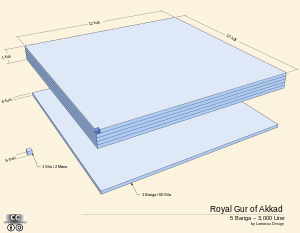
Ancient Mesopotamian units of measurement
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Retrato de Daoiz y Velarde, litografía de Paolo Guglielmi a partir del grupo en mármol de Antonio Solá instalado en la Plaza del Dos de Mayo de Madrid. Biblioteca Nacional de España. Paolo Guglielmi (Roma, 1804-1862) fue un pintor y litógrafo italiano. Biografía y obra Formado en la Academia de Bellas Artes de Roma, conoció en ella a Antonio Canova que lo pensionó por tres años para que trabajase en la reproducción y divulgación de sus obras mediante la estampa. Con este objetivo d...

Cabinet of Japan (January 12 - June 30, 1898) Third Itō Cabinet7th Cabinet of JapanPrime Minister Itō HirobumiDate formedJanuary 12, 1898Date dissolvedJune 30, 1898People and organisationsEmperorMeijiPrime MinisterItô HirobumiHistoryPredecessorSecond Matsukata CabinetSuccessorFirst Ōkuma Cabinet The Third Itō Cabinet is the seventh Cabinet of Japan led by Itō Hirobumi from January 12, 1898, to June 30, 1898. Cabinet Portfolio Minister Political party Term start Term end Prime Minister M...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento religiosi francesi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Pietro Bartolomeo (Marsiglia, ... – Antiochia di Siria, 20 aprile 1099) è stato un monaco cristiano e mistico francese, che accompagnò i cavalieri della prima crociata (Crociata dei baroni). Indice 1 Biografia 2 Bibliografia 3 Altri progetti 4 Colle...

Manchester Metrolink tram stop East DidsburyMetrolink stationGeneral informationLocationDidsbury, ManchesterEnglandCoordinates53°24′44″N 2°13′02″W / 53.41209°N 2.21736°W / 53.41209; -2.21736Grid referenceSJ856905Line(s)South Manchester LinePlatforms2 (island)Other informationStatusIn operationFare zone3Key dates23 May 2013OpenedServices Preceding station Manchester Metrolink Following station Terminus East Didsbury–Shaw and Crompton Didsbury Villagetoward...

Hispano-Suiza E-34 Tipo Entrenador elementalFabricante Hispano-SuizaDiseñado por Vicente Roa MirandaPrimer vuelo 1935Introducido 1936Estado RetiradoN.º construidos 6Desarrollo del Hispano-Suiza E-30[editar datos en Wikidata] El Hispano-Suiza E-34, más tarde redenominado HS-34, fue un entrenador elemental biplano, monomotor y biplaza en tándem, diseñado en España a mediados de los años treinta como entrenador básico. Fue diseñado por el ingeniero Vicente Roa Miranda y constr...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) تمتلك الجزائر العديد من الخلجان على الشريط الساحلي بطول إجمالي يقارب 1 622 كم عبر 14 ولاية على ساحل البح

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) زاين ميتشيل معلومات شخصية الميلاد سنة 1970 (العمر 52–53 سنة)[1][2] جاكسون، مسيسيبي مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية المهنة روائية، وك

Wappen der Earls of Stockton Earl of Stockton ist ein erblicher britischer Adelstitel in der Peerage of the United Kingdom, benannt nach der englischen Stadt Stockton-on-Tees. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Verleihung und nachgeordnete Titel 2 Liste der Earls of Stockton (1984) 3 Einzelnachweise 4 Literatur und Weblinks Verleihung und nachgeordnete Titel Der Titel wurde am 24. Februar 1984 an den früheren britischen Premierminister Harold Macmillan verliehen.[1] Zusammen mit der Earlwürde wur...

Sanggar Prathivi merupakan sebuah studio yang bergerak di bidang pelayanan sosial.[1] Sanggar parathivi juga dapat dikatakan sebagai sanggar yang bergerak di bidang radio, televisi dan film.[1] Sanggar prathivi berdiri pada tahun 1965 dan merupakan studio pertama serta tertua di Jakarta.[1] Ide berdirinya sanggar prathivi pertama kali diprakasai oleh Pater Wolbertus Daniels, S.J.[1] Sanggar ini membuka kursus bagi seseorang yang berminat bergerak di bidang peny...

BogotáDistrik Ibukota BenderaLambangMotto: Bogotá, 2600 metros más cerca de las estrellasBogotá, 2600 meter lebih dekat ke bintang-bintangArea (localidades) dari BogotáNegaraKolombiaDepartemenBogotá, D.C.*Pendirian6 Agustus 1538Pemerintahan • Wali KotaClaudia López HernándezLuas • Distrik Ibukota1.587 km2 (612,7 sq mi) • Luas daratan1,731,9 km2 (668,7 sq mi)Ketinggian2.640 m (8,660 ft)Populasi (perki...

Untuk Cumi-cumi raksasa, lihat Cumi-cumi raksasa. Dosidicus gigas Cumi-cumi jumbo (dosidicus gigas) atau dikenal dengan nama humboldt squid, merupakan makhluk yang bisa tumbuh dengan lebar hingga 1.5 meter (4.9 kaki) dan mampu merobek mangsanya menggunakan paruhnya hingga terpisah. Organ penghisapnya berada pada lengan yang berbaris membentuk jarum gigi tajam. Hewan ini memiliki 3 hati, berdarah biru, dan berkomunikasi melalui Bioluminesensi photophores di kulitnya. Pada beberapa kasus cumi-c...

South Korean ballet dancer For the Goryeo Dynasty diplomat, see Seo Hui. The native form of this personal name is Seo Hee. This article uses Western name order when mentioning individuals. Hee SeoSeo curtain call for The Moor's Pavane on 8 November 2013[1]Born (1986-03-13) 13 March 1986 (age 37)[2][failed verification]Seoul, South Korea[2][3]EducationSunhwa Arts SchoolKirov Academy of BalletJohn Cranko SchuleAmerican Ballet Theatre Studio Compa...

أوراكل لينكسالشعارمعلومات عامةنوع توزيعة لينكس Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivative (en) المنصة أي إيه-32 — إكس86-64 — سبارك — بنية آرم النموذج المصدري حقوق التأليف والنشر محفوظة المطورون أوراكل موقع الويب oracle.com… (الإنجليزية) معلومات تقنيةعائلة نظام التشغيل جنو/لينكس طريقة التحديث يلو دوج أ�...

Anna Demidova Anna Demidova adalah salah satu pelayanan Kanonisasi Keluarga Romanov yang dimasukkan ke dalam daftar para martir oleh Gereja Ortodox Rusia.[1] Ia adalah pelayan dari Alexandra Feodorovna, istri dari Tsar Nikolas II dari Rusia.[2] Ia adalah anak dari Stepan Demidov, seorang pedagang yang cukup besar dari Cherepovets dan lulus dari Institut Yaroslavl dengan sertifikat mengajar.[2] Anna memiliki hubungan dengan Charles Sydney Gibbes, tutor bahasa Inggris un...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This article possibly contains original research. Ple...

Ini adalah nama Batak Toba, marganya adalah Simanjuntak. Ompu iParlindungan Wilfritz Togar SimanjuntakEphorus HKBPGerejaHuria Kristen Batak Protestan (HKBP)Pemilihan17 Februari 1993Pembatalan1 November 1998PendahuluSoritua Albert Ernst NababanPenerusJubil Raplan HutaurukJabatan tandinganSoritua Albert Ernst NababanJabatan lainAnggota Dewan Perwakilan RakyatMasa jabatan1 Februari 1967 – 28 Oktober 1971Grup parlemenPartai Kristen Indonesia Informasi pribadiLahir(1935-07-16)16 Juli 19...

1999 film by Jon Amiel For legal practice, see Entrapment. EntrapmentTheatrical release posterDirected byJon AmielScreenplay byRonald BassWilliam Broyles, Jr.Story byRonald BassMichael HertzbergProduced bySean ConneryMichael HertzbergRhonda TollefsonStarring Sean Connery Catherine Zeta-Jones Will Patton Maury Chaykin Ving Rhames CinematographyPhil MéheuxEdited byTerry RawlingsMusic byChristopher YoungProductioncompaniesFox 2000 Pictures[1]New Regency[1]Distributed by20th Cent...

‹ The template below (Archive) is being considered for merging. See templates for discussion to help reach a consensus. ›This page is an archive of past discussions. Do not edit the contents of this page. If you wish to start a new discussion or revive an old one, please do so on the current talk page. Structured Data on Commons Newsletter - Fall 2018 edition Welcome to the newsletter for Structured Data on Wikimedia Commons! You can update your subscription to the newsletter. Do inform...

Soviet firearms designer (1914–1988) Nikolay MakarovBornNikolay Fyodorovich Makarov22 May 1914 (1914-05-22)[1]Sasovo, Shatsky Uyezd, Tambov Governorate, Russian Empire[1]Died13 May 1988 (1988-05-14) (aged 73)[1]Tula, RSFSR, Soviet UnionAlma materTula State UniversityKnown forMakarov pistol Nikolay Fyodorovich Makarov (Russian: Никола́й Фёдорович Мака́ров; 22 May [O.S. 9 May] 1914 – 13 May 1988) was...

Mallén municipio de EspañaBanderaEscudo MallénUbicación de Mallén en España. MallénUbicación de Mallén en la provincia de Zaragoza.País España• Com. autónoma Aragón• Provincia Zaragoza• Comarca Campo de Borja• Partido judicial Zaragoza[1]Ubicación 41°54′02″N 1°25′08″O / 41.900555555556, -1.4188888888889• Altitud 293[2] mSuperficie 37,34 km²Poblaci...