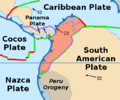
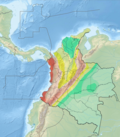
Bogotá Fault
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Aleksey Semenovich ZhadovAleksey ZhadovNama asliАлексе́й Семёнович Жа́довLahir(1901-03-30)30 Maret 1901Oblast Orel, Kekaisaran RusiaMeninggal10 November 1977(1977-11-10) (umur 76)Moskwa, Uni SovietPengabdian Uni SovietLama dinas1919-1969Perang/pertempuran Pertempuran Białystok–Minsk Pertempuran Moskwa Pertempuran Stalingrad Pertempuran Kursk Pertempuran Prokhorovka Serangan Dnieper–Karpatia Aleksey Semenovich Zhadov (bahasa Rusia: Алексе́й

Acceso al Puerto de Marín PO-11 Acceso ao Porto de Marín (en gallego) Pontevedra, Marín, España España Acceso al puerto de MarínDatos de la rutaNombre anterior Identificador Tipo Autovía urbanaNumeración PK 1,3 al PK 5,8Ancho de calzada 2 carriles por sentidoLongitud 4,5 kmAdministraciónAdministración Autoridad Portuaria de Marín y Ría de Pontevedra[1] (pkm 3,63 a pkm 4,25) Gobierno de España (pkm 1,26 a pkm 3,63 y p...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (نوفمبر 2018) كريستي بورك معلومات شخصية الميلاد 27 سبتمبر 1994 (29 سنة) ريفرسايد مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية المهنة ممثلة، وعارضة اللغة الأم الإن�...

Bekithemba Ndlovu Informações pessoais Nome completo Bekithemba Ndlovu Data de nascimento 9 de agosto de 1976 (47 anos) Local de nascimento Bulawayo, Rodésia Informações profissionais Posição Defensor Clubes profissionais Anos Clubes Jogos e gol(o)s Highlanders FC Seleção nacional 2000-2006 Zimbabwe 20 (1) Bekithemba Ndlovu (Bulawayo, 9 de agosto de 1976) é um ex-futebolista profissional zimbabuano que atuava como defensor. Carreira Bekithemba Ndlovu representou o el...

المسجد العظيم إحداثيات 2°12′55″N 102°15′44″E / 2.2151555555556°N 102.26234444444°E / 2.2151555555556; 102.26234444444 معلومات عامة القرية أو المدينة مدينة ملقا الدولة ماليزيا سنة التأسيس 1990 تاريخ بدء البناء 1990 التصميم والإنشاء النمط المعماري عمارة إسلامية معلومات أخرى تعديل مصدري...

Đảng Phục hưngChủ tịchTrần Văn HươngTrần Văn VănThành lập1953Giải tán1963Trụ sở chínhSài GònÝ thức hệChủ nghĩa tự doThuộc quốc gia Quốc gia Việt Nam Việt Nam Cộng hòaKhẩu hiệuTự do - Dân chủ - Công khaiĐối với các định nghĩa khác, xem Đảng Phục hưng. Chủ tịch đảng, ông Trần Văn Hương, phó tổng thống Việt Nam Cộng Hòa (1971-1975) và tổng thống VIệt Nam Cộng Hòa (1975) Đ...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2009. Pertempuran XingyangBagian dari Kampanye melawan Dong ZhuoTanggal190LokasiXingyang, HenanHasil Kemenangan Dong ZhuoPihak terlibat Koalisi Guandong Dong ZhuoTokoh dan pemimpin Cao Cao Xu RongKekuatan 3000+ Tidak diketahui Pertempuran Xingyang (滎陽之�...

Member of the Parliament of England For other people named Henry Bedingfeld, see Henry Bedingfeld (disambiguation). Sir Henry Bedingfeld (1505–1583), at the age of 68 in 1573 Sir Henry Bedingfeld (1505[1]–1583[2]), also spelled Bedingfield, of Oxburgh Hall, King's Lynn, Norfolk, was a Privy Councillor to King Edward VI and Queen Mary I, Lieutenant of the Tower of London, and (in 1557) Vice-Chamberlain of the Household and Captain of the guards.[3] With Sir Henry Je...

Period of Sasanian suzerainty over Iberia Sasanian Iberia255/6–299a363–580b580–627cMap of the Caucasus in 387–591StatusProvince of the Sasanian EmpireCapitalArmaziMtskhetaTbilisiCommon languages Georgian (native language) Middle Persian (royal administration and court) Parthian Greek and Syriac (religious) GovernmentFully subordinate monarchy (up to 580), governorateHistorical eraAntiquity• Established 255/6• Roman conquest 299• Sasanian reconquest under Shap...

River in New Zealand Mangawhero RiverThe Mangawhero Falls on the Mangawhero RiverEtymologyMaori meaning red streamNative nameMangawhero (Māori)LocationCountryNew ZealandRegionManawatū-WhanganuiTownsOhakunePhysical characteristicsSourceMount Ruapehu • locationTūroa skifield • coordinates39°18′4″S 175°32′13″E / 39.30111°S 175.53694°E / -39.30111; 175.53694 • elevation1,800 m (5,900 ft) Mou...

Group of dialects of Finnish Southwest Finnish dialects (Finnish: Lounaismurteet) are Western Finnish dialects spoken in Southwest Finland and Satakunta.[1] The Turku dialect is famous for its seemingly inverted questions. For example, Ei me mittä kaffelle men? looks like it means So we don't go for coffees? but actually means Shall we go for coffees?[2] The Southwest Finnish dialects have pitch accents and Swedish influences, as well as features from other dialect groups (es...

Supermarket chain Raley's Family of Fine StoresRaley's headquarters in West SacramentoTrade nameRaley's SupermarketsType Private family business IndustryRetail (grocery)FoundedFebruary 16, 1935 (88 years ago) (1935-02-16) in Placerville, California, U.S.FounderThomas P. RaleyHeadquartersWest Sacramento, California, United StatesNumber of locations 129 stores (2020)Key peopleMichael Teel, Owner, Chairman Keith Knopf, President & CEOProductsBakery, dairy, deli, frozen foods, g...

Norwegian actor Leif EngerBorn(1900-09-05)September 5, 1900Christiania (now Oslo)DiedNovember 11, 1977(1977-11-11) (aged 77)OsloNationalityNorwegianOccupationActor Leif Omdahl Enger (September 5, 1900 – November 11, 1977) was a Norwegian actor.[1] Enger was born in Christiania (now Oslo).[2] He appeared in a series of roles for the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation's radio theater. He was also a popular film actor, appearing in over 20 films. Among the best-known films...

Ancient form of Christian fasting This article is about the fasting practice. For the band, see Black Fast (band). Jesus Tempted in the Wilderness (Jésus tenté dans le désert), James Tissot, Brooklyn Museum A Black Fast, also known as a strict fast, is an ancient form of early Christian fasting.[1] Those undertaking a Black Fast consume no food or water during the day and then break the fast after sunset with prayer, the meal often but not necessarily being devoid of meat, eggs, da...

This article is missing information about the actual subject. Please expand the article to include this information. Further details may exist on the talk page. (April 2018) The Gas composition of any gas can be characterised by listing the pure substances it contains, and stating for each substance its proportion of the gas mixture's molecule count.Nitrogen N2 78.084 Oxygen O2 20.9476 Argon Ar 0.934 Carbon Dioxide CO2 0.0314 Gas composition of air To give a familiar example, air has a compos...

Gaelic games club in County Kildare, Ireland This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Maynooth GAA – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) MaynoothMáigh NúadFounded:1887County:KildareColours:Black and WhiteGrounds:Páirc Mhuire,...

Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan dari artikel terkait di Wikipedia bahasa Inggris. (Juli 2023) klik [tampil] untuk melihat petunjuk sebelum menerjemahkan. Lihat versi terjemahan mesin dari artikel bahasa Inggris. Terjemahan mesin Google adalah titik awal yang berguna untuk terjemahan, tapi penerjemah harus merevisi kesalahan yang diperlukan dan meyakinkan bahwa hasil terjemahan tersebut akurat, bukan hanya salin-tempel teks hasil terjemahan mesin ke dalam Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia. Jangan...

Coordenadas: 47° 3' N 4° 1' E Arleuf Comuna francesa Localização ArleufLocalização de Arleuf na França Coordenadas 47° 3' N 4° 1' E País França Região Borgonha-Franco-Condado Departamento Nièvre Características geográficas Área total 61,64 km² População total (2018) [1] 728 hab. Densidade 11,8 hab./km² Código Postal 58430 Código INSEE 58010 Arleuf é uma comuna francesa na região administrativa de Borgonha-Fr...

This article is about Doctor Who. For other uses, see War Machine (disambiguation). 1966 Doctor Who serial027 – The War MachinesDoctor Who serialA War Machine, having just been assembled.CastDoctor William Hartnell – First Doctor Companions Jackie Lane – Dodo Chaplet Anneke Wills – Polly Michael Craze – Ben Jackson Others John Harvey – Professor Brett John Cater – Professor Krimpton William Mervyn – Sir Charles Summer Alan Curtis – Major Green Sandra Bryant – Kitty...

1985 Indian filmUpaharamposterDirected bySajanWritten byJimmy LukeKaloor Dennis (dialogues)Screenplay byKaloor DennisProduced byShaji JosephRajan JosephStarringMammoottyRahman (actor)ShobhanaSrividyaSukumariCinematographyAnandakuttanEdited byV. P. KrishnanMusic byJohnsonProductioncompanyPrakash MovietoneDistributed byPrakash MovietoneRelease date 14 November 1985 (1985-11-14) CountryIndiaLanguageMalayalam Upaharam is a 1985 Indian Malayalam film, directed by Sajan and produced ...