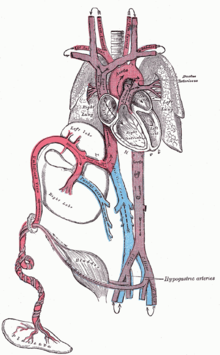
Fetal circulation
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Афанасий Дмитриевич Салынский А. Салынский (справа) и Ф. Панфёров. 1959 Дата рождения 9 сентября 1920(1920-09-09)[1] Место рождения Смоленск, РСФСР Дата смерти 22 августа 1993(1993-08-22) (72 года) Место смерти Москва, Россия Гражданство (подданство) СССР Россия Род деятельности драм�...

ФенетранжFénétrange Країна Франція Регіон Гранд-Ест Департамент Мозель Округ Саррбур-Шато-Сален Кантон Фенетранж Код INSEE 57210 Поштові індекси 57930 Координати 48°50′49″ пн. ш. 7°01′11″ сх. д.H G O Висота 227 - 317 м.н.р.м. Площа 14,49 км² Населення 664 (01-2020[1]) Густота...

Penggambaran lingchi di koran Prancis tahun 1858. Lingchi (Hanzi sederhana: 凌迟; Hanzi tradisional: 凌遲; Pinyin: língchí) adalah bentuk penghukuman mati di Tiongkok yang dipraktikkan dari tahun 900 hingga 1905. Dalam penghukuman ini, terdakwa diikat di tiang kayu di depan umum, lalu bagian tubuhnya diiris satu per satu, dan terdakwa dibiarkan hidup dalam proses ini. Opium kadang-kadang digunakan sebagai belas kasihan atau agar terdakwa tidak pingsan. Referensi Bourgon, Jé...

Bruno Campos Información personalNombre de nacimiento Bruno Aarón CamposNacimiento 3 de diciembre de 1973 (50 años) Río de Janeiro, BrasilNacionalidad Brasileña y estadounidenseLengua materna Inglés EducaciónEducado en Universidad de MíchiganEscuela de Derecho de la Universidad de MichiganUniversidad del NoroesteNorthwestern University School of CommunicationInterlochen Center for the Arts Información profesionalOcupación ActorAños activo desde 1995Empleador Morgan, Lewis &...

Harriet Low (1833)Gemälde von George Chinnery Harriett Low Hillard (* 18. Mai 1809 in Salem; † 1877 in Brooklyn, New York City) war eine US-Amerikanerin, die durch ihre Briefe und Tagebücher bekannt wurde. Von 1829 bis 1833 lebte sie in der portugiesischen Kolonie Macau an der Küste des Südchinesischen Meeres und wurde so eine der ersten jungen Amerikanerinnen, die in China lebten.[1] Low gehörte einer unitaristischen Gemeinde an.[2] Während ihres Aufenthaltes dort sch...

「MIT」はこの項目へ転送されています。その他の用法については「MIT (曖昧さ回避)」をご覧ください。 「マサチューセッツ大学」とは異なります。 マサチューセッツ工科大学Massachusetts Institute of Technology モットー Mens et Manus (ラテン語)モットー (英語) Mind and Hand[1]種別 私立大学ランドグラント大学 4–1–4期制設立年 1861年 (1865年設置)資金 124億ドル(2014年)[2]総

For the community in Ohio, see Freedom Station, Ohio. Freedom StationFormation2006, San Diego, CaliforniaTypenon-profit 501c charitable organizationLocation San Diego, California, United StatesKey peopleSandy Lehmkuhler, President, Glenna Schmidt, Vice PresidentWebsitewww.freedomstation.org[dead link] Freedom Station is a non-profit 501c charitable organization located in San Diego, California whose mission is to assist recovering injured military service members who are awaiting thei...

2013 miniseries directed by Keisuke Toyoshima xxxHolicDVD box of the drama featuring Kimihiro Watanuki and Yuko IchiharaGenre Supernatural Drama Dark fantasy Based onxxxHolicby CLAMPWritten by Jun Tsugita Keisuke Toyoshima Directed byKeisuke ToyoshimaStarring Anne Watanabe Shōta Sometani Masahiro Higashide Karen Miyazaki Yumi Adachi Music byNobuhiko MorinoOpening themeAitai by Suga ShikaoEnding themeYou Tell Me by ChayCountry of originJapanOriginal languageJapaneseNo. of episodes8ProductionP...

English cricket journalist (1907–2000) This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: E. W. Swanton – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (Janua...

Cet article recense de manière non exhaustive les châteaux (de défense ou d'agrément), maisons fortes, manoirs, mottes castrales, situés dans le département français de l'Orne. Le cas échéant, il est fait état des inscriptions et classements au titre des monuments historiques. Liste Légende (Type) Icône Signification Abréviations Château fort = Bastide = Ferme fortifiée = Maison forte = (Néo-)Palladianisme Renaissance = Château gascon = Folie (montpelliéraine) = Manoir, Gent...

College in Youngwood, Pennsylvania, U.S. Westmoreland County Community CollegeMottoAmbitious.TypePublic community collegeEstablished1970PresidentTuesday StanleyLocationYoungwood, Pennsylvania, U.S.40°13′59″N 79°33′59″W / 40.2331°N 79.5664°W / 40.2331; -79.5664Colors Blue and greenNicknameWolfpackSporting affiliationsNJCAAMascotWestly WolfWebsitewww.westmoreland.edu Westmoreland County Community College is a public community college in Youngwood...

Native American tribe in Washington, United States Indian Reservation in Washington, United StatesSquaxin Island Indian ReservationIndian ReservationSouth view of the Squaxin Museum, Library, and Research Center in Kamilche. FlagNickname: People of the WaterSquaxin Island TribeLocation in Washington StateCoordinates: 47°12′N 122°55′W / 47.200°N 122.917°W / 47.200; -122.917CountryUnited StatesStateWashingtonCountyMasonNegotiatedDecember 26, 1854Government&#...

Irish monastic saints in 6th century This article is about the group of Irish saints. For the IRA unit sometimes known as the Twelve Apostles, see The Squad (Irish Republican Army unit). St. Finnian imparting his blessing to the Twelve Apostles of Ireland The Twelve Apostles of Ireland (also known as Twelve Apostles of Erin, Irish: Dhá Aspal Déag na hÉireann) were twelve early Irish monastic saints of the sixth century who studied under St Finnian (d. 549) at his famous monastic school Clo...

Charles Geschke Información personalApodo Chuck Nacimiento 11 de septiembre de 1939 Cleveland (Estados Unidos) Fallecimiento 16 de abril de 2022 (82 años)Los Altos (Estados Unidos) Residencia Los Altos Nacionalidad EstadounidenseLengua materna Inglés EducaciónEducado en Universidad Carnegie MellonUniversidad Xavier Supervisor doctoral William Wulf Información profesionalOcupación Emprendedor, informático teórico y profesor universitario Área Ciencias de la computación Cargos ocupado...

Hindu temple in Andhra Pradesh, India Bhavanarayana TempleReligionAffiliationHinduismDistrictBapatlaDeityBhavanarayanaFestivalsChariot FestivalGoverning bodyTirumala Tirupati DevasthanamsLocationLocationBapatlaStateAndhra PradeshCountryIndiaLocation in Andhra PradeshGeographic coordinates15°54′21″N 80°28′04″E / 15.90588°N 80.46776°E / 15.90588; 80.46776ArchitectureTypeDravidian architectureDate establishedUnknownTemple(s)1InscriptionsDravidian languages and...

Aigüestortes y Estany de Sant Maurici Aigüestortes i Estany de Sant Maurici Categoría UICN II (parque nacional) Lago de San Mauricio.SituaciónPaís España EspañaComunidad Cataluña CataluñaProvincia LéridaLéridaCoordenadas 42°34′38″N 0°56′52″E / 42.57722222, 0.94777778Datos generalesAdministración Gobierno de España[1] - Generalidad de CataluñaGrado de protección Parque nacionalZEPA ES0000022[2]ZEC ES0000022[3]Fec...

1900 children's novel by L. Frank Baum For other uses, see The Wonderful Wizard of Oz (disambiguation). The Wonderful Wizard of Oz Original title pageAuthorL. Frank BaumIllustratorW. W. DenslowCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishSeriesThe Oz booksGenreFantasy, children's novelPublisherGeorge M. Hill CompanyPublication dateMay 17, 1900OCLC9506808Followed byThe Marvelous Land of Oz TextThe Wonderful Wizard of Oz at Wikisource The Wonderful Wizard of Oz is a 1900 children's novel writte...

This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (May 2021) Accelerated hydrogen peroxide (AHP) is a trademark[a] for solution of hydrogen peroxide whose antibacterial efficacy is enhanced by a surfactant and an organic acid.[1][2] It is also a disinfectant/cleaning agent that stabilizes hydrogen peroxide so that it can be used for extended periods of time. Pro...
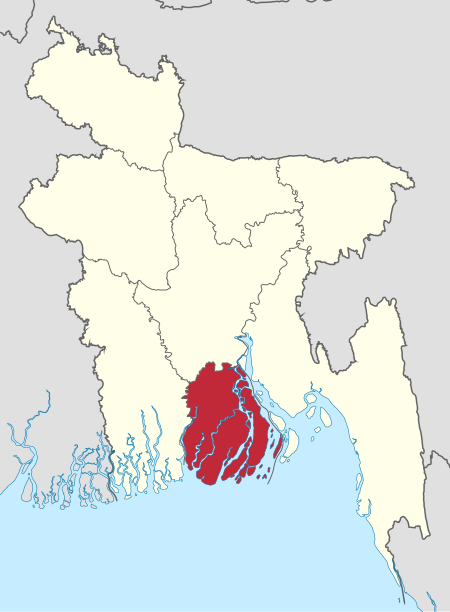
Divisi Barisāl merupakan sebuah divisi di Bangladesh. Distrik ini dulunya dipanggil Bakerganj. Kota utamanya terletak di Sungai Ganges. Munisipalitas ini didirikan pada tahun 1876 dan dipakai untuk kota pada tahun 2002. Divisi Barisāl Wilayah: 13297 km² Penduduk: 7,757,000 Zillas: Barguna, Barisal, Bhola, Jhalakathi, Patuakhali, Pirojpur. Barisal Zilla Area: 2791 Population: 2,299,000 Upazillas: Barisal Sadar, Agailjhara, Babuganj, Bakerganj, Banaripara, Gaurnadi, Hizla, Barisal Sada...

NBC NewsBerita pembagianNBCOrang kunciNoah Oppenheim (presiden)Didirikan21 Februari 1940; 84 tahun lalu (1940-02-21)Markas Besar30 Rockefeller Plaza, Kota New York, A.S.Biro Utama Kantor Pusat West Coast, Universal City, California Kantor Pusat Urusan Pemerintahan, Washington, D.C. Markas Besar Eropa, London, Inggris Kantor Pusat Asia Pasifik, Singapura dan Hong Kong Area yang dilayaniSeluruh DuniaProgram siaran: Hari ini NBC Nightly News Temui Pers Hari Ini Akhir Pekan Baris Tanggal NBC...