Beetle
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Gereja Santo Antonius, KotabaruGereja Katolik Santo Antonius KotabaruLokasiJalan Abubakar Ali Nomor 1, Kotabaru, Gondokusuman, YogyakartaSejarahDidirikan26 September 1926[1]DedikasiSanto Antonius dari PaduaAdministrasiKeuskupanKeuskupan Agung Semarang Gereja Katolik Santo Antonius atau lebih dikenal dengan nama Gereja Katolik Kotabaru (Belanda: Nieuw Wijk Katholieke Kerk) (Jawa: ꦒꦿꦺꦗꦏꦠꦸꦭꦶꦏ꧀ꦱꦤ꧀ꦠꦺꦴꦄꦤ꧀ꦠꦺꦴꦤꦶꦪꦸꦱ꧀...

Трансамазоніка Транспортна мережа Federal Roads in Brazild Офіційна назва порт.-браз. Rodovia Transamazônica Країна Бразилія Адміністративна одиниця ПараїбаСеараПіауїМараньянТокантінсПараАмазонас Проходить над/під Amazonia[d] З'єднується з BR-101d Номер дороги BR-230 Трансамазоніка у Вікіс

Voorbeeld illustratie van een cunette (B) in de gracht Een cunette is een extra diep stuk geul in de lengterichting van een natte gracht te midden van een vestinggracht. Een cunette was bedoeld als hindernis voor belegeraars die door de gracht proberen te waden, waarin altijd water zou staan in het geval dat de gracht zou worden afgetapt. In de winter werd het water ter hoogte van de cunette ijsvrij gehouden. De geul had een gemiddelde omvang van zeven meter breed en twee meter diepte. Zie oo...

Universidad del Norte Santo Tomás de AquinoMottoUniver Cath Thom æ AqviTypePrivateEstablishedAugust 6, 1965ChancellorFray Javier Posse OPPresidentDr.LocationSan Miguel de Tucumán, ArgentinaWebsitewww.unsta.edu.ar The Universidad del Norte de Santo Tomás de Aquino (Saint Thomas Aquinas North University, UNSTA) is a Catholic university located in San Miguel de Tucumán, Tucumán province, Argentina. External links Media related to Universidad del Norte Santo Tomás de Aquino at Wikimedia Co...

Distorsi atau pengerot adalah perangkat elektronik yang mengubah bagaimana sebuah alat musik atau sumber audio lainnya (efek) yang digunakan pada gitar listrik, bas listrik, dan instrumen yang diamplifikasi lainnya seperti Hammond organ, synthesizer, harmonika, dan bahkan vokal yang menggunakan clipping elektronik sinyal. Gitar Volskwagen First Act, yang dilengkapi dengan efek tertanam (built-in effect) Jenis yang paling halus adalah distorsi yang menambahkan rasa ”hangat” pada nada asli,...
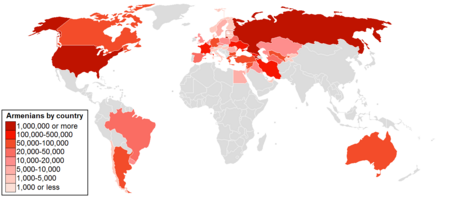
Mapa de la diáspora armenia. La diáspora armenia es un término utilizado para describir las comunidades que han fundado los armenios que viven fuera de Armenia y Alto Karabaj. Del total de la población armenia que vive en todo el mundo (en 2004 se estima en algo más de 12 000 000 de personas), solo alrededor de 3 300 000 viven en Armenia y alrededor de 140 000 en la región de Alto Karabaj. La diáspora armenia se estima en una población aproximada de 8 000...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع عبد الحليم (توضيح). عبد الحليم (بالإندونيسية: Abdoel Halim) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 27 ديسمبر 1911 بوكيتنغي الوفاة 7 يونيو 1987 (75 سنة) جاكرتا مواطنة إندونيسيا العرق المينانغكابو[1] مناصب وزير الدفاع في المنصب1950 – 1951 وزير

One of the two premillennial systems of Christian eschatology Christian eschatology Contrasting beliefs Historicism Interpretations of Revelation Futurism Dispensationalism Preterism Idealism The Millennium Amillennialism Postmillennialism Premillennialism Prewrath rapture Post-tribulation rapture Dispensationalism Biblical texts Daniel Seventy Weeks Synoptic Gospels Olivet Discourse Mark 13 Matthew 24 Sheep and Goats Pauline Epistles 2 Thessalonians Johannine literature Revelation (Events) P...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Mr. T's Commandments – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 1984 EP by Mr. TMr. T's CommandmentsEP by Mr. TReleased1984Recorded1983-1984GenreRapLength29:56LabelColumbia[1]Pr...

Preserved British 4-6-2 locomotive LMS Princess Coronation Class 6233 Duchess of Sutherland6233 Duchess of Sutherland at Monk FrystonType and originPower typeSteamDesignerWilliam StanierBuilderLMS Crewe WorksBuild date1938SpecificationsConfiguration: • Whyte4-6-2 • UIC2'C1'hGauge4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gaugeLeading dia.36 in (910 mm)Driver dia.81 in (2,060 mm)Trailing dia.45 in (1,140 mm)Length73...

2006 Indian filmDharmapuriTheatrical release posterDirected byPerarasuWritten byPerarasuProduced byA. M. RathnamStarringVijayakanthRaai LaxmiCinematographyS. SaravananMusic bySrikanth DevaDistributed bySri Surya MoviesRelease date 20 October 2006 (2006-10-20) Running time146 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageTamil Dharmapuri is a 2006 Indian Tamil-language action drama film written and directed by Perarasu and produced by A. M. Rathnam. It stars Vijayakanth and Raai Laxmi, while Maniv...

This article lacks inline citations besides NRIS, a database which provides minimal and sometimes ambiguous information. Please help ensure the accuracy of the information in this article by providing inline citations to additional reliable sources. (November 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) United States historic placeH. W. Smith BuildingU.S. National Register of Historic Places Show map of FloridaShow map of the United StatesLocationPunta Gorda, Florida, U.S.Coordi...

For other uses, see TRADOC (disambiguation). Training and Doctrine CommandInsignia of the TRADOCActive1998 – presentCountry LithuaniaBranch Lithuanian Land ForceTypeArmy CommandRolemilitary recruitmentbasic military training and educationGarrison/HQVilniusNickname(s)TRADOCCommandersCurrentcommanderColonel Mindaugas SteponavičiusMilitary unit The Training and Doctrine Command (TRADOC) is a training-oriented formation in the Lithuanian Armed Forces, focused on implementing military...

Paramount Home Media DistributionParamount Home Media DistributionJenisSubsidiariIndustriVideo rumahDidirikan1975KantorpusatHollywood, California, Amerika SerikatWilayah operasiSeluruh duniaPemilikGulf+Western (1975–1989) Paramount Communications (1989-1994) Viacom (1994–sekarang)IndukParamount PicturesSitus webparamount.com Paramount Home Media Distribution (PHMD, awalnya Paramount Home Entertainment, Paramount Home Video dan Paramount Video) adalah divisi distribusi video rumah dari Par...

Memorial StadiumView from northwest in 2008SeattleLocation in the United StatesShow map of the United StatesSeattleLocation in WashingtonShow map of Washington (state)Full nameSeattle High School Memorial StadiumAddress401 5th Ave N.LocationSeattle, WashingtonCoordinates47°37′23″N 122°21′00″W / 47.623°N 122.350°W / 47.623; -122.350Elevation100 ft (30 m)Public transit Seattle CenterOwnerSeattle School DistrictCapacity12,000SurfaceAstroTurfConstruct...

2006 video gameSWAT ForceDeveloper(s)KaolinkPublisher(s)Vivendi Universal Games MobileSeriesPolice QuestPlatform(s)MobileReleaseFebruary 28, 2006Genre(s)Shoot 'em upMode(s)Single-player SWAT Force is the first game of the Police Quest series to be released for mobiles, developed by French studio Kaolink. The player controls a two-man team (sharp shooter and demolition expert) and tries to rescue hostages, arrest suspects and secure weapons. It was released February 28, 2006. Gameplay The play...

Decommissioned United States Navy aircraft carrier For other ships with the same name, see USS Enterprise. USS Enterprise (CVN-65) USS Enterprise underway in the Atlantic Ocean Class overview NameEnterprise-class aircraft carrier BuildersNewport News Shipbuilding Operators United States Navy Preceded byKitty Hawk class Succeeded byNimitz class Built1958–1961 In service 1961–2012 (active) 2012–2017 (inactive) Planned6 Completed1 Cancelled5 Retired1 History United States NameEnt...

Human settlement in EnglandGrafhamGrafham Parish ChurchGrafhamLocation within CambridgeshirePopulation630 (2011)OS grid referenceTL170683DistrictHuntingdonshireShire countyCambridgeshireRegionEastCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townHuntingdonPostcode districtPE28PoliceCambridgeshireFireCambridgeshireAmbulanceEast of England UK ParliamentHuntingdonWebsitehttp://www.grafham.org.uk List of places UK England Cambridgeshire 52°18′00″N 0°16�...

Artūras Kasputis Nazionalità Unione Sovietica Lituania Ciclismo Specialità Strada, pista Termine carriera 2001 Carriera Squadre di club 1991 Postobón1992-1995 Chazal1996-1999 Casino2000-2002 AG2R Prévoyance Nazionale 1985-1991 Unione Sovietica1992-2000 Lituania Carriera da allenatore 2003-2007 AG2R Prévoyance2008-2020 AG2R La Mondiale2021- AG2R Citroën Palmarès Giochi olimpici Oro Seul 1988 Ins. sq. Mondiali su pista Bronzo Vi...

Hospital in Yangon Region, MyanmarInsein General HospitalInsein General HospitalGeographyLocationMingyi Road, Taungthugone Quarter, Insein Township, Yangon, Yangon Region, MyanmarCoordinates16°53′31″N 96°06′19″E / 16.891969°N 96.105388°E / 16.891969; 96.105388OrganisationTypeTeachingAffiliated universityUniversity of Medicine 2, Yangon, University of Medical Technology, Yangon, University of Pharmacy, Yangon, University of Nursing, YangonServicesEmergency d...








