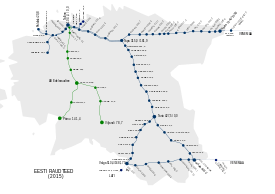
Rail transport in Estonia
|
Read other articles:
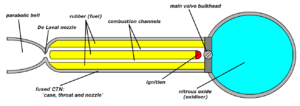
Roket hibrida adalah roket dengan motor roket yang menggunakan propelan di dua bagian yang berbeda dari materi - satu padat dan yang lain baik gas atau cairan. Konsep roket hibrida dapat ditelusuri kembali setidaknya 75 tahun. Hybrid roket memiliki keunggulan dibandingkan kedua roket cair dan roket padat terutama dalam hal kesederhanaan, keamanan, dan biaya. Referensi Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Hybrid rocket engines. Developing and testing of a 2kN hybrid rocket engine (Jerman)...

Jones County Courthouse in Anson, glisdt im NRHP mit da Nr. 03000330[1] Vawoitung US-Bundesstoot: Texas Sitz vo da Vawoitung: Anson Adress vomVawoitungssitz: Jones County CourthouseP.O. Box 552Anson, TX 79501-0552 Grindung: 1858 Buidt aus: Bexar CountyBosque County Vuawoi: 001 325 Demographie Eihwohna: 20.202 (2010) Dichtn: 8,4 Eihwohna/km² Eadkund Flächn gesamt: 2.427 km² Wossaflächn: 16 km² Koartn Koartn vo Jones County innahoib vo Texas Hoamseitn: www.co.j...

انا دريڤ معلومات شخصيه الميلاد 6 اغسطس 1985 (38 سنة) سلوفينج جرادتس الطول المشاركات اوليمبياد شتا 2010 الجنسيه سلوفينيا الوزن تعديل انا دريڤ متزلجه على التلج من سلوفينيا. حياتها انا دريڤ من مواليد يوم 6 اغسطس 1985 فى سلوفينج جرادتس. المشاركات شاركت فى: الالعاب ا�...

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Regional Parks Botanic Garden – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Redwoods shading the forest area of the garden. The Regional Parks Botanic Garden is a 10-acre (4 hectare) botanical garden located in Tilden Regional Park in the...

SFN Наявні структури PDBПошук ортологів: PDBe RCSB Список кодів PDB 1YWT, 1YZ5, 3IQJ, 3IQU, 3IQV, 3LW1, 3MHR, 3O8I, 3P1N, 3P1O, 3P1P, 3P1Q, 3P1R, 3P1S, 3SMK, 3SML, 3SMM, 3SMN, 3SMO, 3SPR, 3T0L, 3T0M, 3U9X, 3UX0, 4DAT, 4DAU, 4DHM, 4DHN, 4DHO, 4DHP, 4DHQ, 4DHR, 4DHS, 4DHT, 4DHU, 4FL5, 4FR3, 4HQW, 4HRU, 4IEA, 4JC3, 4JDD, 4QLI, 5HF3, 4Y5I, 4Y32, 4Y3B, 3SP5 Ідентифікатори Символи SFN, YWHAS, Stratifin Зовнішні ІД OMIM: 601290 M...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع خافيير غارسيا (توضيح). هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يوليو 2019) خافيير غارسيا معلومات شخصية الميلاد 22 يوليو 1966 (57 سنة)[1] برشلونة مواطنة إسبانيا الحياة العملية ا�...

Right of medical staff to refuse participation in abortion Conscientious objection to abortion is the right of medical staff to refuse participation in abortion for personal belief. By country The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with the United States and Europe and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new article, as appropriate. (May 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this tem...

Former association football club in Scotland, UK Football clubLongriggendFull nameLongriggend F.C.Nickname(s)the Nor'Westers,[1] the Moss Men[2]Founded1897Dissolved1902GroundViewhill ParkMatch secretaryPeter M'Kinnie, Thomas Ferguson to 1898 colours from 1898 colours Longriggend Football Club was an association football club from Longriggend in Lanarkshire, active at the turn of the 20th century. History 1899–1900 Scottish Qualifying Cup 1st Round, Longriggend 4–1 Glasgow ...

航空機関士(こうくうきかんし)とは、航空機の運航に携わる職種の航空従事者である。フライトエンジニア(英語: Flight Engineer, FE)とも呼ばれる。 概説 DC-10のコクピット、右手前に着席しているのが航空機関士 航空機の運航においては、多数の計器類を監視することが必要である。そのため、操縦室の電子化が進んでいなかったころは、機器類が多くなると機長�...

1995 Japanese filmDragon Ball Z: Wrath of the DragonJapanese promotional artDirected byMitsuo HashimotoWritten byTakao KoyamaBased onDragon Ballby Akira ToriyamaStarringSee belowNarrated byJōji YanamiCinematographyMasao ShimizuEdited byShinichi FukumitsuMusic byShunsuke KikuchiProductioncompanyToei AnimationDistributed byToei CompanyRelease date July 15, 1995 (1995-07-15) (Japan) Running time52 minutesCountryJapanLanguageJapaneseBox office¥1.7 billion Dragon Ball Z: Wrath...

Indian film Boyz 4Theatrical release posterDirected byVishal DevrukhkarWritten byHrishikesh KoliProduced byLalasaheb ShindeRajendra ShindeSanjay ChhabriaStarringSee belowCinematographyYogesh KoliEdited byGurunath PatilMahesh KillekarMusic byAvdhoot GupteProductioncompaniesEverest EntertainmentSupreme Motion PicturesEkvira ProductionsDistributed byPanorama StudiosRelease date 20 October 2023 (2023-10-20) Running time134 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageMarathiBox officeest.₹4.20 cro...

Village in Opole Voivodeship, PolandIzbickoStubendorfVillageBilingual city limitIzbickoStubendorfCoordinates: 50°35′N 18°9′E / 50.583°N 18.150°E / 50.583; 18.150Country PolandVoivodeshipOpoleCountyStrzelceGminaIzbickoPopulation1,100 Izbicko [izˈbit͡skɔ] is a village in Strzelce County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Izbicko, which has been bilingual in Polish and German since 200...

Untuk tempat lain yang bernama sama, lihat Sukolilo. Koordinat: 7°17′59″S 112°46′13″E / 7.299623°S 112.770350°E / -7.299623; 112.770350 Sukolilo Sukalila ꦱꦸꦏꦭꦶꦭ KecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan SukoliloNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TimurKotaSurabayaPemerintahan • CamatKanti Budiarti, S.Sos, M.SiKode pos60119Kode Kemendagri35.78.09 Kode BPS3578080 Desa/kelurahan7 Sukolilo (Jawa: ꦱꦸꦏꦭꦶꦭ, translit. Sukalila, [suk�...

Civil war in the Sultanate of Muscat and Oman Dhofar WarPart of the Cold War and the Arab Cold WarA soldier of the Sultan of Oman's Armed Forces brewing tea in 1970Date9 June 1963 – 11 March 1976(12 years, 9 months and 2 days)LocationDhofar Province, OmanResult Omani government victory[1] Defeat of insurgents Modernization of OmanBelligerents Oman DLF (1963–1968) PFLOAG (1968–1974) NDFLOAG (1969–1971) PFLO (1974–1976) Iran United Kingdom Jordan ...

Historic site in Chicago, IllinoisLondon Guarantee BuildingLondon Guaranty & Accident BuildingLocation85 E. Wacker Drive at North Michigan AvenueChicago, IllinoisCoordinates41°53′17″N 87°37′30″W / 41.888°N 87.625°W / 41.888; -87.625Built1922ArchitectAlfred S. AlschulerWebsitehttps://londonhousechicago.com/ Chicago LandmarkDesignatedApril 16, 1996 Location of London Guarantee Building in Chicago metropolitan area The London Guarantee Building or London G...

1967 film Five Golden Dragons1967 theatrical posterDirected byJeremy SummersScreenplay byPeter WelbeckProduced byHarry Alan TowersStarringBob CummingsMargaret LeeRupert DaviesCinematographyJohn Von Kotze(lighting cameraman)Edited byDonald J. CohenMusic byComposed and directed by Malcolm LockyerProductioncompanyBlansfilm LimitedDistributed byAnglo-AmalgamatedConstantin FilmRelease date 4 August 1967 (1967-08-04) Running time104 minutesCountriesUnited KingdomWest GermanyLiechtens...

Directed energy weapon SeaLite Beam Director, commonly used as the output for the MIRACL. MIRACL, or Mid-Infrared Advanced Chemical Laser, is a directed energy weapon developed by the US Navy. It is a deuterium fluoride laser, a type of chemical laser. The MIRACL laser first became operational in 1980.[1] It can produce over a megawatt of output for up to 70 seconds,[2] making it the most powerful continuous wave (CW) laser in the US.[3]: 5 Its origina...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Point Lowly Lighthouse – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) LighthousePoint Lowly lighthouse Point Lowly LighthouseLocationPoint LowlyEyre PeninsulaSouth Australia AustraliaCoordinates...
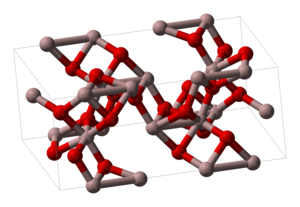
Sel satuan dari corundum Aluminium oksida (alumina) Aluminium oksida adalah sebuah senyawa kimia dari aluminium dan oksigen, dengan rumus kimia Al2O3. Nama mineralnya adalah alumina, dan dalam bidang pertambangan, keramik dan teknik material senyawa ini lebih banyak disebut dengan nama alumina. Sifat-sifat Aluminium oksida adalah insulator (penghambat) panas dan listrik yang baik. Umumnya Al2O3 terdapat dalam bentuk kristalin yang disebut corundum atau α-aluminum oksida. Al2O3 dipakai sebaga...

Species of lizard Persepolis angular-toed gecko Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Squamata Family: Gekkonidae Genus: Cyrtopodion Species: C. persepolense Binomial name Cyrtopodion persepolenseNazarov, Ananjeva & Rajabizadeh, 2010 The Persepolis angular-toed gecko (Cyrtopodion persepolense) is a species of gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to Iran. Geographic range C. persepolense is fou...