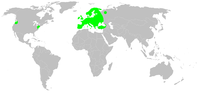
Giant house spider
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Sha Ine FebriyantiLahirSha Ine Febriyanti18 Februari 1976 (umur 47)Semarang, Jawa Tengah, IndonesiaPekerjaanAktrissutradaraTahun aktif1992—sekarangSuami/istriYudi Datau (m. 2003)[1]Anak3, termasuk Nurra DatauKerabat Mutia Datau (ipar) Nunu Datau (ipar) Yuni Shara (sepupu)[1] Krisdayanti (sepupu)[1] Sha Ine Febriyanti (lahir 18 Februari 1976) adalah pemeran dan sutradara asal Indonesia. Karier Ia mengawali karier dari dunia mod...

Keuskupan Agung Samoa–ApiaArchidioecesis Samoa–ApianaPuleaga Fa'aAkiepikopo Samoa–ApiaKatolik Katedral Dikandung Tanpa Noda, ApiaLokasiNegara Negara Independen SamoaWilayah SamoaProvinsi gerejawiSamoa-ApiaStatistikLuas2.922 km2 (1.128 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2010)189.00042,500 (22.5%)Paroki38InformasiDenominasiGereja KatolikRitusRitus RomaPendirian20 Agustus 1850 (173 tahun lalu)KatedralKatedral Dikandung Tanpa NodaKepemimpinan kiniPaus...

Das Herzogtum Schweidnitz-Jauer bestand zeitweise getrennt aus den schlesischen Herzogtümern Jauer und Schweidnitz. Sie waren ab 1346 dauerhaft verbunden und wurden bis 1368 vom Schweidnitzer Zweig der Schlesischen Piasten regiert. Ihre Gebiete gehörten ursprünglich zu den Herzogtümern Liegnitz und Breslau. Residenzorte waren Jauer bzw. Schweidnitz und die Burg Fürstenstein im Waldenburger Bergland. Nach dem Tod des Herzogs Bolko II. von Schweidnitz 1368 fielen die Herrschaftsgebiete von...

Peter MacOwan El autor, c. 1900Información personalNacimiento 1830Kingston upon Hull (Reino Unido) Fallecimiento 1909, 79 añosUitenhage (Sudáfrica) Residencia Inglaterra, SudáfricaNacionalidad inglésFamiliaCónyuge Amelia DayEducaciónEducado en Universidad de Londres Información profesionalÁrea botánico, micólogo, geólogo, docenteAbreviatura en botánica MacOwan[editar datos en Wikidata] Peter MacOwan (Hull, Inglaterra, 14 de noviembre 1830 - Uitenhage, provincia del Cabo...

Sede do Grupo Folha.Capa do jornal Folha de S.Paulo de 6 de fevereiro de 2018. Empresa Folha da Manhã S.A. Periodicidade Diário (segunda a segunda) Formato Standard Sede São Paulo País Brasil Slogan O Jornal do FuturoUm Jornal a Serviço do Brasil Fundação 19 de fevereiro de 1921 (102 anos) Fundador(es) Olival Costa e Pedro Cunha Presidente Luiz Frias Diretor Otavio Frias Filho (1984-2018)Maria Cristina Frias (2018-2019)Sérgio Dávila (2019-) Orientação política Apartidári...

التكية النقشبندية معلومات عامة القرية أو المدينة محافظة دهوك الدولة العراق تاريخ بدء البناء 1290هـ/1873م المواصفات عدد المصلين 100 عدد المآذن 1 التفاصيل التقنية المواد المستخدمة الطابوق التصميم والإنشاء النمط المعماري إسلامية المقاول الشيخ محمد طاهري النقشبندي تعديل مصدري - �...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Hindia Moeda merupakan surat kabar yang terbit pertama kali pada 1 Mei 1917. Koran ini terbit setiap Selasa, Kamis, dan Sabtu.[1] Redaktur koran ini yaitu Mas Atje Padmawiguna, dan di bagian administratur ada Ki Agoes Anang Somad. Hindia Moeda ...

Comics created in Korea For Chinese comics, see Manhua. For Japanese comics, see Manga. This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Manhwa – news · newspapers · bo...

German nordic combined athlete Manuel FaißtFaißt in 2016CountryGermanyBorn (1993-01-11) 11 January 1993 (age 30)Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, GermanyHeight1.71 m (5 ft 7 in)Ski clubSV BaiersbronnPersonal best227.5 m (746 ft)Oberstdorf, 17 March 2022World Cup careerSeasons2012–presentIndividual wins0Team wins1Indiv. podiums5Team podiums8Indiv. starts202Team starts13Overall titles0 – (10th in 2019, 2020, 2021)Discipli...

American oil industry consultant Carter PagePage in 2017Personal detailsBornCarter William Page (1971-06-03) June 3, 1971 (age 52)Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.Political partyRepublicanEducationUnited States Naval Academy (BS)Georgetown University (MA)New York University (MBA)SOAS, University of London (PhD) Fordham University (LLM)OccupationInvestment bankerForeign policy analystMilitary serviceAllegiance United StatesBranch/service United States NavyYears of service1993–...

British actor This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (March 2020) Rafi GavronGavron in 2016BornRaphael Pichey Gavron (1989-06-24) 24 June 1989 (age 34)Hendon, London, EnglandOccupationActorYears active2006–present Raphael Pichey Gavron (born 24 June 1989) is a British actor. He had supporting roles in the films Breaking and Entering (2006), Nick & Norah's Infinite Playlist (2008), A Star Is Bor...

American college football season 1984 Kentucky Wildcats footballHall of Fame Classic, W 20–19 vs. WisconsinConferenceSoutheastern ConferenceRankingCoachesNo. 19APNo. 19Record9–3 (3–3 SEC)Head coachJerry Claiborne (4th season)Offensive schemeI formationBase defenseWide-Tackle SixHome stadiumCommonwealth StadiumSeasons← 19831985 → 1984 Southeastern Conference football standings vte Conf Overall Team W L T W L ...

Constituency of the Haryana legislative assembly in India BarodaConstituency for the Haryana Legislative AssemblyConstituency detailsCountryIndiaRegionNorth IndiaStateHaryanaDistrictSonipatLS constituencySonipatMember of Legislative Assembly14th Haryana Legislative AssemblyIncumbent Indu Raj Narwal PartyIndian National CongressElected year2020 Baroda Assembly constituency is one of the 90 constituencies in the Haryana Legislative Assembly of Haryana a north state of India. Baroda is also part...

Sporting event delegationGuam at the2016 Summer OlympicsIOC codeGUMNOCGuam National Olympic CommitteeWebsitewww.oceaniasport.com/guam/in Rio de JaneiroCompetitors5 in 3 sportsFlag bearer Benjamin Schulte[1]Medals Gold 0 Silver 0 Bronze 0 Total 0 Summer Olympics appearances (overview)1988199219962000200420082012201620202024 Guam competed at the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, from August 5 to 21, 2016. This was the territory's eighth consecutive appearance at the S...

1990 studio album by Edwyn CollinsHellbent on CompromiseStudio album by Edwyn CollinsReleasedJanuary 1990StudioPower Plant Studios, LondonGenreRockLength50:44LabelDiabloProducerEdwyn Collins, Dave AndersonEdwyn Collins chronology Hope and Despair(1989) Hellbent on Compromise(1990) Gorgeous George(1994) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllMusic[1]The Encyclopedia of Popular Music[2] Hellbent on Compromise is an album by Scottish musician Edwyn Collins, relea...

Bagian dari seri artikel mengenaiSejarah Jepang PeriodePaleolitiksebelum 14.000 SMJōmon14.000–300 SMYayoi300 SM – 250 MKofun250–538Asuka538–710Nara710–794Heian794–1185Kamakura1185–1333Restorasi Kemmu1333–1336Muromachi (Ashikaga) Nanboku-chōSengoku 1336–1573Azuchi–Momoyama Perdagangan dengan Nanban 1568–1603Edo (Tokugawa) SakokuPersetujuan KanagawaBakumatsu 1603–1868Meiji Perang BoshinRestorasiPerang Sino-Jepang PertamaPemberontakan BoxerPerang Rusia-Jepang 1868–191...

Australian theologian Sir Alan Edgar WalkerBornAlan Edgar Walker(1911-06-04)4 June 1911Sydney, New South Wales, AustraliaDied29 January 2003(2003-01-29) (aged 91)Sydney, New South Wales, AustraliaNationalityAustralianOther names Mister Methodist The Methodist Pope That Nice Alan Warble Conscience of The Nation[1] EducationDoctor of DivinityOccupation(s)Christian minister, theologian and evangelist, social commentator, activist[2]SpouseWinifred WalkerChildren4Parents ...

Constituency of the Maharashtra legislative assembly in India Osmanabad Assembly constituency is one of the 288 Vidhan Sabha (legislative assembly) constituencies of Maharashtra state in western India.[1] Overview Osmanabad (constituency number 242) is one of the four Vidhan Sabha constituencies located in the Osmanabad district. It covers the entire Kalamb tehsil and part of Osmanabad tehsil of this district.[2] The number of electors in 2009 was 296,247 (male 157,571, female...

Sexual activity that usually excludes penetration For sexual intercourse without vaginal lubrication, see Dry sex. The Kiss, by Francesco Hayez, 1859 Non-penetrative sex or outercourse is sexual activity that usually does not include sexual penetration. It generally excludes the penetrative aspects of vaginal, anal, or oral sex, but includes various forms of sexual and non-sexual activity, such as frottage, manual sex, mutual masturbation, kissing, or cuddling.[1][2][3]...

Opera by Josef Mysliveček This article is about an opera by Josef Mysliveček. For an earlier opera by Thomas Arne on the same theme, see Artaxerxes (opera). For other operas on the same theme, see Artaserse. Josef Mysliveček Artaserse is an opera in three acts by the Czech composer Josef Mysliveček, set to a popular libretto (or dramma per musica) by Metastasio that was originally performed in 1730. It was customary to alter the Metastasian text considerably for operas in the 1770s, but t...