Géraud de Cordemoy
|
Read other articles:

Track and field event High Jump redirects here. For the film, see High Jump (film). AthleticsHigh jumpCanadian high jumper Nicole Forrester demonstrating the Fosbury flopWorld recordsMen Javier Sotomayor 2.45 m (8 ft 1⁄4 in) (1993)Women Stefka Kostadinova 2.09 m (6 ft 10+1⁄4 in) (1987)Olympic recordsMen Charles Austin 2.39 m (7 ft 10 in) (1996)Women Yelena Slesarenko 2.06 m (6 ft 9 in) (2004)World Championship recordsMen ...

Urban Gad FöddPeter Urban Brunn Gad12 februari 1879[1][2][3]Skælskør, DanmarkDöd26 december 1947[1][2][3] (68 år)Köpenhamn[4]BegravdHumlebæks kyrkogård[5]Medborgare iDanmarkSysselsättningFilmregissör, manusförfattare, målareMakaAsta Nielsen(g. 1912–1918)[6]FöräldrarUrban GadEmma GadRedigera Wikidata Peter Urban Gad, född den 12 februari 1879 i Skælskør, död den 26 december 1947 i Köpenhamn, var en dansk regissör och manusförfattare. Han var son till Nicol...

Hen Detailopname met de typische brede stand en dubbele omzoming Het Indisch vechthoen of Indische vechter is een Engels kippenras, dat omtrent 1820 als vleeskip gefokt is uit Aseels, Oud-Engelse vechters en Maleiers[1] Er bestaat ook een krielvariant. Geschiedenis Naar verluidt was het Sir Walter Raleigh Gilbert die rond 1820 door kruisingen van verschillende vechthoenders een nieuw ras creëerde.[2] Het ras droeg de dubbele naam Indische vechter en Cornish game vanwege de oo...

GervaisePoster rilis teatrikalSutradara René Clément Produser Agnès Delahaie Ditulis oleh Jean Aurenche Pierre Bost SkenarioJean AurenchePierre BostBerdasarkanL'Assommoiroleh Émile ZolaPemeranMaria SchellFrançois PérierJany HoltPenata musikGeorges AuricSinematograferRobert JuillardPenyuntingHenri RustDistributorLes Films CoronaTanggal rilis 3 Agustus 1956 (1956-08-03) (Jerman Barat) 5 September 1956 (1956-09-05) (Prancis) Durasi120 menitNegara Prancis Bahasa Pran...

1987 single by The CureWhy Can't I Be You?Single by The Curefrom the album Kiss Me, Kiss Me, Kiss Me B-sideA Japanese DreamReleased6 April 1987[1]Genre New wave pop[2] R&B[3][4] Length3:14LabelFictionSongwriter(s) Boris Williams Simon Gallup Robert Smith Porl Thompson Lol Tolhurst Producer(s) Robert Smith Dave Allen The Cure singles chronology Boys Don't Cry (New Voice) (1986) Why Can't I Be You? (1987) Catch (1987) Music videoWhy Can't I Be You (TopPop, 19...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع الجيش الرابع (توضيح). Armata a 4-a Română الجيش الرابع جنود ألمان ورومانيون أثناء توغّلهم في بيسارابيا، يوليو 1941 الدولة رومانيا الإنشاء 14 أغسطس 1916 - 1947 إبريل 1980 - 2000 الانحلال 2000 الولاء رومانيا ألمانيا النازية الاتحاد السوڤێتي رومانيا الحجم جيش جزء من القو

Berikut ini adalah daftar sungai yang mengalir di wilayah provinsi Jawa Barat:[1][2] Menurut abjad Ci Asem Ci Beet Ci Tarum Ci Binong Ci Bulan Ci Buni Ci Durian Ci Gentis Ci Herang Ci Kaengan Ci Kapundung Ci Karang Ci Kaso (Garut) Ci Kaso (Sukabumi) Ci Katomas Ci Kubang Ci Laki Ci Lamaya Ci Lalanang Ci Langkub Ci Letuh Ci Leuleuy Ci Liwung Ci Mandiri Ci Manuk Ci Muntur Ci Punegara Ci Sadane Ci Sanggarung Ci Tanduy Ci Tarum Ci Ujung Kali Bekasi Kali Pesanggrahan Menurut Kabupat...

Kosovokrieg Teil von: Jugoslawienkriege Datum 28. Februar 1998 bis 10. Juni 1999 Ort Bundesrepublik Jugoslawien, Kosovo Casus Belli Nichtunterzeichnung des Vertrages von Rambouillet durch die Bundesrepublik Jugoslawien Ausgang Militärtechnisches Abkommen von Kumanovo zwischen der NATO und der Bundesrepublik Jugoslawien auf Basis der Verabschiedung der Resolution 1244 im UN-Sicherheitsrat, UN-Verwaltung des Kosovos durch die UNMIK Konfliktparteien UÇKNATO NATO Jugoslawien Bundesrepu...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau pranala luar ke sumber-sumber tepercaya yang dapat menyatakan kelayakan dari subyek yang dibahas.(ajukan diskusi keberatan penghapusan)Artikel ini akan dihapus pada 7 Oktober 2023 jika tidak diperbaiki.Untuk pemulai artikel ini, jika Anda mempertentangkan nominasi penghapusan ini, jangan menghapus peringatan ini. Silakan hubungi sang pengusul, hubungi seorang pengurus, atau pasang tag {{tunggu dulu}} Topik artikel ini mungkin ...

Gereja Bunda Rosario, DohaGereja Katolik Bunda Maria dari RosarioArab: كنيسة سيدة الورديةGereja Bunda Rosario, DohaLokasiAbu Hamour,[1] DohaNegara QatarDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaSitus webSitus web Gereja Bunda Rosario, DohaSejarahTanggal konsekrasi15 Maret 2008[2]ArsitekturStatusParokiStatus fungsionalAktifSpesifikasiKapasitas2.700[3]AdministrasiDivisiVikariat Apostolik Arab UtaraKlerusImam yang bertugasRomo Rally S. Gonzaga, ofmcap. Gereja ...

Dalam Geometri, semiperimeter dari sebuah bangun poligon adalah setengah dari keliling. Umumnya semiperimeter muncul dalam rumus untuk segitiga dan bentuk lainnya dengan nama yang lain. Semiperimeter dinotasikan dengan huruf s. Segitiga Dalam segitiga, jarak antara sisi segitiga dan vertex menuju titik yang berlawanan dengan sudut yang berhadapan tersentuh dengan lingkar luar sama dengan semiperimeter. Pada semiperimeter umumnya untuk segitiga rumusnya adalah sebagai berikut dengan sisi segit...
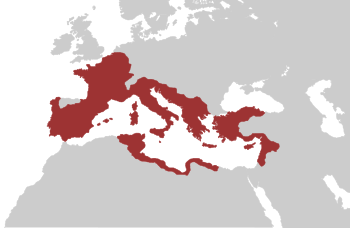
У Вікіпедії є статті про інших людей із прізвищем Квінт Фабій. У Вікіпедії є статті про інших людей із прізвищем Квінт Фабій Амбуст. Квінт Фабій Амбустлат. Q.Fabius M.f.Q.n. AmbustusІм'я при народженні Quintus Fabius AmbustusНародився невідомоСтародавній РимПомер 389 до н. е.(-389)невідомоГромадянс

German philosopher and Protestant theologian (1716-1775) Christian August Crusius Christian August Crusius (10 January 1715 – 18 October 1775) was a German philosopher and Protestant theologian. Biography Crusius was born in Leuna in the Electorate of Saxony. He was educated at the University of Leipzig, and became professor of theology there in 1750, and principal in 1773.[1] Crusius first came to notice as an opponent of the philosophy of Gottfried Leibniz and Christian Wolff ...

Garrison of the People's Liberation Army For the former British garrison, see British Forces Overseas Hong Kong. This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Chinese. (May 2022) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful...

Tottenham High Road Tottenham High Road is the main thoroughfare through the district of Tottenham, in the London Borough of Haringey. It runs from Edmonton in the North (where it becomes Fore Street) to Stamford Hill in the South (where the road becomes Stamford Hill). South of Bruce Grove the road is part of the A10; to the north it is part of the A1010. Tottenham High Road passes through the London postcode areas of N17 and N15 and is 2.3 miles (3.7 kilometers) in length. History Tottenham...

Annual music festival in Orere Point, New Zealand SploreDates21-24 February 2019Location(s)Orere Point, New ZealandYears active1998 - Present[1]Website[1] Screenshot of Festival Logo Splore is an annual boutique music and arts three day festival held at Tapapakanga Regional Park, in Orere Point, New Zealand[2] with approximately 8,000 attendees.[3] The first Splore was held on New Year’s Eve 1998 and the festival ran consecutively for four years and then took a year ...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Права человека (значения). ПравоТеория Естественные и законные права Права требования и права свободы Отрицательные и положительные права Индивидуальные и групповые права Подразделы прав человека Три поколения Гражданс...

QUICPay(クイックペイ)は、ジェーシービー(JCB)及びJCBの提携先が展開する決済(電子決済)サービスである。「Quick & Useful IC Payment」の略。 概要 ソニーが開発したFeliCaを採用した電子決済(非接触決済)サービスである。「Pay」(ペイ)という名称ではあるが、QRコード決済やネット決済に「○○Pay」(○○ペイ)という名称が使われる前からあるため、これらの決�...

1927 film Border BlackbirdsDirected byLeo D. MaloneyWritten byFord BeebeProduced byLeo D. MaloneyStarringLeo D. MaloneyEugenia GilbertNelson McDowellCinematographyEdward A. KullProductioncompanyLeo Maloney ProductionsDistributed byPathé ExchangeRelease date August 28, 1927 (1927-08-28) Running time50 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguagesSilentEnglish intertitles Border Blackbirds is a 1927 American silent Western film directed by Leo D. Maloney and starring Maloney, Eugenia Gil...

Ferrari 248 F1 Visão geral Produção 2006 Fabricante Ferrari Modelo Carroceria Monoposto de corrida Designer Aldo CostaRory Byrne Ficha técnica Motor Ferrari 056 2.4L V8 Transmissão Longitudinal semi-automático sequencial, controle eletrônico,7 velocidades Dimensões Comprimento 4545 mm Entre-eixos 3050 mm Largura 1796 mm Altura 959 mm Peso 605 kg Cronologia Ferrari F2005 Ferrari F2007 O 248 F1 é o modelo da Ferrari da temporada de 2006 da F1. Condutores: Michael Schumacher e Felipe M...


