Brotherhood of Locomotive Engineers and Trainmen
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
2013 video game 2013 video gameDepression QuestDeveloper(s)The Quinnspiracy, Patrick LindseyPublisher(s)The QuinnspiracyWriter(s)Zoë Quinn, Patrick LindseyComposer(s)Isaac SchanklerEngineTwine[1]Platform(s)Browser, Windows, OS X, LinuxReleaseFebruary 14, 2013Genre(s)Interactive fiction, Electronic literatureMode(s)Single-player Depression Quest is a 2013 interactive fiction game dealing with the subject of depression. It was developed by Zoë Quinn using the Twine engine, with writing b…

університет Харківський державний театральний інститут ↑3154746 ·R (Харків)Країна СРСРМісто ХарківРозташування ХарківЗасновано 1939Закрито 1963Випускники Категорія:Випускники Харківського театрального інституту Харківський державний театральний інститут — вищ…

Ця стаття є частиною серії статей про народБілоруси Білоруська культура Архітектура Кухня Кіно Література Мода Музика Народне мистецтво Образотворче мистецтво Спорт Театр Танці Білоруська діаспора Австралія Австрія Аргентина Африка Бельгія Бразилія Велика Британія В

Johanna SpyriJohanna Spyri, 1879LahirJohanna Louise Heusser(1827-06-12)12 Juni 1827Hirzel, SwissMeninggal7 Juli 1901(1901-07-07) (umur 74)Zürich, SwissPekerjaanPenulis cerita pendek, novelisGenreChildren's literature, sastra dewasaKarya terkenalHeidi Johanna Louise Spyri (née Heusser; bahasa Jerman: [joˈhana ˈʃpiːri]; 12 Juni 1827 – 7 Juli 1901) adalah seorang penulis novel Swiss, terutama cerita anak-anak, dan terkenal karena bukunya Heidi. Lahir di Hirzel, …

Red Grange Harold Edward Red Grange (13 Juni 1903 – 28 Januari 1991), berjuluk The Galloping Ghost, adalah seorang pemain sepak bola Amerika untuk Universitas Illinois, Chicago Bears, dan selama jangka pendek New York Yankees. Penandatanganan kontraknya dengan Bears membantu melegitimasi National Football League (NFL).[1] Ia adalah anggota carter dari College dan Pro Football Hall of Fame. Referensi ^ Red Grange, Football Hero of 1920's, Dead at 87. The New York Times. 29…

Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan agar dapat memenuhi kriteria sebagai entri Wikipedia.Bantulah untuk mengembangkan artikel ini. Jika tidak dikembangkan, artikel ini akan dihapus. Noa Tsurushima (鶴嶋乃愛 Tsurushima Noa; lahir 24 Mei 2001 di Prefektur Kochi, Jepang) adalah aktris dan model asal Jepang. Noa TsurushimaNama asal鶴嶋乃愛Lahir24 Mei 2001 (umur 22)Kōchi, JepangKebangsaanJepangPekerjaanModel, artisTinggi163 cm (5 ft 4 in) Kelahiran Tsurushima lahir di Pre…

臺灣豫劇團Taiwan Bangzi Opera Company原名國立國光劇團豫劇隊、飛馬豫劇隊、中州豫劇團、新生豫劇團成立時間1950年創始人張岫雲、李久濤地址 臺灣81343高雄市左營區實踐路102號 網站bangzi.ncfta.gov.tw 臺灣豫劇團(英語:Taiwan Bangzi Opera Company),隸屬於中華民國文化部,是中華民國國家級的豫劇表演團體,同時是臺灣目前僅有的一個豫劇團,是國立傳統藝術中心的派出單位。 歷史 …
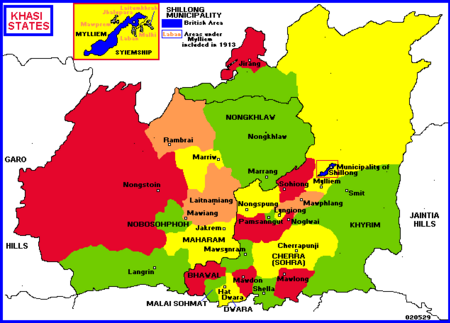
Sohra redirects here. For places in Iran, see Sohra, Iran. Town in Meghalaya, IndiaCherrapunji SohraTownSohra has held the record for highest rainfall multiple times in the pastCherrapunjiLocation in MeghalayaShow map of MeghalayaCherrapunjiCherrapunji (India)Show map of IndiaCoordinates: 25°17′02″N 91°43′16″E / 25.284°N 91.721°E / 25.284; 91.721CountryIndiaStateMeghalayaDistrictEast Khasi HillsElevation1,430 m (4,690 ft)Population (2011) �…

Japanese paper company Nippon Paper Industries Co., Ltd.TypePublic (K.K)Traded asTYO: 3863Nikkei 225 ComponentIndustryPulp and paperFounded(August 1, 1949 (1949-08-01))Headquarters4-6, Kanda-Surugadai, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0062, JapanArea servedWorldwideKey peopleYoshio Haga, (CEO and President)ProductsPaperPaperboardHousehold paper productsSpecialty papersLogs and lumberChemicalsFunctional filmsRevenue $ 10.905 billion USD (FY 2012) (¥ 1,025 billion JPY) (FY 2012)Net income $ 1…

المقالات المختارة المقالة رقم 1 ع - ن - ت منتخب المغرب لكرة القدم و يلقب أيضا بأسود الأطلس نسبة إلى الأسود التي كانت تعيش في جبال الأطلس حتى القرن 20 ،هو منتخب يضم أحسن لاعبي كرة القدم المغاربة ، و تسيره الجامعة الملكية المغربية لكرة القدم. بعد أن أصبح من البلدان المستقلة …

Municipality in Quebec, CanadaFassettMunicipalityLocation within Papineau RCMFassettLocation in western QuebecCoordinates: 45°39′N 74°52′W / 45.650°N 74.867°W / 45.650; -74.867[1]CountryCanadaProvinceQuebecRegionOutaouaisRCMPapineauSettled1815ConstitutedJuly 1, 1855Government[2] • MayorMichel Rioux • Federal ridingArgenteuil—Papineau—Mirabel • Prov. ridingPapineauArea[2][3] • Total…

2013 studio album by PondHobo RocketStudio album by PondReleased6 August 2013 (2013-08-06)GenrePsychedelic rock, neo-psychedelia, hard rockLength34:02LabelModularProducerKevin ParkerPond chronology Beard, Wives, Denim(2012) Hobo Rocket(2013) Man, It Feels Like Space Again(2015) Singles from Hobo Rocket Giant TortoiseReleased: 11 June 2013[1] XanmanReleased: 18 June 2013[2] O DharmaReleased: 23 December 2013[3] Professional ratingsAggregate scoresSou…

Bài viết này là một bài mồ côi vì không có bài viết khác liên kết đến nó. Vui lòng tạo liên kết đến bài này từ các bài viết liên quan; có thể thử dùng công cụ tìm liên kết. (tháng 8 năm 2020) Barbara Mulwana (sinh năm 1965) là một kỹ sư điện và nhà khoa học máy tính người Uganda, là chủ tịch của Hiệp hội các nhà sản xuất Uganda. Vào tháng 5 năm 2017, bà thay thế chức vụ này của Amos Nzeyi, …

Bangladeshi streaming television series MorichikaGenreCrime thrillerDirected byShihab ShaheenCountry of originBangladeshOriginal languageBengaliNo. of seasons1No. of episodes8ProductionEditorJobayar Abir PealOriginal releaseNetworkChorkiRelease21 July 2021 (2021-07-21) Morichika is a Bangladeshi crime thriller streaming television series directed by Shihab Shaheen.[1][2] It aired on Chorki on 12 July 2021.[3] Cast Afran Nisho as Salaam Sharif Babu[4]…

Book series Cover of the first edition of Encyclopedia Brown: Boy Detective (1963) Encyclopedia Brown is a series of books featuring the adventures of boy detective Leroy Brown, nicknamed Encyclopedia for his intelligence and range of knowledge. The series[1][2] of 29 children's novels was written (one co-written) by Donald J. Sobol, with the first book published in 1963 and the last published posthumously in 2012. In addition to the main books, the Encyclopedia Brown series has …

Shopping mall in Iowa, United StatesCoral Ridge MallLocation1451 Coral Ridge Avenue, Coralville, Iowa, United StatesCoordinates41°41′28″N 91°36′11″W / 41.691°N 91.603°W / 41.691; -91.603Opening dateJuly 29, 1998; 25 years ago (1998-07-29)DeveloperGeneral Growth PropertiesManagementBrookfield PropertiesOwnerBrookfield PropertiesNo. of stores and services114 (as of August 2008)[1]No. of anchor tenants19[1]Total retail floor area…

СПУ 9П78-1 ОТРК 9К720 з ТПУ під крилаті ракети «Р-500» на польовому виході в ході СКШУ «Центр--2015» 92-га ракетна ордена Кутузова бригада — ракетне з'єднання Сухопутних військ Збройних сил Російської Федерації. Бригада дислокується у селі Тоцьке Оренбурзької області. Умовне най…

WAKO Pro World Grand PrixFormation1991TypeFederation of national associationsHeadquartersItalyLocationMonza, Monza and Brianza, LombardyRegion served WorldwideMembership National associationOfficial language EnglishPresidentEnnio FalsoniWebsitehttp://www.wakopro.org/en/ WAKO Pro World Grand Prix, was a kickboxing promotion featuring events held in between national teams since 2011 by the WAKO-Pro organization in association with national kickboxing organizations. Rules All the tournament fights …

This article is about the 1964 film. For the 1976 film, see Shoot (film). 1964 filmThe ShootDirected byRobert SiodmakWritten byKarl May (novel)Georg MarischkaRobert SiodmakProduced byArtur BraunerGötz Dieter WulfHeinz WillegStarringLex BarkerMarie VersiniRalf WolterCinematographyAleksandar SekulovicEdited byUrsula KahlbaumMusic byMartin BöttcherProductioncompaniesCCC FilmSerena FilmCriterion FilmAvala FilmHoche ProductionsRegina FilmDistributed byGloria FilmRelease date20 August 1964Running ti…

Neighbourhood in Calgary, Alberta, CanadaChinatownNeighbourhoodDragon dance in Calgary's ChinatownChinatownLocation of Chinatown in CalgaryCoordinates: 51°03′03″N 114°03′54″W / 51.05083°N 114.06500°W / 51.05083; -114.06500Country CanadaProvince AlbertaCity CalgaryQuadrantSEWard7Government[1] • MayorJyoti Gondek • Administrative bodyCalgary City Council • CouncillorTerry WongArea • Tota…



