C. E. Wynn-Williams
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Questa voce sugli argomenti allenatori di calcio portoghesi e calciatori portoghesi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Alberto Augusto Nazionalità Portogallo Calcio Ruolo Attaccante Termine carriera 1937 Carriera Squadre di club1 1917-1919 Benfica? (?)1919-1920Leoes Santarem? (?)1920-1924 Benfica? (?)1924-1925 América? (?)1925-1926 Braga? (?)1927-1928 S...

مراد قرايلان (بالكردية: Mirad Qarayîlan) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 5 يونيو 1954 البيرة الوفاة 16 سبتمبر 2023 (69 سنة) [1] البصرة[2] مواطنة تركيا الديانة مسلم سني مناصب رئيس اتحاد مجتمعات كردستان في المنصب2010 – 2013 جميل بايق الحياة العملية المهنة آمر

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) ديف هامبتون معلومات شخصية الميلاد 7 مايو 1947 (76 سنة) آكرون مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الوزن 210 رطل الحياة العملية المهنة لاعب كرة قدم أمريكية الريا
هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (مارس 2023) حاسوب آي بي إم الشخصيالشعارمعلومات عامةالنوع آي بي إم المتوافق الصانع آي بي �...

American politician (1952–2022) This article's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines. Please improve this article by removing excessive or inappropriate external links, and converting useful links where appropriate into footnote references. (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Dave TomassoniPresident pro tempore of the Minnesota SenateIn officeJanuary 5, 2021 – August 11, 2022Preceded byMary KiffmeyerSucceeded byAnn ...

Bài này nói về tỉnh Đài Loan, một tỉnh được quản lý bởi Trung Hoa Dân Quốc. Về tinh được tuyên bố chủ quyền bởi Cộng hoà Nhân dân Trung Hoa, xem Tỉnh Đài Loan (Cộng hòa Nhân dân Trung Hoa) Tỉnh Đài Loan臺灣省 Tỉnh Đài Loan (Trung Hoa Dân Quốc) (màu xám đen). Quần đảo Điếu Ngư Đài/Senkaku ở phía đông bắc đảo Đài Loan, tuyên bố chủ quyền bởi Trung Hoa Dân Quốc không được thể hiện t...

Not to be confused with the other peoples known by similar names (such as Hima or Huma) in the African Great Lakes region. For other uses, see Hema (disambiguation) and Hima (disambiguation). Hema peopleMap showing the location of Ituri Province in the Democratic Republic of the CongoTotal populationc.160,000[1]Regions with significant populationsIturi Province, Democratic Republic of the CongoLanguagesNorthern Hema: Kilendu or Batha languages Southern Hema: Oruhema or Kinyoro languag...

Anabella DrummondPermaisuri SkotlandiaPeriode1390–1401Penobatan1390Informasi pribadiKelahiranskt. 1350Biara Dunfermline, Dunfermline, Fife, SkotlandiaKematianOktober 1401 (usia 51 tahun)Istana Scone, Scone, PerthPemakamanBiara DunfermlineWangsaWangsa DrummondAyahSir John Drummond, Thane Lennox ke-11IbuMary MontifexPasanganRobert III dari Skotlandia Menikah 1367; †4 April 1406AnakElizabeth, Baroness DalkeithMary, Comtesse AngusEgidiaMargaret, Comtesse DouglasRobertDavid Stewart, Adipati Ro...

1951 Buenos Aires Grand Prix Race Formula Libre of in the 1951 Formula One season Race detailsDate February 18, 1951Official name V Gran Premio del General Juan Perón y de la Ciudad de Buenos AiresLocation Aeroparque Costanera Buenos AiresCourse Public roadsCourse length 3.50 km (2.17 miles)Distance 45 laps, 157.5 km (90.689 miles)Pole positionDriver Juan Manuel Fangio MercedesTime 1:58.4 (106.42 km/h / 66.13 m/h)Fastest lapDriver Juan Manuel Fangio MercedesTime 2:02.4 (102.94 km/h / 63.96 m...
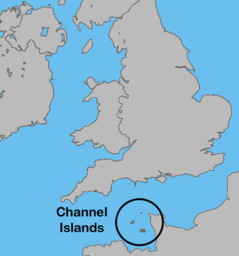
Channel Islands Îles de la Manche (French) Îles d'la Manche (Norman)Location of the Channel IslandsGeographyLocationWestern EuropeAdjacent toEnglish ChannelTotal islands8 inhabitedAdministration Bailiwick of Guernsey Bailiwick of Jersey The list of shipwrecks in the Channel Islands lists some of the ships that wrecked on or sank in the waters of the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Bailiwick of Jersey. The list includes ships that sustained a damaged hull, which were later refloated and r...

1998 video gameEuropean Air WarDeveloper(s)MicroProsePublisher(s)MicroProseProducer(s)Martin DeRisoDesigner(s)Tsuyoshi KawahitoProgrammer(s)Tsuyoshi KawahitoComposer(s)Roland J. RizzoPlatform(s)WindowsReleaseEU: 1998NA: November 3, 1998[1]Genre(s)Air combat simulationMode(s)Single-player, multiplayer European Air War is a combat flight simulator developed and published by MicroProse and published for Microsoft Windows in 1998. It is a sequel to 1942: The Pacific Air War.[2] It...

Official seal of the government of the state of Telangana Emblem of Telanganaతెలంగాణ రాష్ట్ర అధికారిక చిహ్నంArmigerThe Government of TelanganaAdopted2 June 2014CrestThe National Emblem of IndiaBlazonKakatiya Kala Thoranam, CharminarSupportersKakatiya Kala ThoranamCharminarUseAs State Emblem The Emblem of Telangana is the state emblem of Telangana in South India.[1] The arms has the Kakatiya Kala Thoranam in the middle, and the Ch...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Чеджу. Особая автономная провинция (тхыкпёль чачхидо)Чеджудо제주도濟州道Jeju-do Флаг Герб 33°21′56″ с. ш. 126°31′41″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Южная Корея Входит в Регион Чеджу Включает 2 си Адм. центр Чеджу История и география Площад�...

Strona z Kodeksu Cozcatzin Kodeks Cozcatzin – średniowieczny manuskrypt pochodzący z Texcoco w Meksyku. Opis Kodeks Cazcatzin powstał w 1572 roku. Jego nazwa pochodzi od nazwiska Don Juan Luis Cozcatzin, które znajdowało się na jednej ze stron. Został namalowany oryginalną techniką aztecką na 18 arkuszach, czyli 36 stronach europejskiego papieru. Napisy wykonane zostały w języku Nahuatl i hiszpańskim. Kodeks składa się z kilku części. W pierwszej znajduje się lista posiad�...

Kamerun i olympiska spelen IOK-landskodCMR KommittéKameruns Olympiska KommittéOlympiska sommarspelen 2000 i SydneyDeltagare34 deltagare i 4 grenar Medaljsummering Guld1 Silver0 Brons0 Totalt1 Placering49:e Kamerun i olympiska sommarspelen1964 • 1968 • 1972 • 1976 • 1980 • 1984 • 1988 • 1992 • 1996 • 2000 • 2004 • 2008 • 2012 • 2016 • 2020Kamerun i olympiska vinterspelen2002&...

Mexican professional wrestler Bobby BonalesBirth nameRoberto AcevesBorn(1916-09-25)September 25, 1916[1]Morelia, Michoacán, MexicoDiedJune 26, 1994(1994-06-26) (aged 77)[1]Spouse(s)Alba VillagranChildrenDaniel AcevesRoberto AcevesCristina AcevesNorma AcevesProfessional wrestling careerRing name(s)Bobby BonalesBilled fromMorelia, Michoacán, MexicoTrained byDiablo Velasco[2]Debut1934 Roberto Aceves, (September 25, 1916 – June 26, 1994), better known under the ri...

У слова «Забой» есть и другие значения: см. Забой (значения). Клавиша Backspace Backspace (букв. «пробел назад»), BS, erase, C (изредка в мобильных телефонах), ←, ⌫, забой, возврат, шаг назад — клавиша на клавиатуре компьютера, служащая для удаления символа, находящегося перед курсором (�...

Village in Powys, Wales Human settlement in WalesSennybridgeWelsh: PontsenniSennybridge, view southwest down High StreetSennybridgeLocation within PowysOS grid referenceSN9228CommunityMaescarPrincipal areaPowysPreserved countyPowysCountryWalesSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townBRECONPostcode districtLD3Dialling code01874PoliceDyfed-PowysFireMid and West WalesAmbulanceWelsh UK ParliamentBrecon & RadnorshireSenedd Cymru – Welsh ParliamentBrecon &...

Icebox cake Charlotte Russe redirects here. For the clothing store, see Charlotte Russe (retailer). CharlotteChocolate and pear charlotte, with the typical ladyfinger biscuitsAlternative namesIcebox cakeCourseDessertPlace of origin FranceServing temperatureHot or coldMain ingredientsBread, sponge cake or biscuits; fruit puree or custardVariationsCharlotte russe Media: Charlotte A charlotte is a type of bread pudding that can be served hot or cold. It is also referred to as an i...

Revolution group formed in 1966 The (Central) Cultural Revolution Group (CRG or CCRG; Chinese: 中央文革小组; pinyin: Zhōngyāng Wéngé Xiǎozǔ) was formed in May 1966 as a replacement organisation to the Central Committee Secretariat and the Five Man Group, and was initially directly responsible to the Standing Committee of the Politburo. It consisted mainly of radical supporters of Mao, including Chen Boda, the Chairman's wife Jiang Qing, Kang Sheng, Yao Wenyuan, Zhang Chunq...


