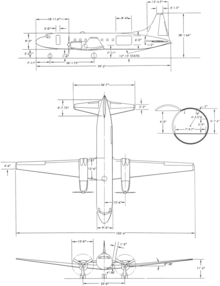
Convair C-131 Samaritan
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

جرمياس ريختر معلومات شخصية الميلاد 10 مارس 1762(1762-03-10)جيلينيا جورا الوفاة 4 مايو 1807 (45 سنة) ، 14 أبريل 1807برلين مواطنة ألمانيا عضو في الأكاديمية البافارية للعلوم والعلوم الإنسانية، والأكاديمية الروسية للعلوم الحياة العملية المهنة كيميائي اللغات الألمانية مجال العم

v · mTraitement du combustible nucléaire usé France Usine de retraitement de la Hague Allemagne Usine de retraitement de Wackersdorf; Kerntechnische Entsorgung Karlsruhe Royaume-Uni Site nucléaire de Sellafield États-Unis Usine de retraitement de West Valley Japon Usine nucléaire de Rokkasho Russie Complexe nucléaire Maïak Voir aussi : Transport du combustible nucléaire Documentation de palette[créer] [purger] Ceci est la documentation du modèle {{Pa...

Universitas of TriesteUniversità degli Studi di Triestebahasa Latin: Universitas Studiorum TergestumJenisNegeriDidirikan1924RektorProf. Maurizio FermegliaStaf administrasi1.000Jumlah mahasiswa15.177LokasiTrieste, ItaliaTim olahragaCUS TriesteAfiliasiAlmalaurea, CEI Jaringan Universitas, Nettuno (accessed 26 February 2014)Situs webwww.units.it Universitas Trieste (bahasa Italia: Università degli Studi di Trieste, or UniTS) adalah universitas di Trieste di wilayah Friuli-Venezia Giuli...

Japanese manga series Seraphim 266613336Wingsセラフィム 2億6661万3336の翼(Seraphim: 2-oku 6661-man 3336 no Tsubasa) MangaWritten byMamoru OshiiSatoshi KonIllustrated bySatoshi KonPublished byTokuma ShotenEnglish publisherDark Horse ComicsMagazineAnimageDemographicSeinenOriginal runMarch 1994 – November 1995Volumes1 Seraphim 266613336Wings (Japanese: セラフィム 2億6661万3336の翼, Hepburn: Seraphim: 2-oku 6661-man 3336 no Tsubasa) is an unfinished Japanese man...

20th-century Austrian politician Edmund Glaise-HorstenauPortrait by Max FenichelVice-Chancellor of AustriaIn office11 March 1938 – 13 March 1938ChancellorArthur Seyß-InquartPreceded byLudwig HülgerthSucceeded byAdolf Schärf (1945)Minister of the InteriorIn office6 November 1936 – 16 February 1938ChancellorKurt SchuschniggPreceded byEduard Baar-Baarenfels [de]Succeeded byArthur Seyß-Inquart Personal detailsBornEdmund Glaise von Horstenau(1882-02-27)27 Feb...

歩兵第2連隊 歩兵第2連隊の練兵場跡に建立された「水戸歩兵部隊の跡」の碑(茨城県水戸市堀原)創設 1871年廃止 1944年11月24日玉砕所属政体 大日本帝国所属組織 大日本帝国陸軍部隊編制単位 連隊兵科 歩兵所在地 佐倉・宇都宮 - 水戸編成地 水戸通称号/略称 照7746補充担任 水戸連隊区上級単位 東京鎮台 - 第1師団 - 第14師団最終位置 パラオ諸島 ペリリュー島主な戦�...

Treatise by Thomas Malthus An Essay on the Principle of Population Title page of the original edition of 1798AuthorThomas Robert MalthusCountryEnglandLanguageEnglishPublisherJ. Johnson, LondonPublication date1798 The book An Essay on the Principle of Population was first published anonymously in 1798,[1] but the author was soon identified as Thomas Robert Malthus. The book warned of future difficulties, on an interpretation of the population increasing in geometric progression (so as ...

Leeward Islands Air Transport IATA ICAO Kode panggil — LIA LIAT Didirikan20 Oktober 1956 (sebagai Leeward Islands Air Transport Services)[1]Pusat operasi Bandar Udara Internasional Grantley Adams (Bridgetown) Bandar Udara Internasional Piarco (Port of Spain) Bandar Udara Internasional V. C. Bird (St. John's) Armada18Tujuan22SloganTHE Caribbean AirlineKantor pusatBandar Udara Internasional V. C. BirdSaint George Parish, AntiguaTokoh utamaBrian Challenger (CEO) Ag.Jean Stewart Holder ...

Municipality in MontenegroBudva Municipality Opština BudvaMunicipality Coat of armsBudva Municipality in MontenegroCountryMontenegroSeatBudvaArea • Total122 km2 (47 sq mi)Population (2019) • Total22,061 • Density180/km2 (470/sq mi)Time zoneUTC+1 (CET) • Summer (DST)UTC+2 (CEST)Postal code85310Area code+382 33ISO 3166-2 codeME-05Car platesBDClimateCsaWebsitebudva.me Budva Municipality is one of the municip...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (December 2012) This article has an unclear citation style. The reason given is: In particular, use a consistent style. The references used may be m...

2006 San Francisco Board of Supervisors election ← 2004 November 7, 2006 2008 → Elections in California Federal government U.S. President 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 1892 1896 1900 1904 1908 1912 1916 1920 1924 1928 1932 1936 1940 1944 1948 1952 1956 1960 1964 1968 1972 1976 1980 1984 1988 1992 1996 Dem Rep 2000 Dem Rep 2004 Dem Rep 2008 Dem Rep 2012 Dem Rep 2016 Dem Rep 2020 Dem Rep 2024 Dem Rep U.S. Senate 1849 1850 1852 sp 1856 1857 sp 1860 1860 ...

Guling bambu buatan Korea. Guling Bambu (bahasa Korea: 죽부인/jukbuin, Hanzi:竹夫人) adalah guling yang terbuat dari bambu. Peralatan ini populer di Korea, Tiongkok, dan Jepang sebagai teman tidur, terutama pada saat musim panas. Dalam bahasa Inggris disebut pula Dutch wife. Disebut demikian, karena guling bambu pernah populer di kalangan para pedagang Belanda di Hindia Belanda, yang merasa kesepian karena jauh dari istrinya. Guling bambu dibuat dari jalinan bambu tipis yang dibuat ...

Metropolitan rail project in Melbourne, Australia Western Rail PlanMap of Rail Lines in Melbourne's West that go through Sunshine. Blue means the line will be or is electrified, purple means it is a regional line.OverviewStatusCancelledWebsiteOfficial website The Western Rail Plan is a metropolitan rail infrastructure project being undertaken in Melbourne, Australia. The project was initially announced during the 2018 Victorian state election by the State Government. It includes the electrifi...

British films released in 1955 Cinema of theUnited Kingdom List of British films British horror 1888–1919 1920s 1920 1921 1922 1923 19241925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1930s 1930 1931 1932 1933 19341935 1936 1937 1938 1939 1940s 1940 1941 1942 1943 19441945 1946 1947 1948 1949 1950s 1950 1951 1952 1953 19541955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960s 1960 1961 1962 1963 19641965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970s 1970 1971 1972 1973 19741975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980s 1980 1981 1982 1983 19841985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990...

Commercial building in Malton, North Yorkshire, England The Palace CinemaThe Palace CinemaLocationYorkersgate, MaltonCoordinates54°08′05″N 0°47′54″W / 54.1347°N 0.7983°W / 54.1347; -0.7983Built1846Architectural style(s)Neoclassical style Listed Building – Grade IIOfficial nameFormer Palace Cinema and Cinema ShopDesignated10 June 1974Reference no.1220592 Shown in North Yorkshire The Palace Cinema is a commercial building in Yorkersgate in Malton, Nort...

Bawang hitam Bawang hitam adalah produk fermentasi dari bawang putih segar yang disimpan pada suhu 60–70 derajat Celsius selama 30–40 hari[1][2]. Proses fermentasi ini menyebabkan perubahan warna, tekstur, dan rasa pada bawang putih[1][3]. Bawang hitam bukanlah varietas bawang baru[1], melainkan modifikasi dari bawang putih dengan menggunakan suhu tinggi[1][2]. Manfaat kesehatan Bawang hitam diklaim memiliki berbagai manfaat bagi kes...

Artikel ini bukan mengenai Menoreh. Lihat pula: Menorah (Hanukkah) Menorah adalah kata bahasa Ibrani untuk Kandil atau Kaki Dian (disebut juga Kaki Pelita atau Pelita saja; bahasa Ibrani: מנורה - menôrâh. Dalam rangka pembangunan Kemah Suci Allah memerintahkan untuk membuat sebuah Menorah, yaitu Kandil atau Kaki Pelita, berhias terbuat dari emas (Keluaran 25:31). Dari batang tiang utama yang menyangga pegangan pelita, muncul 3 pasang cabang dengan arah berlawanan, yang pada ujung-ujung...

National Scouting organization of Eritrea Please add Ge'ez script to this article, where needed. National Scout Association of EritreaCountryEritreaFounded(1950) Scouting portal The National Scout Association of Eritrea is the national Scouting organization of Eritrea. Scouting in Eritrea shares a common history with that of Ethiopia, where Scouting was founded in 1950. Scouting in Eritrea has become active again after many years of government banning, and is in its infancy. Political u...

The Weinstein Company LLCJenisSwastaIndustriFilmPenerusLantern EntertainmentDidirikan10 Maret 2005PendiriBob WeinsteinHarvey WeinsteinDitutup04 Agustus 2018 (2018-08-04)KantorpusatNew York City, New York, USAProdukGambar gerakKaryawan200[1]DivisiDimension FilmsDimension ExtremeOvation TV (dimiliki bersama Hubbard Media Group)Dragon Dynasty (dimiliki bersama Gaiam Vivendi Entertainment)Third Rail ReleasingTWC-DimensionRadius-TWCKaleidoscope-TWCThe Miriam CollectionAnakusahaStarz D...

Area of Glasgow Human settlement in ScotlandRosshallGreen space on the banks of the White Cart, looking towards Cairnhill CircusRosshallLocation within GlasgowPopulation700 [1]OS grid referenceNS518633Council areaGlasgow City CouncilLieutenancy areaGlasgowCountryScotlandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townGlasgowPostcode districtG52 3Dialling code0141PoliceScotlandFireScottishAmbulanceScottish UK ParliamentGlasgow South WestScottish ...