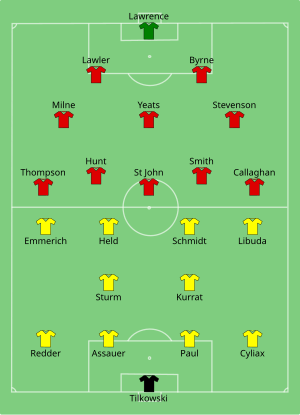
1966 European Cup Winners' Cup final
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Ritratto di giovane donnaAutoreEdgar Degas Data1867 Tecnicaolio su tela Dimensioni27×22 cm UbicazioneMuseo d'Orsay, Parigi Ritratto di giovane donna (Portrait de jeune femme) è un dipinto del pittore francese Edgar Degas, realizzato nel 1867 e conservato al Musée d'Orsay di Parigi. Descrizione Sebbene presenti problemi di datazione - indicata fra il 1862 e il 1870 - l'opera può essere avvicinata cronologicamente al 1867; esposta alla terza mostra Impressionista, nel 1877, l'opera per...

«Ma di tutto bisogna scorgere la fine, dove una cosa vada a terminare. Perché certo molti ai quali Egli aveva fatto intravedere la felicità, sconvolse un dio dalle radici.» (Erodoto, Storie, 1,32,9) Busto erodoteo Erodoto, detto di Alicarnasso o di Thurii (in greco antico: Ἡρόδοτος?, Hēródotos, pronuncia: [hɛːródotos]; Alicarnasso, 484 a.C. – Thurii, circa 425 a.C.), è stato uno storico greco antico. Fu considerato da Cicerone come il «padre della storia».[1] Ne...

Герб Лейпцига Лейпциг является крупнейшим городом Германии и восьмым по численности населения[1], а также наиболее быстро растущим из крупных[2] городов страны. Содержание 1 Ранняя история 2 В Средневековье 3 В Новое время 4 В XIX веке 5 Лейпциг в XX веке 5.1 В годы национа

Fire at SeaPoster filmSutradaraGianfranco RosiProduser Gianfranco Rosi Paolo Del Brocco Donatella Palermo Ditulis oleh Gianfranco Rosi Penata musikStefano GrossoSinematograferGianfranco RosiPenyuntingJacopo QuadriDistributor01 DistributionTanggal rilis 13 Februari 2016 (2016-02-13) (Berlin) 18 Februari 2016 (2016-02-18) (Italia) Durasi108 menitNegara Italia Bahasa Italia Pendapatankotor$1 juta[1] Fire at Sea (bahasa Italia: Fuocoammare) adalah film dokument...

Walter Planckaert Persoonlijke informatie Volledige naam Walter Planckaert Geboortedatum 8 april 1948 Geboorteplaats Nevele, België Sportieve informatie Huidige ploeg gestopt Discipline(s) Weg Ploegen 1970197119721973 -19741975197619771978197919801981 -198219831984 - 1985 Geens-Watney Goldor Watney-Avia Watney-Maes Maes-Watney Maes-Rokado Maes-Miniflat C&A Miniflat-VDB Miniflat-Galli Wickes-Splendor Splendor-Euroshop Panasonic Beste prestaties Milaan-San Remo 5e (1976) Gent-Wevelgem 2e (...

Association football club in England Football clubAnstey NomadsFull nameAnstey Nomads Football ClubNickname(s)The NomadsFounded1946GroundCropston Road, AnsteyChairmanKarl WatsonManagerTony BlanchardLeagueNorthern Premier League Division One Midlands2022–23United Counties League Premier Division North, 1st of 20 (promoted)WebsiteClub website Home colours Away colours Anstey Nomads Football Club is a football club based in Anstey, Leicestershire, England. They are currently members of the Nor...

许多观众正在观看足球比赛。 观赏性体育运动(英語:spectator sport)是指将一流选手进行的高规格比赛,展现给体育迷观赏的运动,这类体育运动有很多观众,可以是职业运动(英语:Professional sports)或业余运动(英语:Amateur sports),且有较高的休闲娱乐性和经济消费效益。 这类比赛具有参赛要求,例如需要有经过专门训练的运动员,一般人无法直接参加,惟有通过观赏...

沙姆解放組織هيئة تحرير الشام領導人 阿布·穆罕默德·朱拉尼 (2017年10月起任軍事首長、正式領導人)[1][2] 阿布·賈比爾·謝赫 (修羅議會領袖,官方領袖至2017年10月)[3][2] 阿布·凱爾·馬斯里 † (基地組織副頭目)[4] 阿布·烏貝達·堪薩夫拉 †(最高軍事指揮官)[5] 活躍期2017年1月28日—至今盟友 叙利亚救国政府[...

上野 響平オリックス・バファローズ #124 2023年7月8日、紀三井寺野球場にて基本情報国籍 日本出身地 大阪府貝塚市生年月日 (2001-04-26) 2001年4月26日(22歳)身長体重 172 cm74 kg選手情報投球・打席 右投右打ポジション 遊撃手プロ入り 2019年 ドラフト3位初出場 2021年4月13日年俸 450万円(2024年)[1]経歴(括弧内はプロチーム在籍年度) 京都国際高等学校 北海道日本ハ

Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Gedung Reichstag – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR ReichstagGedung ReichstagLokasi di BerlinInformasi umumLokasiPlatz der Republik 1, 11011 BerlinKotaBerlinNegara JermanKoordinat52°31�...

Ancient Egyptian tomb QV66Burial site of NefertariNefertari playing SenetQV66Coordinates25°43′40.3″N 32°35′33.4″E / 25.727861°N 32.592611°E / 25.727861; 32.592611LocationValley of the QueensDiscovered1904DecorationBook of the DeadLayoutGenerally straight← PreviousQV65Next →QV67 QV66 is the tomb of Nefertari, the Great Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses II, in Egypt's Valley of the Queens. It was discovered by Ernesto Schiaparelli (the director of the Eg...

Research institute A non-profit genomics research institute. This article contains content that is written like an advertisement. Please help improve it by removing promotional content and inappropriate external links, and by adding encyclopedic content written from a neutral point of view. (March 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 33°27′10.68″N 112°4′1.83″W / 33.4529667°N 112.0671750°W / 33.4529667; -112.0671750 Translational Genomi...

Angkat besi pada Olimpiade Musim Panas 2008LokasiGelanggang Olahraga Universitas BeihangBeijingTanggal9–19 Agustus 2008Jumlah disiplin15Peserta255 dari 84 negara← 20042012 → Angkat besi pada Olimpiade Musim Panas 2008 adalah pelaksanaan cabang olahraga angkat besi pada penyelenggaraan Olimpiade Musim Panas 2008. Kompetisi pada cabang olahraga ini berlangsung di Gelanggang Olahraga Universitas Beihang, Beijing. Edisi ini menandingkan 15 nomor. 255 atlet d...

Отка́занная обра́тная городска́я па́ртия — дебют в русских шашках. Табия дебюта возникает после ходов 1.cb4 fe5 2.ef4 ba5 См. рис. Название дебюта по характеристике игры — отказ от развития в дебют обратная городская партия, который представляет собой городскую партию, разыгра�...

Seventh generation of Volkswagen large van Motor vehicle Volkswagen Multivan (T7)OverviewManufacturerVolkswagen Commercial VehiclesProductionNovember 2021[1][2] – presentModel years2022–presentAssemblyGermany: HanoverBody and chassisClassLarge MPV (M)Light commercial vehicle (M)Body style5-door MPV5-door panel vanLayoutFront-engine, front-wheel-drivePlatformVolkswagen Group MQB EvoPowertrainEnginePetrol:1.5 L TSI I42.0 L TSI I4Petrol plug-in hybrid:1.4&...

Untuk minyak mentah yang ditemukan dalam deposit geologi, lihat Minyak bumi. Minyak mineral dalam botol yang dijual di A.S. Minyak mineral atau minyak parafin adalah berbagai campuran ringan tak berwarna dan tak berbau dari alkana tinggi [en] yang berasal dari sumber mineral, terutama distilat minyak bumi.[1] Nama minyak mineral itu sendiri kurang tepat, tetapi telah digunakan untuk banyak minyak khusus selama beberapa abad. Nama lainnya juga kurang tepat, termasuk minyak...

This article is about the destinations of the Dutch airline. For the destinations of its French counterpart, see List of Transavia France destinations. This is a list of scheduled year-round and seasonal destinations served by Dutch low-cost airline Transavia (formerly transavia.com) as of December 2020:[1] List Countries in which Transavia operates as of October 2023[2][3][4] Transavia Boeing 737-800 This section needs additional citations for verification. Pl...

University press based in New York City, affiliated with Columbia University This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Columbia University Press – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Columbia University PressParent companyColumbi...

Japanese anthropologist For Japanese-American historian, see Edwin M. Yamauchi. Masao YamaguchiBorn(1931-08-20)August 20, 1931Bihoro, Hokkaidō, Empire of JapanDiedMarch 10, 2013(2013-03-10) (aged 81)Mitaka, Tokyo, JapanNationalityJapaneseAlma materUniversity of TokyoScientific careerFieldsAnthropology Masao Yamaguchi (山口 昌男, Yamaguchi Masao, August 20, 1931 – 10 March 2013)[1][2] was a Japanese anthropologist. Overviews Yamaguchi was born in Bihoro, Hokkai...

Barroco siciliano temprano: Quattro Canti, Palermo construido alrededor de 1610. Giulio Lasso († 1617) , arquitecto italiano natural de Florencia, conocido por sus trabajos en Palermo , Sicilia. Fue el proyectista de la plaza de los Quattro Canti en el centro de Palermo. Esta plaza octogonal, que actualmente es un cruce de calles, es uno de los primeros ejemplos de estilo barroco en Sicilia, y también una muestra temprana de planificación urbana. Quattro Canti, oficialmente conocida como ...