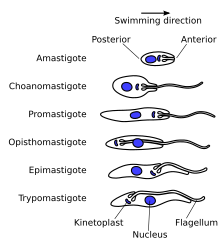
Trypanosoma
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

1999–00 North Dakota Fighting Sioux men's ice hockey seasonNCAA Division I National ChampionBadger Showdown, championWCHA Tournament, championNCAA Tournament, champion Conference2nd WCHAHome iceRalph Engelstad ArenaRankingsUSCHO2USA Today1RecordOverall31–8–5Conference17–6–5Home14–4–1Road9–4–4Neutral8–0–0Coaches and captainsHead coachDean BlaisAssistant coachesScott SandelinMark PoolmanJeff BowenLee DavidsonCaptain(s)Peter ArmbrustAlternate captain(s)Lee GorenJason UlmerN...

Gunung PulosariTitik tertinggiKetinggian1.346 m (4.416 kaki)Koordinat6°20′31″S 105°58′41″E / 6.342083°S 105.977945°E / -6.342083; 105.977945Koordinat: 6°20′31″S 105°58′41″E / 6.342083°S 105.977945°E / -6.342083; 105.977945 GeografiGunung PulosariLetak Gunung Pulosari di Provinsi BantenLetakPandeglang, Banten, IndonesiaGeologiJenis gunungStratovolcanoLetusan terakhirtidak diketahuiPendakianRute termudahDesa Cilentung...

Infeksi jamur pada kuku kaki manusia Jamur kuku atau dalam dunia kedokteran sering disebut tinea unguium atau onychomycosis merupakan infeksi jamur yang terjadi pada kuku tangan maupun kuku kaki.[1] Walaupun bukan termasuk keadaan berbahaya tapi onychomycosis adalah infeksi kuku jamur yang bisa menular ke orang lain melalui beberapa cara seperti kontak kulit langsung ke kulit ataupun penularan yang terjadi melalui penumpahan sel kulit mati yang mengalami infeksi jamur. Awal mula jamur...

Patung dengan khiton pendekKhiton kusir Ionia Khiton (bahasa Yunani Kuno: χιτών, translit. khitōn) adalah sejenis tunik yang diikatkan di bahu, dikenakan oleh pria dan wanita Yunani Kuno dan Romawi.[1][2] Ada dua jenis utama khiton. Salah satunya adalah khiton Doria dan kemudian khiton Ionia. Menurut Herodotus, legenda terkenal adalah bahwa wanita Athena mulai memakai khiton sebagai lawan dari peplos setelah beberapa wanita menikam seorang utusan sampai mati den...

Bahnhof Seebrugg Strandbad Seebrugg Seehotel Hubertus Seebrugg, auch Seebruck[1] geschrieben, ist ein zum Ortsteil Faulenfürst gehöriger Weiler der Gemeinde Schluchsee im Naturpark Südschwarzwald. Der Ort liegt in 935 m Höhe am östlichen Ende des Schluchsees nahe der Staumauer des Schluchseewerkes. Er ist Ausgangspunkt für Wanderungen in diesem Gebiet. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Geschichte 2 Bauwerke und Sehenswürdigkeiten 3 Verkehr 4 Weblinks 5 Einzelnachweise Geschichte Seebru...

تايشو-كو خريطة الموقع تاريخ التأسيس 1 أكتوبر 1932 تقسيم إداري البلد اليابان [1][2] التقسيم الأعلى أوساكا خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 34°39′01″N 135°28′22″E / 34.650402777778°N 135.4727°E / 34.650402777778; 135.4727 [3] المساحة 9.43 كيلومتر مربع السكان التعداد السكاني 64...

Sub-region of Cape Town, South Africa This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Southern Suburbs, Cape Town – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2020) Place in Western Cape, South AfricaSouthern SuburbsClaremont Civic CentreSouthern SuburbsShow map of Western CapeSouthern Su...

This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (November 2010) This article is part of a series on theEconomy of theUnited States Economic history Agricultural history Banking history Petroleum history Shipbuilding Industrial Revolution in the United States History of the United States dollar Lumber history Tariff History United States dollar § History History by state Sectors Primary sector Agriculture Energy Petrol...

Paderborn Hauptbahnhof Through stationGeneral informationLocationBahnhofstr. 29, Paderborn, North Rhine-WestphaliaGermanyCoordinates51°42′47″N 8°44′26″E / 51.71306°N 8.74056°E / 51.71306; 8.74056Line(s) Hamm–Warburg line (KBS 430) Senne Railway (KBS 403) Platforms5Other informationStation code4846[1]DS100 codeEPD[2]IBNR8000297Category2[1]Fare zoneWestfalentarif: 77701[3]Websitewww.bahnhof.deHistoryOpened4 October 1850&...

19th-century depiction of the Chief Black Eunuch (left), a court dwarf (middle) and the Chief White Eunuch (right) The Kapi Agha (Turkish: Kapı ağası, Agha of the Gate), formally called the Agha of the Gate of Felicity (Bâbüssaâde ağası), was the head of the eunuch servants of the Ottoman Seraglio until the late 16th century, when this post was taken over by the Kizlar Agha.[1] In juxtaposition with the latter office, also known as the Chief Black Eunuch as its holders were dr...

Hindu temple in Tamil Nadu, India Thirumalpurதிருமால்பூர்ReligionAffiliationHinduismDistrictRanipet DeityMaal Vanangia Eesar, Manikandeswarar (Shiva) Karunai Nayaki, Anjanakshi (Parvathi)LocationLocationTirumalpurStateTamil NaduCountryIndiaLocation in Tamil NaduGeographic coordinates12°57′24″N 79°40′25″E / 12.95667°N 79.67361°E / 12.95667; 79.67361ArchitectureTypeDravidian architecture Thirumarperu Manikandeswarar Temple is a Hindu t...

2019 Canadian film AcadianaFilm posterDirected byGuillaume FournierSamuel MatteauYannick NolinWritten byGuillaume FournierProduced byJean-Pierre VézinaCinematographyYannick NolinEdited bySamuel MatteauMusic byMathieu CantinSamuel MatteauMathieu RobineauProductioncompanyProjet KinomadaDistributed bySpiraRelease date January 26, 2019 (2019-01-26) (Slamdance) Running time10 minutesCountryCanadaLanguageEnglish Acadiana is a 2019 Canadian short documentary film directed by Guil...

A soldier's sketch of British troops brewing up (making tea) in the Libyan desert, 1940 to 1943. The Benghazi burner or Benghazi cooker was an improvised petrol stove or brazier used by British Army troops and their Commonwealth and Imperial allies in the Second World War, during and after the North African Campaign. The Western Desert campaign As used in the Western Desert campaign, the Benghazi burner itself consisted of a single empty steel fuel can - usually a 4 gallon (18 litre) type, kn...

The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to be merged, redirected, or deleted.Find sources: Pablo's Inferno – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2019) (...

Village in Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, PolandNarajtyVillageNarajtyCoordinates: 53°36′N 20°45′E / 53.600°N 20.750°E / 53.600; 20.750Country PolandVoivodeshipWarmian-MasurianCountySzczytnoGminaPasym Narajty [naˈrai̯tɨ] is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Pasym, within Szczytno County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland.[1] It lies approximately 6 kilometres (4 mi) south-west of Pasym, 17 km (11 mi) west o...

Municipal banner of the city of Indianapolis, Indiana IndianapolisProportion2:3[1]AdoptedMay 20, 1963; 60 years ago (1963-05-20)[1]DesignA white star within a red circle within a white circle, with four white stripes moving outward perpendicularly, on a field of dark blue.Designed byRoger E. Gohl The flag of Indianapolis has a dark blue field with a white five-pointed star pointing upwards in the center. Around the star is a circular field in red. Surrou...

For those of a similar name, see George Wolff (disambiguation). SS-HauptsturmführerGeorg WolffBorn2 February 1914Died1996Allegiance Nazi GermanyService/branch SchutzstaffelRankSS-HauptsturmführerBattles/warsWorld War IIOther workEditor at Der Spiegel Georg Wolff (14 February 1914 – 1996) was a German SS Hauptsturmführer and journalist. During the Second World War, Wolff was a Head of Division III for the Sicherheitspolizei command in Oslo. He was later a leading editor for news...

Catholic diocese in France This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Roman Catholic Diocese of Le Puy-en-Velay – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Diocese of Le Puy-en-VelayDioecesis AniciensisDiocèse du Puy-en-VelayLe Puy C...

Reciprocating internal combustion engine V8 engineA 331 series V8 from the 1950sOverviewManufacturerCadillac (General Motors)Also calledType 51, Monobloc, LaSalle, Northstar, BlackwingProduction1914-presentLayoutConfiguration90° V8Displacement244 cu in (4.0 L)267 cu in (4.4 L)279 cu in (4.6 L)307 cu in (5.0 L)314 cu in (5.1 L)322 cu in (5.3 L)341 cu in (5.6 L)346 cu in (5.7 ...

1961 studio album by Barry Harris QuintetNewer Than NewStudio album by Barry Harris QuintetReleased1961RecordedSeptember 28, 1961New York CityGenreJazzLength39:57LabelRiversideRLP 413ProducerOrrin KeepnewsBarry Harris chronology Listen to Barry Harris(1961) Newer Than New(1961) Chasin' the Bird(1962) Newer Than New is an album by pianist Barry Harris recorded in 1961 and released on the Riverside label.[1] Reception Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingDown Beat[2&...