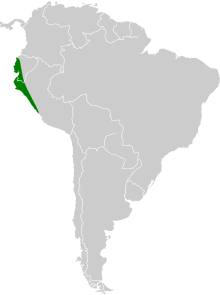
Fraternal fruit-eating bat
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
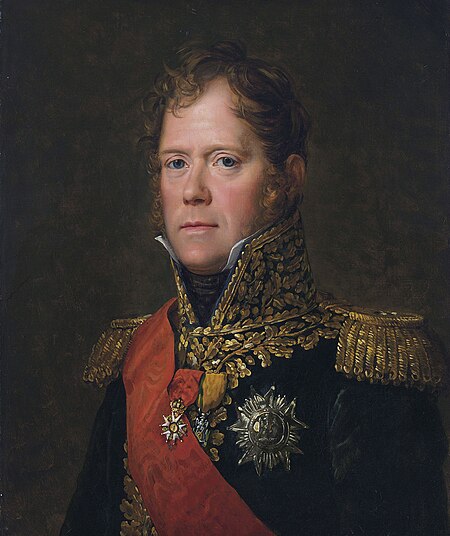

French military commander Marshal of the EmpireMichel NeyPrince de la MoskowaPortrait by François Gérard, 1805Nickname(s) Le Brave des braves Le Rougeaud Born(1769-01-10)10 January 1769Sarrelouis, France; modern-day GermanyDied7 December 1815(1815-12-07) (aged 46)Paris, FranceBuriedPère Lachaise CemeteryAllegiance Kingdom of France Kingdom of the French French First Republic First French Empire Bourbon Restoration BranchFrench ArmyService years1787�...
Method of burial used by Native Americans Stone box graves were a method of burial used by Native Americans of the Mississippian culture in the Midwestern United States and the Southeastern United States. Their construction was especially common in the Cumberland River Basin, in settlements found around present-day Nashville, Tennessee. Construction A stone box grave is a coffin of stone slabs arranged in a rectangular shape, into which a deceased individual was placed. Common materials used ...

ولاد العربي غبال تقسيم إداري البلد المغرب الجهة الرباط سلا القنيطرة الإقليم سيدي قاسم الدائرة ورغة الجماعة القروية لمرابيح المشيخة الزوايد السكان التعداد السكاني 222 نسمة (إحصاء 2004) • عدد الأسر 41 معلومات أخرى التوقيت ت ع م±00:00 (توقيت قياسي)[1]، وت ع م+01:00 (توقيت �...

2003 EP (Split) by the Suicide Machines/PotshotThe Suicide Machines / PotshotEP (Split) by the Suicide Machines/PotshotReleased2003 The Suicide Machines / Potshot is a 2003 split EP album by American punk rock band the Suicide Machines and Japanese J-ska band Potshot. Track listing Songs performed by Potshot Endless Future – 2:25 Islands (Suicide Machines cover) – 2:12 Songs performed by The Suicide Machines High Anxiety – 2:04 Smile (Potshot cover) – 2:09 vteThe Suici...
Мару — термін, який має кілька значень. Ця сторінка значень містить посилання на статті про кожне з них.Якщо ви потрапили сюди за внутрішнім посиланням, будь ласка, поверніться та виправте його так, щоб воно вказувало безпосередньо на потрібну статтю.@ пошук посилань саме...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (نوفمبر 2018) مايكل أوشيا معلومات شخصية الميلاد 17 مارس 1906 هارتفورد، كونيتيكت الوفاة 4 ديسمبر 1973 (67 سنة) دالاس، تكساس سبب الوفاة نوبة قلبية مواطنة الولا

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Cinattus wulingensis Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Kelas: Arachnida Ordo: Araneae Famili: Salticidae Genus: Cinattus Spesies: Cinattus wulingensis Nama binomial Cinattus wulingensisPeng & Xie, 1995 Cinattus wulingensis ad...

Sporting event delegationColombia at the2023 World Aquatics ChampionshipsFlag of ColombiaFINA codeCOLNational federationFederación Colombiana de NataciónWebsitefecna.comin Fukuoka, JapanCompetitors15 in 4 sportsMedalsRanked 21st Gold 0 Silver 1 Bronze 0 Total 1 World Aquatics Championships appearances197319751978198219861991199419982001200320052007200920112013201520172019202220232024 Colombia is scheduled to compete at the 2023 World Aquatics Championships in Fukuoka, Japan from 14 to 30 Ju...

Bundle of skeletal muscle fibers Muscle fascicleStructure of a skeletal muscle. (Fascicle labeled at bottom right.)DetailsPart ofSkeletal muscleIdentifiersLatinfasiculus muscularisTA22006THH3.03.00.0.00003 Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata]Not to be confused with Nerve fascicle. A muscle fascicle is a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium, a type of connective tissue.[1] Structure Muscle cells are grouped into muscle fascicles by enveloping perimysium con...

1927 film The Strange Case of Captain RamperDirected byMax ReichmannScreenplay by Curt Johannes Braun Paul Wegener[1] Based onRamperby Max MohrStarring Paul Wegener Mary Johnson Cinematography Friedrich Weinmann Herbert Körner[2] Music byWalter Ulfig[2]ProductioncompanyDeutsche Film-Union AG[2]Release date 31 October 1927 (1927-10-31) (Berlin) CountryGermany[2]LanguageSilent The Strange Case of Captain Ramper (German: Ramper, der Tie...

Television channel Lumiere MoviesLumiere Movies LogoCountryIndiaBroadcast areaSouth Asia, particularly IndiaHeadquartersMumbai, Maharashtra, IndiaProgrammingLanguage(s)English (subtitles)Picture format480i (SDTV)720p (HDTV)OwnershipOwnerTurner Broadcasting System (WarnerMedia)HistoryLaunched2009Closed2012 Lumière Movies was an Indian 24-hour movie channel dedicated to foreign films owned by Turner Broadcasting System (a subsidiary of Time Warner) based in Mumbai.[1] The channel was l...

Indian actress Anya SinghSingh in 2017BornDelhi, IndiaNationalityIndianOccupationActressYears active2016–present Anya Singh is an Indian actress who made her debut in Bollywood film Qaidi Band (2017). After making her acting debut as a minor artist, Singh played her first leading role in Habib Faisal's musical drama film Qaidi Band in 2017, alongside Aadar Jain.[1] Filmography Films Key † Indicates a film that has not yet been released Year Title[a] Role Notes Ref. 20...

中华人民共和国国务院副总理中华人民共和国国徽中华人民共和国国旗現任丁薛祥(常务)何立峰张国清刘国中2023年3月12日就任中华人民共和国国务院尊称副总理阁下、同志类别政府副首脑地位国家级副职公务员党和国家领导人所属国务院全体会议(作为国务院组成人员)国务院常务会议直屬中华人民共和国国务院总理官邸中南海(无正式规定)機關所在地 中华人民共�...

Method for representing or encoding numbers Glossary of terms used in the positional numeral systems Part of a series onNumeral systems Place-value notation Hindu-Arabic numerals Western Arabic Eastern Arabic Bengali Devanagari Gujarati Gurmukhi Odia Sinhala Tamil Malayalam Telugu Kannada Dzongkha Tibetan Balinese Burmese Javanese Khmer Lao Mongolian Sundanese Thai East Asian systems Contemporary Chinese Suzhou Hokkien Japanese Korean Vietnamese Historic Counting rods Tangut Other systems His...

Species of cactus Lobivia ferox Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Order: Caryophyllales Family: Cactaceae Subfamily: Cactoideae Genus: Lobivia Species: L. ferox Binomial name Lobivia feroxBritton & Rose Synonyms Echinopsis ferox (Britton & Rose) Backeb. 1934 Furiolobivia ferox (Britton & Rose) Y.Itô 1957 Pseudolobivia ferox (Britton & Rose) Backeb...

American novelist Anna de KovenBornAnna Farwell(1862-11-19)November 19, 1862Chicago, IllinoisDiedJanuary 12, 1953(1953-01-12) (aged 90)Northeast Harbor, MaineEducationLake Forest UniversityOccupationWriterSpouse Reginald de Koven (m. 1884; died 1920)Children1ParentsCharles B. Farwell (father)Mary Evelyn Farwell (mother)RelativesRose Farwell Chatfield-Taylor (sister) Anna de Koven (née Farwell; November 19, 1862 – January 12, 1953...

1987 live album by Liza MinnelliAt Carnegie HallLive album by Liza MinnelliReleasedSeptember 1987Recorded1987GenreJazz, vocal, traditionalLabelTelarc International CorporationProducerLarry Marks, Robert WoodsLiza Minnelli chronology Live at Carnegie Hall(1981) At Carnegie Hall(1987) Results(1989) At Carnegie Hall is the fifth live album by American singer and actress Liza Minnelli.[1] Released in 1987, it marks the singer's first work released under the independent label Telar...

American soccer player Justen Glad Glad with Real Salt Lake in 2021Personal informationFull name Justen Thomas GladDate of birth (1997-02-28) February 28, 1997 (age 26)Place of birth Pasadena, California, United StatesHeight 6 ft 0 in (1.83 m)[1]Position(s) DefenderTeam informationCurrent team Real Salt LakeNumber 15Youth career2012–2014 Real Salt Lake AZSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2014– Real Salt Lake 206 (12)2015–2019 Real Monarchs 9 (1)International...

Este artículo o sección tiene referencias, pero necesita más para complementar su verificabilidad.Este aviso fue puesto el 28 de septiembre de 2013. Movimiento Comunista Fundación 1972Disolución 1991 [1]Partidos fusionados LCR (1991-1993)Ideología ComunismoMarxismoLeninismo(1983- hasta su disolución)Facciones:(1972-1983)MaoísmoTroskismoBordiguismoLuxemburguismoAntirrevisionismoPosición Extrema izquierdaPartidoscreadores Movimiento Comunista Vasco Organización Comunista de Zara...

City in the Flemish part of Belgium For other uses, see Bruges (disambiguation). You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Dutch. (April 2023) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text in...