lit raspberry spirit, also known as raspberry spirit obtained by maceration and distillation,[1] eau de vie de framboise[2] or simply framboise[3]) is a geist (a type of eau de vie or Schnapps) made from raspberries. It is produced mainly in Germany and the Alsace region of France. Rather distilling a fermented mash of fresh fruit into liquor, like a fruit bra...

2019 novel by Charlie Jane Anders The City in the Middle of the Night First editionAuthorCharlie Jane AndersCover artistMark SmithCountryU.S.LanguageEnglishGenreClimate fictionPublisherTor BooksPublication date2019Media typePrint HardcoverAwardsLocus Award for Best Science Fiction NovelISBN978-0-7653-7996-2 The City In the Middle of the Night is a 2019 climate-fiction novel by Charlie Jane Anders.[1] It is set on a tidally locked planet, where human life, surrounded by hosti...

Тімоті Кастань Особисті дані Народження 5 грудня 1995(1995-12-05)[1][2][3] (27 років) Арлон, Бельгія Зріст 1,85 см Вага 80 кг Громадянство Бельгія[4][5] Позиція захисник Інформація про клуб Поточний клуб «Лестер Сіті» Номер 27 Юнацькі клуби 2004—20062006—20112011—2...

伊勢電気鉄道デハニ131形電車(いせでんきてつどうデハ131がたでんしゃ)は伊勢電気鉄道が1927年に導入した、制御電動車形式の電車である[注 1]。のちに関西急行鉄道に引き継がれモニ5131形となり、後年荷物室の撤去によりモ5131形となった。保有企業の合併・改名により、運行を終了した時点では近畿日本鉄道に所属していた。 概要 1926年に電化した伊勢電気鉄�...

Demographics of BudapestPopulation pyramid of Budapest in 2022Population1,706,851 (2022) The population of Budapest was 1,735,041 on 1 January 2013.[1] According to the 2011 census, the Budapest metropolitan area was home to 2,530,167 people and the Budapest commuter area (real periphery of the city) had 3.3 million inhabitants.[2] The Hungarian capital is the largest in the Pannonian Basin and the ninth largest in the European Union. Budapest is also the primate city of Hunga...

PabelanKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan PabelanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenSemarangPemerintahan • CamatHabib Sholeh, M.PdPopulasi • Total- jiwaKode pos50771Kode Kemendagri33.22.05 Kode BPS3322050 Luas47,97 km²Desa/kelurahan17 Pabelan (Jawa: ꦥꦧꦺꦭꦤ꧀, translit. Pabélan) adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Semarang, Jawa Tengah, Indonesia. Kecamatan ini berjarak sekitar 30 kilometer dari ibukota kabupaten Semarang ke arah tenggara...

2003 novel by Suki Kim For the 1965 novel by Wole Soyinka, see The Interpreters (novel). The Interpreter AuthorSuki KimCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishGenreNovelPublisherFarrar, Straus & GirouxPublication date2003Media typePrint (Paperback)Pages464 pp (first edition, paperback)ISBN978-0-312-42224-0OCLC606927844 The Interpreter is a 2003 murder mystery novel by Suki Kim. A twenty-nine-year-old Korean American court interpreter, Suzy Park, is startled to discover during a case that ...

Everlast Worldwide IncorporatedJenisAnak perusahaanIndustriPeralatan olahragaTekstilAlas kakiDidirikan1910; 112 tahun lalu (1910) di The Bronx, New York CityPendiriJacob GolombKantorpusatManhattan, Amerika SerikatWilayah operasiSeluruh duniaProdukPeralatan dan sarung tinju, pakaian, sneakersIndukFrasers GroupSitus webeverlast.com Everlast adalah sebuah merek peralatan olahraga asal Amerika Serikat yang fokus pada tinju, seni bela diri campuran, dan kebugaran. Perusahaan ini memasarkan pr...

Turkish Naval Forces Components Structure Installations Special Forces Underwater Offence Group Underwater Defence Group Underwater Search and Rescue Naval infantry Amphibious Marine Brigade History History of the Naval Forces Equipment Active ships Active aircraft Entire fleet Ranks vte List of major active Turkish Naval Forces installations. Naval Bases Aksaz Naval Base Bartın Naval Base Erdek Naval Base Foça Naval Base Gölcük Naval Base Iskenderun Naval Base Pasha Liman Base Sürmene N...

For socialist newspaper published by Lithuanian-Americans, see Naujienos (socialist newspaper). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Naujienos apolitical newspaper – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Cover page of the ...

Book published in 1842 by Charles Darwin Canton Island typifies the isolated coral atolls dotting the Pacific Ocean The Structure and Distribution of Coral Reefs, Being the first part of the geology of the voyage of the Beagle, under the command of Capt. Fitzroy, R.N. during the years 1832 to 1836, was published in 1842 as Charles Darwin's first monograph, and set out his theory of the formation of coral reefs and atolls. He conceived of the idea during the voyage of the Beagle while still in...

Social Epidemiologist Monica MaltaMalta in 2022Born (1970-09-20) September 20, 1970 (age 53)BrazilAlma materJohns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public HealthScientific careerFieldsSocial EpidemiologyInstitutionsJohns Hopkins University University of Toronto Monica Malta is a Brazilian researcher who works mostly to address health inequalities faced by LGBTQ persons.[1] She is currently a professor at the University of Toronto and a scientist at the Centre for Addiction and Men...