Castle of Mogadouro
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

La gastronomía de Turquía corresponde al conjunto de costumbres culinarias de los habitantes de las regiones de Turquía. La cocina turca es muy conocida en la actualidad y parece haber influido a otras gastronomías en el uso de especias o el asado de carnes. Es conocida por sus características puente entre las cocinas del Oriente Medio y la cocina balcánica, y se puede decir que se encuentra en una posición destacada entre las cocinas de origen mediterráneo debido no solo a la posici�...
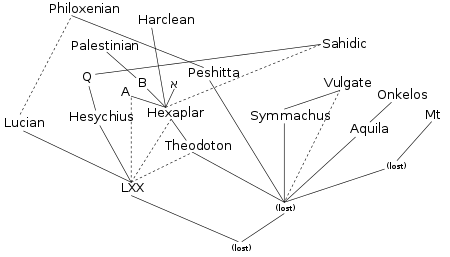
Isi Artikel utama: Kanon Alkitab dan Perkembangan kanon Perjanjian Lama Perjanjian Lama berisikan 39 (Protestan), 46 (Katolik), atau lebih (Ortodoks dan lainnya) kitab-kitab yang secara luas terbagi dalam Taurat, kitab sejarah, kitab hikmat, dan kitab para nabi.[1] Tabel Tabel di bawah ini menggunakan pengejaan dan penamaan dalam edisi-edisi modern Alkitab saat ini, seperti misalnya New American Bible Revised Edition, Revised Standard Version, dan English Standardisasi Version, untuk ...

Dispassion, detachment, or renunciation in Hinduism and Jainism This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Vairagya – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Vairāgya (वैराग्य) is a Sanskrit term used in Hindu as we...

Part of a series on the History of Belarus Prehistory Early East Slavs Middle ages Kievan Rus' Principality of Polotsk Principality of Turov Golden Horde Grand Duchy of Lithuania Early Modern Early elective monarchy (1569–1648) Deluge and decline (1648–1764) Three partitions (1764–95) Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Modern Russian Empire (1795–1917) Belarusian People's Republic(from 1918) Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic(1919�...

Thai footballer Seksan Piturat Personal informationFull name Seksan PituratDate of birth (1976-01-02) 2 January 1976 (age 47)Place of birth Mae Hong Son, ThailandHeight 1.75 m (5 ft 9 in)Position(s) strikerSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1996–2003 Sinthana 131 (77)2003–2004 BEC Tero Sasana 18 (4)2005 PEA 10 (3)2006–2007 TOT 22 (9)2007–2008 Raj-Vithi 31 (9)2008 Royal Thai Police 19 (7)2010–2012 North Bangkok College 8 (2)Total 239 (111)International career1999�...

Antoni Kiliński Antoni KilińskiAntoni Kiliński Nascimento 20 de outubro de 1909 Morte 6 de maio de 1989Varsóvia Sepultamento Cemitério Militar de Powązki Cidadania Polónia Alma mater Universidade de Tecnologia de Varsóvia Ocupação professor universitário, cientista de computação, engenheiro Prêmios Prêmio Pioneiro da Computação (1996)Honorary badge "For Merits for Warsaw"Silver Medal of Merit for National DefenceMedalha de Bronze de Mérito pela Defesa NacionalMedal f...

Kekasih HalalPoster resmiGenre Drama Drama romantis Komedi romantis Keluarga PembuatVerona PicturesDitulis olehTeam VeronaSutradara Lakonde Ai Manaf Pemeran Adinda Thomas Wafda Saifan Wanda Hamidah Penggubah lagu temaRian & RamaLagu pembukaDiam Tanpa Kata – d'MasivLagu penutupDiam Tanpa Kata – d'MasivPenata musikAry LogamNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. musim1Jmlh. episode19 (daftar episode)ProduksiProduser eksekutifTitin SuryaniProduser Titin Suryani (Produs...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要精通或熟悉相关主题的编者参与及协助编辑。 (2014年2月6日)請邀請適合的人士改善本条目。更多的細節與詳情請參见討論頁。 此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2007年10月8日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而�...

Canadian scholar (1929–2023) Eva KushnerOC FRSCBornEva Milada Ruth Dubska(1929-06-18)June 18, 1929Prague, CzechoslovakiaDiedJanuary 28, 2023(2023-01-28) (aged 93)Toronto, Ontario, CanadaEducationMcGill University (BA, MA, PhD)Spouse Donn Kushner (m. 1949; died 2001)Children3 Eva Milada Ruth Kushner OC FRSC (née Dubska; June 18, 1929 – January 28, 2023) was a Canadian scholar of Comparative literature and French, Renaissance...

The Bastard Prince Paperback EditionAuthorKatherine KurtzCover artistEdwin HerderCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishSeriesThe Heirs of Saint CamberGenreFantasyPublisherDel Rey BooksPublication date1994Media typePrint (hardback & paperback)Pages421 (first edition, hardcover)ISBN0-345-33262-8 (first edition, hardcover)OCLC29638319Dewey Decimal813/.54 20LC ClassPS3561.U69 B37 1994Preceded byKing Javan's Year Followed byKing Kelson's Bride (next published), In th...

19th century Apostolic Vicar of Luxembourg Jean-Théodore Laurent Jean-Théodore Laurent (6 July 1804 – 20 February 1884)[1] was the Apostolic Vicar of Luxembourg from 1841 to 1856. Biography Laurent was born in 1804 in Aachen[1] to a family of modest means. His father, the Luxembourger Franz Laurent, had 14 children with his wife Gertrude Schönen, originally from Aachen. After attending a Gymnasium in Aachen, Laurent studied theology for two years in Bonn.[1] A...

Fictional character from Carroll's Through the Looking-Glass Fictional character White QueenAlice characterAlice and the White Queen Art by John Tenniel (1865)First appearanceThrough the Looking-GlassCreated byLewis CarrollPortrayed byAnne Hathaway (Alice in Wonderland, Alice Through the Looking Glass)Emma Rigby (Once Upon a Time in Wonderland)Carol Channing (Alice in Wonderland)In-universe informationSpeciesHumanGenderFemaleOccupationQueen Evil Manipulative QueenSpouseWhite KingChildrenLily ...
Lifestyle publishing brand This article may have been created or edited in return for undisclosed payments, a violation of Wikipedia's terms of use. It may require cleanup to comply with Wikipedia's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. (March 2020) DuJourCategoriesLifestyleFrequencyQuarterlyTotal circulation100,000[1]FounderJason BinnFirst issueSeptember 2012CompanyDuJour MediaCountryUnited StatesBased inNew York CityLanguageEnglishWebsitewww.dujour.com DuJour is a pr...

Archaeological site in Peru For the battle in Peru, see Battle of Maraycalla. Maray QallaMaray QallaLocationPeru, Ancash RegionCoordinates9°04′43″S 77°14′23″W / 9.07861°S 77.23972°W / -9.07861; -77.23972HistoryCulturesInca Maray Qalla (Quechua maran, maray batan or grindstone, maray to tear down, to knock down, qalla carved stone, cobblestone; circular spindle disk; cheek,[1][2] also spelled Maraycalla, Maraycalle) is an archaeological site ...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Federal Service of Military-Technical Cooperation Russia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2017) Federal Service for Military-Technical CooperationFSVTS of RussiaAbbreviationFSVTSAgency overviewFormed2004Jurisdictional structure...

City in Hebei province, China For other uses, see Handan (disambiguation). Prefecture-level city in Hebei, People's Republic of ChinaHandan 邯郸市HantanPrefecture-level cityClockwise from the top: Skyline of Handan, Guangfu Ancient City, Qibugou Scenic Area, wide view of downtown, Congtai Park, statue of foreign-clothed cavalryNickname: Dream City (梦城)Location of Handan City jurisdiction in HebeiHandanLocation of the city center in HebeiShow map of HebeiHandanHandan (Northern Chin...

CarriacouNama lokal: KayryouacouJulukan: Land of Reefs (Tanah Terumbu)GeografiLokasiKaribiaKoordinat12°28′00″N 61°27′00″W / 12.46667°N 61.45000°W / 12.46667; -61.45000Koordinat: 12°28′00″N 61°27′00″W / 12.46667°N 61.45000°W / 12.46667; -61.45000KepulauanKepulauan GrenadineLuas12 sq mi (31 km2)Panjang7 mil (11 km) (mohon hapus nilai dalam mil [mi])Lebar2 mil (3 km) (mohon hapus ...

Month of 1964 1964 January February March April May June July August September October November December << January 1964 >> Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 The following events occurred in January 1964: January 25, 1964: Echo 2, largest artificial satellite ever, put into orbit January 11, 1964: U.S. government panel links cigarettes to lung cancer January 29, 1964: Josef Rieder opens the Wint...

Politika ti Hapon Gobierno Batay-linteg ti Hapon Pakasaritaan Linlinteg Ti Monarkia Emperador ti Hapon Naruhito Balangat a Prinsipe Fumihito Imperial a Kamara Ahensia ti Imperial a Sangkabalayan Lehislatura Nailian a Dieta Kamara dagiti Pannakabagi Tagabitla Tadamori Oshima (LDP) Bise Tagabitla Hirotaka Akamatsu (CDP) Kamara dagiti Konsehal Presidente Akiko Santō (LDP) Bise Presidente Toshio Ogawa (CDP) Mangipangulo ti Oposision Yukio Edano (CDP) Ehekutibo Kangrunaan a Ministro ti Hapon Yosh...

Comité Paralímpico Mexicano,(COPAME) Tipo Comité Paralímpico NacionalMiembro de Comité Paralímpico InternacionalComité Paralímpico de las Américas[editar datos en Wikidata] El Comité Paralímpico Mexicano, (COPAME) es el comité paralímpico nacional que representa a México. Esta organización es la responsable de las actividades deportivas paralímpicas en el país. Es miembro del Comité Paralímpico Internacional y del Comité Paralímpico de las Américas.[1][2...





