Fort Walton Mound
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

2002 single by S Club 7 YouSingle by S Club 7from the album Sunshine B-sideThe Long and Winding RoadReleased11 February 2002 (2002-02-11)Length3:26 (album version)3:31 (single version)LabelPolydor19Songwriter(s)Eliot KennedyTim LeverMike PercyTim WoodcockProducer(s)SteelworksS Club 7 singles chronology Have You Ever (2002) You (2002) Alive (2002) You is a song by British pop group S Club 7, released on 11 February 2002 as the final single from their third studio album, Sunshine...
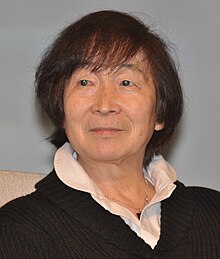
Toshio Furukawa古川登志夫Lahir16 Juli 1946 (umur 77) Ohira, Prefektur TochigiPekerjaanSeiyū, aktor, narator, playwright, gitarisSuami/istriShino Kakinuma Toshio Furukawa (古川 登志夫code: ja is deprecated , Furukawa Toshio, lahir 16 Juli 1946) adalah seorang pengisi suara, aktor dan narator asal Jepang. Dia dikenal dengan peran-perannya dari serial anime sebagai Ataru Moroboshi dalam serial Urusei Yatsura, sebagai Kagege dalam Sersan Keroro, sebagai Kai Shiden dalam serial Mob...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يناير 2022) الثقافة الأم هي عبارة عن ثقافة قامت في وقت سابق لها تأثير كبير وعلى نطاق واسع على بعض الثقافات التي أتت في �...

Templo de Vidia Shankará. El famoso centro religioso de Sringeri, (Shringeri, Śŗngeri, Śŗngagiri, Ŗshyaśŗnga-giri), está localizado en el distrito de Chikmagalur en el estado indio de Karnataka, es el sitio de primer matha establecido por Adi Shankará, teólogo hindú y exponente de la doctrina advaita vedanta, en el siglo VIII a. C. Origen Localizado sobre las orillas del río Tunga. Según la leyenda, Adi Shankará, seleccionó el sitio como un lugar para quedarse y...

Sifat intensif adalah sifat makroskopis yang tidak tergantung pada massa sistem,[1][2][3] contohnya titik didih, titik lebur, suhu, rapat massa, tekanan, dan viskositas. Sifat insensif ini nilainya dapat ditentukan pada tiap titik dalam sistem itu dan yang dapat berubah dari titik satu ke titik lain, bila tidak ada keseimbangan. Sifat–sifat seperti itu tidak aditif dan tidak memerlukan sesuatu spesifikasi tentang contoh yang diacunya. Macam-macam sifat intensif Sifat...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع أبغرم (توضيح). أبغرم تقسيم إداري البلد إيران [1] إحداثيات 33°32′59″N 54°56′02″E / 33.5497°N 54.9339°E / 33.5497; 54.9339 الرمز الجغرافي 145059 تعديل مصدري - تعديل أبغرم هي قرية في مقاطعة خور وبيابانك، إيران. في تعداد عام 2006، لوحظ وجودها، ولكن لم ...

Genus of rodents TachyoryctesTemporal range: Late Pliocene - Recent East African mole-rat, (Tachyoryctes splendens) Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Rodentia Family: Spalacidae Tribe: TachyoryctiniMiller & Gidley, 1918 Genus: TachyoryctesRüppell, 1835 Type species Bathyergus splendens Species Tachyoryctes ankoliae Tachyoryctes annectens Tachyoryctes audax Tachyoryctes daemon Tachyoryctes ibeanus Tachyoryctes macrocephal...

French philosopher, feminist and novelist (1872–1942) Léontine Zanta (14 February 1872 – 15 June 1942) was a French philosopher, feminist and novelist. One of the first two women to gain a doctorate in France, and the first to do so in philosophy, Zanta was an intellectual celebrity in her day, active in journalism and in the feminist movement of the 1920s.[1] Life Zanta was born in Mâcon. Her doctoral thesis, defended in May 1914, was on the 16th-century revival of Stoicism. Sh...
هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (أغسطس 2023) الدوري التونسي لكرة اليد للرجال الموسم 1963-1964 البلد تونس المنظم الجامعة التو...

17 AD earthquake in the Roman province of Asia Location of some of the affected towns and cities in Asia Minor The AD 17 Lydia earthquake caused the destruction of at least twelve cities in the region of Lydia in the Roman province of Asia in Asia Minor (now part of Turkey). The earthquake was recorded by the Roman historians Tacitus and Pliny the Elder, and the Greek historians Strabo and Eusebius. Pliny called it the greatest earthquake in human memory (Nat. Hist. 2:86 §200).[1] Th...

This is a list of sieges, land and naval battles of the War of the Sixth Coalition (3 March 1813 – 30 May 1814). It includes: the German campaign of 1813; the campaign in north-east France; the Campaign in south-west France (final stage of the Peninsular War); the Illyrian campaign, part of the wider Adriatic campaign of 1807–1814; the Italian campaign (6 September 1813 – 18 April 1814); and the Low Countries campaign (12 November 1813[1] – 12 May 1814). War of the Sixth Coali...

Military conflict between Brunei and Spain This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Castilian War – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Castilian WarDate16 April - 26 June 1578LocationBorneo, Mindanao, and Sulu...

American baseball player (1891–1971) Baseball player Carl MaysMays in 1915PitcherBorn: November 12, 1891Liberty, Kentucky, U.S.Died: April 4, 1971(1971-04-04) (aged 79)El Cajon, California, U.S.Batted: LeftThrew: RightMLB debutApril 15, 1915, for the Boston Red SoxLast MLB appearanceSeptember 24, 1929, for the New York GiantsMLB statisticsWin–loss record207–126Earned run average2.92Strikeouts862 Teams Boston Red Sox (1915–1919) New York Yankees (1919...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Назайкинский. Евгений Владимирович Назайкинский Дата рождения 12 августа 1926(1926-08-12)[1] Место рождения Новая Малыкла, Мелекесский уезд, Ульяновская губерния, СССР Дата смерти 3 апреля 2006(2006-04-03) (79 лет) Место смерти Москва, Р...

Konsonan geser langit-langit bersuaraʝNomor IPA139Pengkodean karakterEntitas (desimal)ʝUnikode (heks)U+029DX-SAMPAj\KirshenbaumC<vcd>Braille Gambar Sampel suaranoicon sumber · bantuan Konsonan desis langit-langit bersuara adalah jenis dari suara konsonan langit-langit yang digunakan dalam berbagai bahasa. Simbol IPAnya adalah ⟨ʝ⟩. Dalam bahasa Indonesia tidak ada huruf yang mewakili [ʝ]. Huruf tersebut berbunyi seperti mengucapkan huruf gh yang diartikulasi...

2015 Indian filmAlifTheatrical release posterDirected byN. K. Muhammed KoyaWritten byN. K. Muhammed KoyaScreenplay byN. K. Muhammed KoyaProduced byM. S. BijuStarringLena, Zeenath, Kalabhavan ManiCinematographyM. J. RadhakrishnanEdited byB. Ajith KumarMusic byRamesh NarayanDistributed byMahadeva CinemasRelease date 27 February 2015 (2015-02-27) CountryIndiaLanguageMalayalam Alif is a 2015 Indian Malayalam-language film directed by N. K. Muhammed Koya.[1][2][3...

Experimental parasite fighter XF-85 Goblin XF-85 serial number 46-523 in the National Museum of the United States Air Force Role Parasite fighterType of aircraft National origin United States Manufacturer McDonnell Aircraft First flight 23 August 1948 Status Canceled, 1949 Number built 2 The McDonnell XF-85 Goblin is an American prototype fighter aircraft conceived during World War II by McDonnell Aircraft. It was intended to deploy from the bomb bay of the Convair B-36 bomber as a parasite f...

1991 film by Barry Sonnenfeld The Addams FamilyTheatrical release posterDirected byBarry SonnenfeldWritten by Caroline Thompson Larry Wilson Based onCharactersby Charles AddamsProduced byScott RudinStarring Anjelica Huston Raul Julia Christopher Lloyd CinematographyOwen RoizmanEdited by Dede Allen Jim Miller Music byMarc ShaimanProductioncompanies Paramount Pictures[1] Scott Rudin Productions[2] Distributed by Paramount Pictures (North America/South America)[1][2&#...

UTC+00:30Zona waktuPeta dunia dengan zona waktu berwarnaPerbedaan UTCUTCUTC+00:30Waktu kini03:19, 8 December 2023 UTC+00:30 [refresh]Meridian utama7,5 derajat TKelompok tanggal-waktuZ* UTC+0:30 digunakan pada lokasi berikut: Swiss lbsWaktu Universal Terkoordinasi (UTC)Perbedaan UTC untuk waktu standar dan waktu musim panas (DST)Miring: historis atau tidak resmi180° ke < 90°B −12:00 −11:00 −10:30 −10:00 −09:30 −09:00 −08:30 −08:00 −07:00 90°B ke < 0° −06:00 −05:...

Landform in Mohave County, Arizona Artillery MountainsArtillery Peak above Alamo Lake State ParkHighest pointPeakArtillery Peak-(volcanic plug)Elevation1,200 ft (370 m)DimensionsLength12 mi (19 km) NW x EWidth5 mi (8.0 km)GeographyCountryUnited StatesStateArizonaBorders onBig Sandy River–Arrastra Mountain Wilderness-N & EAlamo Lake State Park-SRawhide Mountains & Wilderness-SW The Artillery Mountains are a mountain range in Mohave County in wes...