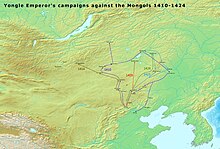
Ming dynasty in Inner Asia
|
Read other articles:

نجمة ادريس الدكتور نجمة إدريس في حفل تكريم جائزة المرأة العربية المتميزة في مجال الأدب 2013 معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة نجمة عبدالله ادريس الميلاد 25 ديسمبر 1952 (71 سنة) الكويت - الصالحية الجنسية الكويت الأولاد 3 الحياة العملية المواضيع الرواية العربية الحديثة [لغ�...

Milan Biševac Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Milan BiševacTanggal lahir 31 Agustus 1983 (umur 40)Tempat lahir Titova Mitrovica, SFR YugoslaviaTinggi 1,85 m (6 ft 1 in)Posisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini Olympique LyonnaisNomor 15Karier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2001–2003 BASK 52 (5)2003 FK Sopot 15 (1)2004 Železnik 14 (1)2004–2007 Red Star Belgrade 58 (3)2007–2008 RC Lens 35 (1)2008–2011 Valenciennes 100 (4)2011–2012 Paris Saint-Germain 19 (1)2012�...
Contoh hasil penelitian radioaktivitas untuk orientasi akademis Penelitian murni adalah salah satu jenis penelitian sosial yang memiliki orientasi pada bidang akademis.[1] Jenis penelitian ini tidak bertujuan untuk memberikan solusi atas suatu masalah atau fenomena sosial tertentu.[1] Ciri utama dari penelitian ini adalah banyak digunakan dalam lingkup akademis, memiliki tingkat abstrak yang tinggi, manfaatnya tidak dapat dirasakan secara langsung, serta mengembangkan ide, teo...
Village in West Bengal, IndiaDhandadihivillageDhandadihiLocation in West Bengal, IndiaShow map of West BengalDhandadihiDhandadihi (India)Show map of IndiaCoordinates: 23°37′39″N 87°09′01″E / 23.627541°N 87.150311°E / 23.627541; 87.150311Country IndiaStateWest BengalDistrictPaschim BardhamanPopulation (2011) • Total3,843Languages • OfficialBengali, EnglishTime zoneUTC+5:30 (IST)Vehicle registrationWBLok Sabha constituencyAsa...

باول برستون (بالإنجليزية: Paul Preston) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 21 يوليو 1946 (77 سنة) ليفربول[1] مواطنة المملكة المتحدة عضو في الأكاديمية البريطانية الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم كلية أوريل بجامعة أكسفورد شهادة جامعية دكتوراه في الفلسفة[2] طلاب الدكتو

Outline of road naming conventions in Great Britain Odonymy refers to the street or road naming conventions in the toponymy of the United Kingdom. History Houndsditch, an example of a street name with no suffix in the City of London Studied by the English Place-Name Society. Many towns (particularly in England) will refer to their main thoroughfare as the High Street or Main Street, and many of the ways leading off it will be suffixed Road. In the City of London, according to tradition, there...

Juhi ChawlaLahirJuhi S. Chawla13 November 1967 (umur 56) Ambala, HaryanaKebangsaanIndiaTahun aktif1986 - sekarangSuami/istriJai Mehta (m. 1995) Juhi Chawla (Hindi: जूही चावला) (lahir 13 November 1967) adalah aktris Bollywood, produser film dan pengusaha India. Setelah memenangkan kontes kecantikan Miss India 1984, ia membuktikan dirinya sebagai salah satu aktris terkemuka di sinema Hindi dari akhir 1980-an hingga awal 2000-an.[1] ...

العلاقات الرواندية الفنلندية رواندا فنلندا رواندا فنلندا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الرواندية الفنلندية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين رواندا وفنلندا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة ر

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Kirey – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR NurzairinaLahirNurzairina16 Oktober 1976 (umur 47) Selong, Lombok Timur, Nusa Tenggara Barat, IndonesiaNama lainKireyPekerjaanPenyanyi,...

2006 single by NinaSomedaySingle by Ninafrom the album Nina ReleasedNovember 13, 2006Recorded2006GenrePopLength3:34LabelWarner Music PhilippinesSongwriter(s)Nyoy VolanteProducer(s)Neil GregorioNina singles chronology I Do (2006) Someday (2006) I Can't Make You Love Me (2007) Someday is a song by Filipino singer Nina from her 2006 self-titled fourth album.[1] It was released as the album's second commercial single in November 2006 by Warner Music Philippines. The song was written and c...

Гел Робсон-Кану Гел Робсон-Кану Особисті дані Народження 21 травня 1989(1989-05-21) (34 роки) Актон, Лондон, Англія Зріст 183 см Вага 83 кг Громадянство Англія Уельс Позиція фланговий півзахисник Юнацькі клуби 2004–2007 «Редінг» Професіональні клуби* Роки Клуб І (г) 2007–2016 «Ред

Species of butterfly Adelpha fessonia Sucking on a banana top Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Lepidoptera Family: Nymphalidae Genus: Adelpha Species: A. fessonia Binomial name Adelpha fessoniaHewitson, 1847 Adelpha fessonia, the band-celled sister or Mexican sister, is a species of butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Panama north through Central America to Mexico. It is a periodic resident in the lower...

German speed skater Andreas DietelAndreas Dietel in 1978Personal informationNationalityGermanBorn (1959-10-20) 20 October 1959 (age 64)Langenbernsdorf, East GermanySportSportSpeed skating Andreas Dietel (born 20 October 1959) is a German speed skater. He competed at the 1980 Winter Olympics and the 1984 Winter Olympics.[1] References ^ Evans, Hilary; Gjerde, Arild; Heijmans, Jeroen; Mallon, Bill; et al. Andreas Dietel Olympic Results. Olympics at Sports-Reference.com. Sports...

American actor This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Walter Baldwin – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2013) (Learn how and w...

For the island in the Gulf of Carpentaria, see Mornington Island. Suburb of Mount Isa, Queensland, AustraliaMorningtonMount Isa, QueenslandMorningtonCoordinates20°44′02″S 139°29′45″E / 20.7340°S 139.4959°E / -20.7340; 139.4959 (Mornington (centre of suburb))Population1,764 (2016 census)[1] • Density1,760/km2 (4,570/sq mi)Postcode(s)4825Area1.0 km2 (0.4 sq mi)Time zoneAEST (UTC+10:00)LGA(s)City of Mount Is...

The Immanent FrameSecularism, Religion, and the Public SphereEditorMona OrabyCategoriesDigital PublicationPublisherSocial Science Research CouncilFounderJonathan VanAntwerpenFounded2007CountryUnited StatesBased inBrooklyn, New YorkLanguageEnglishWebsitehttp://tif.ssrc.org/ The Immanent Frame is a digital forum that publishes interdisciplinary perspectives on secularism, religion, and the public sphere. It was formed in conjunction with projects on religion and the public sphere at the Social ...

San MattiaEsternoStato Italia RegioneLazio LocalitàRoma Coordinate41°56′46.68″N 12°33′08.46″E / 41.946301°N 12.55235°E41.946301; 12.55235Coordinate: 41°56′46.68″N 12°33′08.46″E / 41.946301°N 12.55235°E41.946301; 12.55235 Religionecattolica Diocesi Roma Consacrazione16 dicembre 1978 Inizio costruzione1968 Completamento1969 Sito webSito della parrocchia Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La chiesa di San Mattia è una chiesa d...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع إنا (توضيح). هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يناير 2019) إنا (باليابانية: 伊奈町) إنا (اليابان) خريطة الموقع تاريخ التأسيس 15 يوليو 1943، و1 نوفمبر 1970 تقسيم إداري الب...

Maghrebi Arab lexicographer of the Arabic language (c.1233-c.1312) Ibn ManẓūrBornJune/ July 1233Tripoli Ifriqiya (now LibyaDiedDecember 1311/ January 1312 (aged 78)Cairo, Bahri Mamluks, now EgyptOccupationLexicographer, Judge qadi in Tripoli, Libya and Egypt, Clerk in Diwan al-Insha'Notable worksLisān al-ʿArab (completed in 1290) Al-Maṭbaʿa al-Kubra al-Amirīya, Muhammad ibn Mukarram ibn Alī ibn Ahmad ibn Manzūr al-Ansārī al-Ifrīqī al-Misrī al-Khazrajī (Arabic: محمد بن �...

Национальная библиотека Украины имени Ярослава Мудрогоукр. Національна бібліотека України імені Ярослава Мудрого Тип национальная научная библиотека Страна Украина Адрес Киев, ул. М. Грушевского, 1 Основана 1866 Фонд Объём фонда ок. 4 млн единиц Доступ и пользование ...