Xantocillin
![]()
|
|
|
| Names
|
Preferred IUPAC name
4,4′-[(1Z,3Z)-2,3-Diisocyanobuta-1,3-diene-1,4-diyl]diphenol |
| Other names
Xanthocillin X, Ophthocillin
|
| Identifiers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ChEMBL
|
|
| ChemSpider
|
|
|
|
|
| UNII
|
|
|
|
|
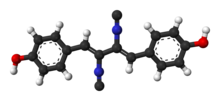
[C-]#[N+]C(=CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)C(=CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)[N+]#[C-]
|
| Properties
|
|
|
C18H12N2O2
|
| Molar mass
|
288.306 g·mol−1
|
| Appearance
|
Yellow crystals
|
| Melting point
|
200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) (decomposes)
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
Chemical compound
Xantocillin[1] (INN), also known as xanthocillin X or ophthocillin, was the first reported natural product found to contain the isocyanide functional group. It was first isolated from Penicillium notatum by Rothe in 1950[2] and subsequently from several other sources.[3][4]
See also
References