Byzantine units of measurement
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1962 studio album by Archie SheppArchie Shepp – Bill Dixon QuartetStudio album by Archie SheppReleased1962RecordedOctober 1962GenreAvant-garde jazzLabelSavoyProducerArchie Shepp, Bill DixonArchie Shepp chronology Archie Shepp – Bill Dixon Quartet(1962) Four for Trane(1964) Bill Dixon chronology Archie Shepp – Bill Dixon Quartet(1962) Bill Dixon 7-tette/Archie Shepp and the New York Contemporary 5(1964) Peace Cover Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmu...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Adé. Adé Vue d'ensemble d'Adé. Blason Administration Pays France Région Occitanie Département Hautes-Pyrénées Arrondissement Argelès-Gazost Intercommunalité Communauté d'agglomération Tarbes-Lourdes-Pyrénées Maire Mandat Jean-Marc Boya 2020-2026 Code postal 65100 Code commune 65002 Démographie Gentilé Adéens Populationmunicipale 826 hab. (2020 ) Densité 114 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 43° 08′ 05″ nord, 0°&...

Albanian politician, educator and mathematician Sotir Jovan PeciSotir PeciBorn(1873-07-13)July 13, 1873Dardhë, Ottoman EmpireDiedApril 10, 1932(1932-04-10) (aged 58)Florina (Greece)NationalityAlbanianOccupation(s)teacher, mathematician, politicianKnown forHaving been the Minister of Education of AlbaniaSignature Sotir Peci (1873–1932) was an Albanian politician, educator and mathematician. In 1906 he published the first Albanian-language newspaper in the United States of America ...

Arms of Brownlow: Or, an escutcheon within an orle of martlets sable John Brownlow, 1st Viscount Tyrconnel Viscount Tyrconnel was a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created in 1718 for Sir John Brownlow, 5th Baronet, Member of Parliament for Grantham and Lincolnshire. He was made Baron Charleville, in the County of Cork, at the same time, also in the Peerage of Ireland. The Brownlow Baronetcy, of Humby in the County of Lincolnshire, was created in the Baronetage of England on 27 July 1...
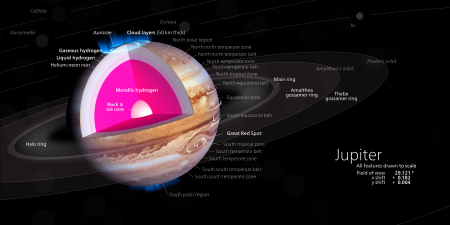
Fifth planet from the Sun This article is about the planet. For the Roman god, see Jupiter (god). For other uses, see Jupiter (disambiguation). JupiterFull disk view of Jupiter in natural color, with the shadow of its largest moon Ganymede cast onto it and the Great Red Spot at the left horizon.DesignationsPronunciation/ˈdʒuːpɪtər/ ⓘ[1]Named afterJupiterAdjectivesJovian /ˈdʒoʊviən/SymbolOrbital characteristics[2]Epoch J2000Aphelion816.363 Gm (5.4570 AU...

This article is about the parent holding company Bell Inc. For the telecommunications company, see Bell Canada. For the media company, see Bell Media. For mobile/cellular, see Bell Mobility. Canadian telecommunications and media company Bell Canada Enterprises Inc.Trade nameBCE Inc.TypePublicTraded asTSX: BCENYSE: BCES&P/TSX 60 componentIndustryTelecommunicationsMass mediaFounded1983; 40 years ago (1983)HeadquartersVerdun, Quebec, Canada[1]Key peopleMir...

Reserved area that separates opposing lanes of traffic on divided roadways Central reservation redirects here. For other uses, see Central reservation (disambiguation). See also: Road verge This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material ma...

Isabella Blow beim Turner Prize (Dezember 2005) Isabella Blow (* 19. November 1958 in London; † 7. Mai 2007 in Gloucester) war eine britische Stylistin, Modejournalistin und Mäzenatin. Sie entdeckte und förderte zahlreiche Modedesigner, wie Alexander McQueen und Philip Treacy, sowie Models, wie Sophie Dahl und Stella Tennant. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Kindheit und Jugend 2 Karriere 3 Krankheit und Tod 4 Ehrungen 5 Isabella Blow Foundation 6 Ausstellungen 7 Literatur 8 Weblinks 9 Einzelnachweis...

Genus of birds Gorsachius Malayan night heron (Gorsachius melanolophus) Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: Pelecaniformes Family: Ardeidae Subfamily: Ardeinae Genus: GorsachiusBonaparte, 1855 Type species Nycticorax goisagi[1]Temminck, 1836 Species 4, see text Gorsachius is a genus of Old World night herons typically found near water in forested regions. These are medium-sized herons which are migratory in the colder parts...

American politician Andrew RenzulloRenzullo at the 2022 Hazlitt Summit hosted by Young Americans for Liberty FoundationMember of the New Hampshire House of Representativesfrom the Hillsborough 37th districtIncumbentAssumed office December 2016In office2004 – December 2014 Personal detailsBorn (1944-10-25) October 25, 1944 (age 79)Political partyRepublicanResidence(s)Hudson, New Hampshire, U.S. Andrew Renzullo (born October 25, 1944) is an American politician in...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: AIKA Online – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 2009 video gameLogo for Aika OnlineDeveloper(s)HanbitSoftPublisher(s) HanbitSoft CBM Interactive GameNet HAPPYTUK OngameSeriesEPIC:I Tris...

Atletismo nosJogos Pan-Americanos de 2019 Provas de pista 100 m masc fem 200 m masc fem 400 m masc fem 800 m masc fem 1500 m masc fem 5000 m masc fem 10000 m masc fem 100 m com barreiras fem 110 m com barreiras masc 400 m com barreiras masc fem 3000 mcom obstáculos masc fem Revezamento 4×100 m masc fem Revezamento 4×400 m masc fem Provas de estrada Maratona masc fem 20km marcha atlética masc fem 50km marcha atlética masc fem Provas de campo Salto em distância masc fem Salto trip...

Not to be confused with Pahlavi (disambiguation). Thematic line of a song in carnatic music It has been suggested that this article be merged into Ragam Thanam Pallavi. (Discuss) Proposed since June 2023. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Pallavi – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (J...

2002 live album by Jerry Granelli and Jamie SaftThe Only JuanLive album by Jerry Granelli and Jamie SaftReleasedAugust 6, 2002Recorded2001VenuePequot Library, Southport, CTGenreJazzLength48:01LabelLove Slave Lvs 105Jamie Saft chronology Breadcrumb Sins(2002) The Only Juan(2002) Astaroth: Book of Angels Volume 1(2005) The Only Juan is a live album by drummer Jerry Granelli and keyboardist Jamie Saft which was recorded in Southport, Connecticut and released on the Love Slave label in 20...

1992 single by Take ThatOnce You've Tasted LoveSingle by Take Thatfrom the album Take That & Party B-sideGuess Who Tasted LoveReleased27 January 1992 (1992-01-27)[1]GenreHousedanceLength3:33LabelRCASongwriter(s)Gary BarlowProducer(s)Duncan BridgemanTake That singles chronology Promises (1991) Once You've Tasted Love (1992) It Only Takes a Minute (1992) Alternative coverUK limited-edition 7-inch vinyl Alternative coverUK limited-edition 12-inch vinyl Music videoOnce ...

Music venue in Manhattan, New York, United States This article is about the music venue. For other uses, see Terminal 5. Terminal 5Address610 West 56th StreetLocationNew York City, New York 10019 U.S.Coordinates40°46′11″N 73°59′34″W / 40.76965°N 73.99275°W / 40.76965; -73.99275Public transitNew York City Subway: at 59th Street–Columbus Circle station NYCT Bus: M5, M7, M10, M12, M20, M104 MTA Bus: BxM2OwnerThe Bowery Pre...

2018 American filmThe Holiday CalendarFilm posterDirected byBradley WalshWritten byAmyn KaderaliProduced byBrad KrevoyStarring Kat Graham Quincy Brown Ethan Peck Ron Cephas Jones CinematographyPeter BenisonEdited byGordon McClellanMusic bySean Nimmons-PatersonProductioncompanyMPCADistributed byNetflixRelease date November 2, 2018 (2018-11-02) Running time95 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglish The Holiday Calendar is a 2018 American Christmas romantic comedy film directed...

For the song by American metalcore band Myka Relocate, see The Young Souls. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Bring You Home – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 2006 studio album by Ronan KeatingBring You HomeStud...

The Cleveland Guardians are a professional baseball team based in Cleveland, Ohio. They are in the Central Division of Major League Baseball's American League. Since 1994, they have played in Progressive Field. The Cleveland team originated in 1900 as the Lake Shores, when the American League (AL) was officially a minor league. One of the AL's eight charter franchises, the major league incarnation of the club was founded in Cleveland in 1901. 1896–1946: Beginning to middle The Columbus Buck...

2019 Czech filmDaughterDirected byDaria KashcheevaWritten byDaria KashcheevaProduced byZuzana Roháčová, Ondřej Šejnoha, Martin VandasCinematographyDaria KashcheevaEdited byAlexander KashcheevMusic byPetr VrbaProductioncompaniesFAMU - Film and TV School of the Academy of Performing Arts in Prague, MAUR filmDistributed byMiyu DistributionRelease date 12 June 2019 (2019-06-12) Running time15 minutesCountryCzech RepublicBudget750,000 CZK[1] Daughter (Czech: Dcera) is a...





