Diocese
|
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Baldassarre NegroniNegroni pada 1914Lahir(1877-01-21)21 Januari 1877Roma, ItaliaMeninggal18 Juli 1948(1948-07-18) (umur 71)Roma, ItaliaPekerjaanSutradara, penulis naskahTahun aktif1912-1945 Baldassarre Negroni (21 Januari 1877 –&#...

Este artigo não cita fontes confiáveis. Ajude a inserir referências. Conteúdo não verificável pode ser removido.—Encontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Novembro de 2020) Perlaza Informações pessoais Nome completo José Luis Perlaza Data de nascimento 6 de outubro de 1981 (42 anos) Local de nascimento Esmeraldas, Equador Altura 1,93 metros Apelido Zancudo Informações profissionais Clube atual Olme...

The King Uzziah Stricken with Leprosy, by Rembrandt, 1635. Uzia (Ibrani: עֻזִּיָּהוּ, YHWH adalah kekuatanku; bahasa Yunani: Οζίας; bahasa Latin: Ozias); bahasa Inggris: Uzziah), atau yang dikenal juga dengan nama Azarya (Ibrani: עֲזַרְיָה, YHWH telah menolong; bahasa Yunani: Αζαρις; bahasa Inggris: Azariah) adalah raja ke-10 kerajaan Yehuda (791 SM - 739 SM). Ayahnya adalah raja Amazia[1][2] dan ibunya bernama Yekholy...

Ця стаття не містить посилань на джерела. Ви можете допомогти поліпшити цю статтю, додавши посилання на надійні (авторитетні) джерела. Матеріал без джерел може бути піддано сумніву та вилучено. (серпень 2018) Off the WallСингл Майкла Джексона з альбому Off the WallВипущений 1979Форма�...

Aspect of history This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: History of Santa Monica, California – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (Januar...

Ekonomi SingapuraDowntown Core, SingapuraMata uangDolar Singapura (SGD/S$)Tahun fiskal1 April – 31 MaretOrganisasi perdaganganWTO, APEC, IOR-ARC, ASEANStatistikPDBUS$445,172 milyar (2014 est, PPP)Pertumbuhan PDB2.8% (2014)PDB per kapita$81.345 (PPP, 2014 est.),[1] $56,112 (nominal, 2014 est.)[2]PDB per sektorpertanian: 0%; industri: 26.6%; jasa: 73.4% (2011 est.)Inflasi (IHK)1.5%[3]Pendudukdi bawah garis kemiskinanN/AKoefisien gini47.3 (2011)Angkatan kerjaberdasarkan...

2005 Israeli filmFree ZoneDirected byAmos GitaiWritten byAmos Gitai Marie-Jose SanselmeProduced byNicolas Blanc Michael Tapuah Laurent TruchotStarringNatalie Portman Hiam Abbass Hanna LasloCinematographyLaurent BrunetDistributed byBac FilmsRelease dateJune 9, 2005 (2005-06-09)Running time93 minutesCountryIsraelLanguagesEnglishHebrewBox office$32,381 [1] Amos Gitai with Hana Laszlo and Natalie Portman on the set of Free Zone, 2005 Free Zone is a 2005 film directed by Amos Gitai....

Höxter, St. Peter und Paul Die römisch-katholische Pfarrkirche St. Peter und Paul ist ein im Jahr 1960 eingeweihtes Kirchengebäude im Petrifeld, einem Stadtteil von Höxter, Nordrhein-Westfalen. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Geschichte 2 Beschreibung 3 Ausstattung 4 Orgel 5 Geläut 6 Weblinks 7 Einzelnachweise Geschichte Weil im Jahrzehnt nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg viele Zuwanderer, unter anderem aus ostdeutschen Gebieten, Wohnraum im Petrifeld westlich der Innenstadt Höxters fanden, wuchs der Wun...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Drop Dead Live – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 1998 live album by LunachicksDrop Dead LiveLive album by LunachicksReleasedAugust 18, 1998RecordedConey Island High, NYC, F...

English cricket journalist Norman PrestonBornNorman Preston(1903-03-18)18 March 1903Died6 March 1980(1980-03-06) (aged 76)OccupationSports journalistKnown forCricket historian & writerSpouseEdith Mary Caroline (Molly)ChildrenBrian, David, HelenAwardsMBE Norman Preston, MBE (18 March 1903 – 6 March 1980) was an English cricket journalist. He began his career with the old Pardon's Cricket Reporting Agency in 1933 and served on three overseas tours as Reuters' correspondent. ...

Templo de Jerusalén LocalizaciónPaís Estado de PalestinaDivisión JerusalénCoordenadas 31°46′40″N 35°14′08″E / 31.777777777778, 35.235555555556Información religiosaCulto islam[editar datos en Wikidata] Maqueta del Segundo Templo de Jerusalén en el siglo I a. C. Indumentaria sacerdotal, Menorá (candelabro de siete brazos), Arca de la Alianza y demás utensilios del Templo de Jerusalén. El templo de Jerusalén (hebreo: בית המקדש...

Para otros usos de este término, véase TEA. «Tía (mitología)» redirige aquí. Para otras acepciones, véase Tuya (mitología). En el friso del Altar de Zeus de Pérgamo (Berlín), se conjetura que la diosa que lucha detrás de Helios es Tea.[1] En la mitología griega, Tea o Tía (en griego Θεία, también Teia, Thea, Thia o Theia), era considerada como la titánide de donde procede toda la luz,[2] y descrita con menor frecuencia como Etra (Αιθρη, Aethra, que sugie...

2007 American filmThe Oates' ValorDirected byTim Thaddeus CahillWritten byTim Thaddeus CahillProduced byAndy Bruntel, Leo Jaramillo (co-producers) Tim Thaddeus Cahill, Ross Danielson, Victory Palmisano, Ali Zubik (producers)StarringConrad ApfellDaniel CarpenterJordan DavidGrant GimbyShannon HoltAdèle JacquesJack MooreAmanda O'BrienRyan PattersonWhitney RydbeckCinematographyDavid RomEdited byMatt BarberDistributed byIndependentRelease date April 19, 2007 (2007-04-19) Running ti...
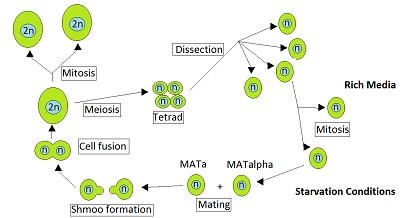
Sexes that reside in different individuals Look up heterothallism in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Heterothallic species have sexes that reside in different individuals. The term is applied particularly to distinguish heterothallic fungi, which require two compatible partners to produce sexual spores, from homothallic ones, which are capable of sexual reproduction from a single organism. In heterothallic fungi, two different individuals contribute nuclei to form a zygote. Examples of heter...

The history of local government in Sussex is unique and complex. Founded as a kingdom in the 5th century, Sussex was annexed by the kingdom of Wessex in the 9th century, which after further developments became the Kingdom of England. It currently corresponds to two counties, East Sussex and West Sussex. After the Reform Act 1832 Sussex was divided for purposes of administration into an eastern and a western division; these divisions were coterminous with the two archdeaconries of Chichester a...

出典は列挙するだけでなく、脚注などを用いてどの記述の情報源であるかを明記してください。記事の信頼性向上にご協力をお願いいたします。(2014年3月) 宮森小学校米軍機墜落事故 事故後の現場風景出来事の概要日付 1959年6月30日概要 整備不良によるエンジントラブル現場 米国統治下 沖縄県石川市(現:うるま市)宮森小学校乗客数 0乗員数 1負傷者数 0死者数 0生...

هذه المقالة عن قصبة. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع قصبة (توضيح). قصبة بطليوسمعلومات عامةنوع المبنى قصبة أندلسية — معلم تذكاري[1] المكان بطليوس — Badajoz city (en) المنطقة الإدارية بطليوس[1] البلد إسبانيا[1] بني بطلب من الدولة الموحدية معلومات أخرىالإحداثيات 38°53′01″N 6°58′0...

Species of gastropod Aldisa expleta Body of Aldisa expleta (holotype in the MNHN, Paris) Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Gastropoda Subclass: Heterobranchia Order: Nudibranchia Suborder: Doridina Superfamily: Doridoidea Family: Cadlinidae Genus: Aldisa Species: A. expleta Binomial name Aldisa expletaOrtea, Pérez & Llera, 1982[1] Aldisa expleta is a species of sea slug, a dorid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the...

This article is about the Dungeons & Dragons book. For other uses of the term Hallowed Ground, see Hallowed Ground. On Hallowed Ground AuthorColin McCombCover artistRobh RuppelLanguageEnglishPublisherTSR, Inc.Publication dateOctober 1996Pages192ISBN978-0-7869-0430-3 On Hallowed Ground is an accessory book for the Advanced Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game, for the Planescape campaign setting. Contents This book contains information about the planar domains of deities f...

Giorgio De Marchi Giorgio De Marchi con la maglia del L.R. Vicenza (1965) Nazionalità Italia Altezza 184 cm Peso 79 kg Calcio Ruolo Mediano Termine carriera 1968 Carriera Giovanili 1950-1951 P.G.S. Concordia Schio1951-1952 Schio Squadre di club1 1952-1956 Schio88 (10)1956-1957 Cuneo29 (2)1957-1966 L.R. Vicenza219 (10)1966-1967 Schio30 (0)1967-1968 Trento7 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbol...




