Stablecoin
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Stasiun Ōka. Stasiun Oka岡駅Stasiun Oka pada April 2005LokasiOka-Shiroiwa, Kakuda-shi, Miyagi-ken 981-1524JepangKoordinat38°01′9.02″N 140°46′49.99″E / 38.0191722°N 140.7805528°E / 38.0191722; 140.7805528Koordinat: 38°01′9.02″N 140°46′49.99″E / 38.0191722°N 140.7805528°E / 38.0191722; 140.7805528PengelolaAbukumaExpressJalur■ Jalur Abukuma ExpressLetak dari pangkal47.7 km dari FukushimaJumlah...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) أرتو ليندسي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 28 مايو 1953 (70 سنة)[1][2][3] ريتشموند مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية المهنة عازف قيثارة، و�...

魔法老師 魔法先生ネギま! Magister Negi Magi! 假名 まほうせんせい ネギま 罗马字 Mahō Sensei Negima 類型 少年漫畫、魔法、科幻、學園、後宮 作品原名 魔法先生ネギま!/ネギま!? 正式譯名 魔法老師/魔法老師!?( 木棉花國際) 電視動畫 原作 赤松健 導演 宮崎渚(1話-13話)羽原信義(18話-26話) 劇本統籌 大河内一樓 編劇 大河内一樓 人物設定 加藤はつえ 音樂 光宗信吉 ...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع سيلينا (توضيح). سيلينا الإحداثيات 36°32′54″N 85°30′07″W / 36.548379°N 85.50198°W / 36.548379; -85.50198 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة كلاي عاصمة لـ مقاطعة كلاي خصائص جغرافية المساحة 4.394727

Fundación ICO LocalizaciónPaís EspañaLocalidad MadridInformación generalTipo fundación privada y organizaciónSede Edificio ICOHistoriaFundación 1993[editar datos en Wikidata] La Fundación del Instituto de Crédito Oficial, más conocida como Fundación ICO, es una institución española fundada en 1993.[1] Su sede se encuentra en el Edificio ICO situado en el Paseo del Prado de Madrid, y está integrada dentro del Paisaje de la Luz, el paisaje cultural declarado Patr...

City in Turkey Not to be confused with Antakya, Anatolia, or Antaliya. Attalia redirects here. For other uses, see Attalia (disambiguation). Metropolitan municipality in Mediterranean, TurkeyAntalyaMetropolitan municipalityKonyaaltı BeachHadrian's GateHıdırlık TowerDüden WaterfallsAntalya TramAntalya HarbourKaleiçi Seal of Antalya Metropolitan MunicipalityNickname(s): Capital of Tourism(Turkish: Turizmin Başkenti)AntalyaLocation of AntalyaShow map of TurkeyAntalyaAntalya (Mediterr...

Gletscherschrammen (Kritzung) beim Gletschertor des Aletschgletschers Die Detersion bezeichnet die abschleifende Tätigkeit eines Gletschers, der sich über einen Gesteinskörper hinwegbewegt. Als Synonym wird auch der Begriff Gletscherschliff verwendet, wobei letzterer Begriff auch das Resultat der Detersion bezeichnet. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Entstehung 2 Siehe auch 3 Weblinks 4 Einzelnachweise Entstehung Gletscherschliff an Geschiebe mit fast idealen Flächen (Nordbrandenburg)Glatte Schlifffl...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Serbia and Montenegro in the Eurovision Song Contest 2004 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Eurovision Song Contest 2004Country Serbia and MontenegroNational selectionSelectio...

Letov Š-3 Letov Š-3 Role Single-seat fighterType of aircraft National origin Czechoslovakia Manufacturer Letov Kbely Designer Alois Šmolik First flight Early 1922 Number built 2 (the first destroyed before flying) The Letov Š-3 was a single-seat, single-engine parasol wing fighter aircraft designed and built in Czechoslovakia in the early 1920s. Only one was completed and flown, its makers preferring to develop a biplane fighter. Design and development The Letov Š-3, originally known as ...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Salemba – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Salemba tempo dulu Salemba, Januari 2023. Salemba adalah nama sebuah kawasan di Kecamatan Senen, Jakarta Pusat. Nama Salemba bisa pula merujuk ...

Emily VanCampVanCamp pada 2013LahirEmily Irene VanCamp12 Mei 1986 (umur 37)Port Perry, Ontario, KanadaTempat tinggalLos Angeles, California, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1999–sekarangSuami/istriJosh Bowman (m. invalid year) Emily Irene VanCamp (lahir 12 Mei 1986)[1] adalah seorang pemeran asal Kanada yang dikenal karena peran-perannya pada seri televisi The WB Everwood, drama-drama ABC Brothers & Sisters dan Revenge, dan seba...

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: How the Earth Was Made – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) American TV series or program How the Earth Was MadeTitle screenGenreDocumentaryNarrated byCorey JohnsonJonathan KeebleComposerTim GarlandCountry of originUnited State...

International airport serving Manaus, Amazonas state, Brazil Manaus–Eduardo Gomes International AirportAeroporto Internacional de Manaus–Eduardo GomesIATA: MAOICAO: SBEGLID: AM0001SummaryAirport typePublicOperator Infraero (1976–2021) Vinci (2021–present) ServesManausOpenedMarch 31, 1976 (1976-03-31)Focus city forAzul Brazilian AirlinesTime zoneBRT−1 (UTC−04:00)Elevation AMSL81 m / 264 ftCoordinates03°02′28″S 060°03′02″W / 3....
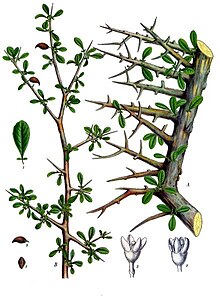
Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Mur. Pohon Commiphora myrrha, salah satu sumber perolehan mur yang utama. Minyak Mur (dari Commiphora myrrha) dalam cawan gelas tembus pandang Mur (bahasa Inggris: myrrh /ˈmɜːr/; dari bahasa Arab مر, mur) adalah suatu resin aromatik dari sejumlah pohon kecil berduri dari genus Commiphora.[1] Minyak mur digolongkan sebagai oleoresin. Resinmur merupakan gom alamiah. Telah digunakan di sepanjang sejarah sebagai parfum, kemenyan dan obat. Juga dapat dim...

Poudrerie nationale de VongesEntrée principale de la poudrerie nationale de Vonges route de Pontailler Août 2012.FonctionnementOpérateur TitanobelLocalisationSituation Vonges (Côte-d'OrBourgogne-Franche-Comté)Coordonnées 47° 17′ 31″ N, 5° 24′ 02″ Emodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata La poudrerie nationale de Vonges est une ancienne poudrerie royale fondée en 1691 et nationalisée en 1905 située sur la commune de Vonges, en Côte...

Brazilian mixed martial artist (born 1989) In this Portuguese name, the first or maternal family name is Oliveira and the second or paternal family name is da Silva. Charles OliveiraOliveira in 2021BornCharles Oliveira da Silva[1] (1989-10-17) 17 October 1989 (age 34)Guarujá, São Paulo, BrazilNicknamedo BronxHeight5 ft 10 in (178 cm)Weight155 lb (70 kg; 11 st 1 lb)Division Featherweight(2012–2016) Lightweight(2008–2011)(2017–present)...
Vermont, United States newspaper The Burlington Free PressTypeDaily newspaperFormatTall TabloidOwner(s)GannettEditorAki SogaFounded1827(as the Free Press Weekly)LanguageEnglishHeadquarters426 Industrial Ave #160Williston,[1][2] VT 05495 United StatesCirculation5,484 Daily 7,152 Sunday (as of 2022)[3]ISSN0894-8844OCLC number9390458 Websitewww.burlingtonfreepress.com The Burlington Free Press (sometimes referred to as BFP or the Free Press) is a digital and prin...
Spoorlijn 122Y Melle - Geraardsbergen Totale lengte28,5 kmSpoorwijdtenormaalspoor 1435 mmAangelegd doorChemin de fer de Braine-le-Comte à GandGeopend5 januari 1867Huidige statusin gebruikGeëlektrificeerdneeAantal sporen2Baanvaksnelheid90 km/uTreindienst doorNMBS Traject lijn 50 van Gent-Sint-Pieters 0,0 Y Mellelijn 50 naar Brussel-Noord Y Melle50A/4 naar Y Meulewijk lijn 50A, Oostende - Brussel-Zuid A10E40 1,5 Gontrode 2,8 Landskouter 4,8 Moortsele 6,7 Scheldewindeke 8,9 Balegem-Dorp 11,8 B...

Science fiction novel series This section may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. You can help. The talk page may contain suggestions. (February 2014) The Catteni Series (also called the Freedom Series) is a tetralogy of science fiction novels by American writer Anne McCaffrey. In this universe, humans are slaves of aliens, the humanoid Catteni. Woven through all four of the books are details of the relationship between Kristin Bjornsen, a former slave, and Zain...

Toilet that is easily moved around A portable urine-diverting dry toilet as marketed by SOIL in Haiti under the name EkoLakay A portable or mobile toilet (colloquial terms: thunderbox, porta-john or porta-potty) is any type of toilet that can be moved around, some by one person, some by mechanical equipment such as a truck and crane. Most types do not require any pre-existing services or infrastructure, such as sewerage, but are completely self-contained. The portable toilet is used in a vari...
