Frog galvanoscope
|
Read other articles:

نادي سالزبري سيتي تأسس عام 1947 البلد المملكة المتحدة الدوري دوري الجنوب الوطني المدرب داريل كلارك الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل نادي سالزبري سيتي (بالإنجليزية: Salisbury City F.C.) هو نادي كرة قدم بريطاني تأسس في 1947 ، يقع مقره الرئيسي في ساليسبر

ENI S.p.A. Beurs Euronext: ENI Oprichting 10 februari 1953 Eigenaar beursgenoteerd, Italiaanse Staat heeft 30% van de aandelen Sleutelfiguren Claudio Descalzi (CEO) Hoofdkantoor Rome, Italië Werknemers 32.689 (2021) Producten aardolie, aardgas en olieproducten Sector energie Omzet/jaar € 76,6 miljard (2021) Winst/jaar € 5,8 miljard (2021) Marktkapitalisatie € 44 miljard (31 dec. 2021) Website www.eni.it Portaal Economie Eni (Italiaans: Ente nazionale idrocarburi) is een It...

جزء من سلسلة مقالات حولتاريخ روسيا بلغاريا القديمة العظمى 632–668 خانية الخزر 650-969 خانية الروس القرن التاسع للميلاد بلغار الفولغا القرون 9←13 للميلاد خاقانات الروس 882–1240 دوقية فلاديمير 1157–1331 جمهورية نوفغورود 1136–1478 القبيلة الذهبية 1240–1480 دوقية موسكو الكبرى 1283–1547 روسيا �...

Starr School Plaats in de Verenigde Staten Vlag van Verenigde Staten Locatie van Starr School in Montana Locatie van Montana in de VS Situering County Glacier County Type plaats Census-designated place Staat Montana Coördinaten 48° 35′ NB, 113° 8′ WL Algemeen Oppervlakte 10,6 km² - land 10,6 km² - water 0,0 km² Inwoners (2000) 248 Hoogte 1428 m Overig FIPS-code 70825 Portaal Verenigde Staten Starr School is een plaats (census-designated place) in de Amerikaanse ...

مقاطعة في إسبانيامعلومات عامةصنف فرعي من التقسيم الإداري في إسبانياإقليمالمستوى الثاني من التقسيم الإداري جزء من region of Spain (en) (1833 – 1980)مناطق إسبانيا ذات الحكم الذاتي(1980 – ) البداية 1835 الاسم الأصل provincia de España (بالإسبانية) البلد إسبانيا الكمية 50 لديه جزء أو أجزاء مدينة في إسب�...

Namit KhannaLahir29 Oktober 1985 (umur 38)Delhi, IndiaPekerjaanaktorTahun aktif2017–sekarangDikenal atasYeh Pyaar Nahi Toh Kya HaiSanjivani Namit Khanna (lahir 29 Oktober 1985)[1] adalah model dan aktor India yang terkenal karena menggambarkan Siddhant Sinha di Yeh Pyaar Nahi Toh Kya Hai dan Dr. Siddhant Sid Mathur di Sanjivani.[2] Kehidupan awal Namit berasal dari Delhi[3] dan dilahirkan dalam keluarga bisnis kelas tinggi. Ia menyelesaikan Sarjana Administ...

Japanese manga series and franchise This article is about the manga series. For the Spanish-language court show, see Caso Cerrado. For other uses, see Case Closed (disambiguation). Case Closed36th North American volume cover, featuring Conan Edogawa名探偵コナン(Meitantei Konan)GenreMystery[1]Thriller[1] MangaWritten byGosho AoyamaPublished byShogakukanEnglish publisherNA: Viz MediaSEA: Shogakukan Asia (as Detective Conan)ImprintShōnen Sunday ComicsMagazineWeek...

MV Ark Futura MV Ark Futura in Cuxhaven harbour History Name 1996–2000: Dana Futura 2000–2011: Tor Futura 2011–present: Ark Futura Owner 1996–2000: DFDS Italia Srl, Genoa 2000–2006: DFDS, Copenhagen 2006–present: DFDS Logistics Rederi, Oslo[1] OperatorDFDS[2] Port of registry 1996–2000: Italy 2000–2004: Denmark 2004–2004: Isle of Man 2004–present: Denmark BuilderCantiere Navale Visentini, Porto Viro Yard number179 Launched13 October ...
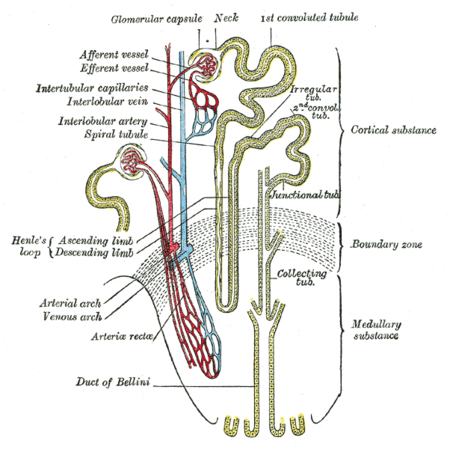
Descending limb of loop of HenleScheme of renal tubule and its vascular supply. (Labeled at center left.)Nephron ion flow diagramDetailsIdentifiersLatinPars descendens ansae nephricaeFMA17719 17705, 17719Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] Within the nephron of the kidney, the descending limb of loop of Henle is the portion of the renal tubule constituting the first part of the loop of Henle. Physiology The permeability is as follows: Substance Permeability ions Low permeability. Sod...

2017 Indian filmGodhaTheatrical release posterDirected byBasil JosephWritten byRakesh MantodiProduced byAnoopMukesh R. Mehta C. V. SarathiStarringTovino ThomasWamiqa GabbiNarrated byVineeth SreenivasanCinematographyVishnu SarmaEdited byAbhinav Sunder NayakMusic byShaan RahmanProductioncompaniesAVA ProductionsE4 EntertainmentDistributed byE4 EntertainmentRelease date 19 May 2017 (2017-05-19) Running time120 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageMalayalamBudget₹ 6.5 croreBox office₹20 c...

Chronological list of systems of plant taxonomy A pioneering system of plant taxonomy, Linnaeus's Systema Naturae, Leiden, 1735 This list of systems of plant taxonomy presents taxonomic systems used in plant classification. A taxonomic system is a coherent whole of taxonomic judgments on circumscription and placement of the considered taxa. It is only a system if it is applied to a large group of such taxa (for example, all the flowering plants). There are two main criteria for this list. A s...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Empire of the Obscene – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 2008 studio album by RevocationEmpire of the ObsceneStudio album by RevocationReleasedFebruary 2008Recorded2007Studio...

Saudi businessman (1955–2016) SheikhAl-Walid bin Ahmed Al JuffaliBorn(1955-04-30)30 April 1955Jeddah, Saudi ArabiaDied20 July 2016(2016-07-20) (aged 61)Zurich, SwitzerlandEducationLe RoseyAlma materUniversity of San Diego Imperial College LondonKnown forChairman, E. A. Juffali and BrothersSpouse(s)Basma Al-Sulaiman (1980–2000) Christina Estrada (2001–14) Loujain Adada (m. 2012)Children6ParentsAhmed Abdullah Juffali (father)Suad bint Ibrahim ...

Hilton-branded hotel in Milwaukee, Wisconsin Hilton Milwaukee City CenterHilton Milwaukee City Center in May 2021Hotel chainHilton HotelsGeneral informationArchitectural styleNeoclassical architecture, Art decoAddress509 West Wisconsin AveMilwaukee, WisconsinOpening1928OwnerMarcus CorporationDesign and constructionArchitect(s)Holabird & RocheOther informationNumber of rooms729Number of restaurants3ParkingParking garagePublic transit access MCTSWebsitehiltonmilwaukee.com The Hilton Milwauk...

2022 video game This article needs a plot summary. Please add one in your own words. (July 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 2022 video gameWeird WestDeveloper(s)WolfEye StudiosPublisher(s)Devolver DigitalDirector(s)Raphaël ColantonioDesigner(s)Christophe CarrierJoachim DaviaudMonte MartinezGaël GiraudeauProgrammer(s)Borut PfeiferArtist(s)Etienne AubertEmmanuel PetitWriter(s)Lucas LoredoErin FirestineElizabeth LaPenséeComposer(s)Choose HellthEngineUnreal Engine 4&#...

2022 film by Mithran R Jawahar ThiruchitrambalamTheatrical release posterDirected byMithran R. JawaharWritten byMithran R. JawaharProduced byKalanithi MaranStarring Dhanush Nithya Menen Bharathiraja Prakash Raj Raashii Khanna Priya Bhavani Shankar CinematographyOm PrakashEdited byPrasanna GKMusic byAnirudh RavichanderProductioncompanySun PicturesDistributed byRed Giant MoviesAyngaran International[1]Release date 18 August 2022 (2022-08-18) Running time133 minutes[2&...

American television personality For other uses, see Snooky. SnookiSnooki in 2011BornNicole Elizabeth Polizzi (1987-11-23) November 23, 1987 (age 36)Santiago, ChileNationalityAmericanAlma materBrookdale Community College[1][2]Years active2009–presentHeight4 ft 8 in (1.42 m)Spouse Jionni LaValle (m. 2014)[3][4]Children3Websitesnookinicole.com Nicole Elizabeth LaValle (née Polizzi; born November 23, 1...

Botticelli, pemahkotaan Sang Perawan Suci Maria di surga Ad caeli reginam adalah sebuah ensiklik dari Paus Pius XII, diberikan di Roma, dari Basilika Santo Petrus, pada hari perayaan Kebundaan Perawan Suci Maria, pada hari kesebelas bulan Oktober 1954, pada tahun ke-16 masa kepausannya. Ensiklik ini merupakan suatu unsur penting dari Mariologi Paus Pius XII. Dokumen ini membentuk hari perayaan Keratuan Maria. Sumber Paus Pius XII, ensiklik dan bulla Mariologi: Encyclical Fulgens Corona on the...

Ballot measure regarding bail Issue 1 November 8, 2022 Determining Bail Amount Based on Public Safety AmendmentResults Choice Votes % Yes 3,107,629 77.50% No 901,997 22.50% Valid votes 4,009,626 95.44% Invalid or blank votes 191,742 4.56% Total votes 4,201,368 100.00% Registered voters/turnout 8,029,950 52.32% Yes 80–90% 70–80% 60–70% Source: Ohio Secretary of State Elections in Ohio Federal government U.S. President 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828...

Takatori高取駅Takatori StationGeneral informationLocation1-4-28, Takatori-kita, Asaminami-ku, HiroshimaJapanCoordinates34°28′31″N 132°26′18″E / 34.4753°N 132.4383°E / 34.4753; 132.4383Line(s)Astram LinePlatforms1 island platformTracks2ConstructionStructure typeelevated stationHistoryOpened20 August 1994; 29 years ago (1994-08-20)Services Preceding station Hiroshima Rapid Transit Following station Kamiyasutowards Hondōri Astram Line Ch�...

