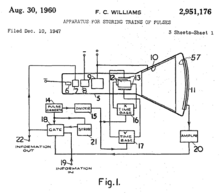
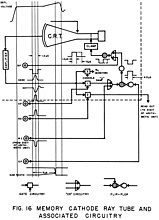
Williams tube
|
Read other articles:

Переписна місцевість Вілроудс-Гарденсангл. Wilroads Gardens --> Координати 37°43′ пн. ш. 99°55′ зх. д. / 37.717° пн. ш. 99.917° зх. д. / 37.717; -99.917Координати: 37°43′ пн. ш. 99°55′ зх. д. / 37.717° пн. ш. 99.917° зх. д. / 37.717; -99.917 Країна СШАСША�...

Джироламо СаккеріНародився не раніше 4 вересня 1667 і не пізніше 5 вересня 1667Санремо, Провінція Імперія, Лігурія, Італія[1]Помер 25 жовтня 1733(1733-10-25)[2][3][…] (66 років)Мілан, Міланське герцогство[1]Діяльність математик, філософ, викладач університе�...

PT MNC Teknologi NusantaraNama dagangMotionPayIndustriTeknologi informasiDidirikan2 November 2019 (sebagai SPIN)3 Juni 2021 (sebagai MotionPay)KantorpusatMNC News Center, Lantai 2Jalan KH. Wahid Hasyim No. 36-38,Kompleks MNC Center,Kebon Sirih, Jakarta Pusat, IndonesiaTokohkunciJessica Tanoesoedibjo (CEO)IndukMNC Financial ServicesSitus webmotionpay.id Logo SPIN (2 November 2019-3 Juni 2021) Logo MNC Teknologi Nusantara yang digunakan secara korporat MotionPay (PT MNC Teknologi Nusantara) mer...

ʻAbdu'l-BaháInformasi pribadiLahir`Abbás23 Mei 1844Teheran, PersiaMeninggal28 November 1921(1921-11-28) (umur 77)Haifa, PalestinaMakamKuil `Abdu'l-Bahá32°48′52.59″N 34°59′14.17″E / 32.8146083°N 34.9872694°E / 32.8146083; 34.9872694Koordinat: 32°48′52.59″N 34°59′14.17″E / 32.8146083°N 34.9872694°E / 32.8146083; 34.9872694AgamaBaha'iKebangsaanPersiaPasanganMunírih Khánum (m. 1873)An...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع أبو الفرج (توضيح). عبد الواحد بن نصر النصيبي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 313هـ925-926منصيبين تاريخ الوفاة شعبان 398هـمايو 1008م مواطنة الدولة العباسية الحياة العملية الفترة العصر العباسي النوع شعر عربي تقليدي الحركة الأدبية الشعر في العصر العباسي الثاني (تج�...

American athlete (born 1965) This article is about the athlete. For the American sprinter, see Angela Williams (sprinter, born 1965). For the Colorado politician, see Angela Williams (politician). Angela Williams Medal record Women's athletics Representing United States World Championships 2003 Paris 4x100 m relay Pan American Games 2003 Santo Domingo 100 m World Indoor Championships 2008 Valencia 60 m 2003 Birmingham 60 m 2001 Lisbon 60 m Angela Williams (born January 30, 1980 in Bellf...

Main article: 1972 United States presidential election 1972 United States presidential election in Illinois ← 1968 November 7, 1972 1976 → Turnout75.99% Nominee Richard Nixon George McGovern Party Republican Democratic Home state California South Dakota Running mate Spiro Agnew Sargent Shriver Electoral vote 26 0 Popular vote 2,788,179 1,913,472 Percentage 59.03% 40.51% County Results Nixon 50-60% 60-70% 70-8...

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Dick Traum – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) American disability runner Dr. Dick Traum is the founder of the Achilles Track Club for disabled athletes. In 1976, he completed the New York City Marathon, becoming the first runn...

British politician Mark GarnierMPChair of the Committees on Arms Export ControlsIncumbentAssumed office 6 July 2020Preceded byGraham JonesParliamentary Under Secretary of State for International TradeIn office15 July 2016 – 9 January 2018Prime MinisterTheresa MayPreceded byPosition establishedSucceeded byGraham StuartMember of Parliament for Wyre ForestIncumbentAssumed office 6 May 2010Preceded byRichard TaylorMajority21,413 (42.4%) Personal detailsBornMark Robert Timothy G...

Misteri Toko AntikGenre Drama Misteri Horor PembuatMD EntertainmentPemeran Aditya Suryo Saputro Nadia Celia Yuniza Icha Nafa Urbach Ponco Buwono Dicky Wahyudi Tarzan Ibnu Ibrahim Hasan Elnino Fiona Fachru Nisa Baron Yusuf Siregar Penggubah lagu temaNicky AstriaLagu pembukaGelombang Kehidupan — Nicky AstriaLagu penutupGelombang Kehidupan — Nicky AstriaNegara asalIndonesiaBahasa asliBahasa IndonesiaJmlh. musim1Jmlh. episode4 (daftar episode)ProduksiProduser Dhamoo Punjabi Manoj Punjabi Peng...

Species of snake Three-lined kukri snake Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Squamata Suborder: Serpentes Family: Colubridae Genus: Oligodon Species: O. trilineatus Binomial name Oligodon trilineatus(Duméril, Bibron & Duméril, 1854) The three-lined kukri snake (Oligodon trilineatus) is a species of snake of the family Colubridae. Geographic range The snake ...

Richardus Kardis Sandjaja Richardus Kardis Sandjaja[1] (20 Mei 1914 – 20 Desember 1948) adalah seorang pastor (romo) Projo yang berkarya dan terbunuh pada masa perjuangan kemerdekaan Republik Indonesia. Riwayat hidup Sandjaja (dibaca: Sanjoyo) dilahirkan di desa Sedan, Muntilan, Provinsi Jawa Tengah, Indonesia, pada tanggal 20 Mei 1914. Ayahnya bernama Willem Kromosendjojo, bekerja sebagai pembantu perawat di sebuah klinik Katolik yang dipimpin oleh misionaris Yesuit d...

Pudji Hartanto IskandarDirektur Jenderal Perhubungan Darat Kementerian PerhubunganMasa jabatan7 April 2016 – 18 Agustus 2017PendahuluDjoko SasonoPenggantiAgus SantosoKepala Kepolisian Daerah Sulawesi Selatan dan Sulawesi BaratMasa jabatan3 September 2015 – 14 April 2016PendahuluAnton SetiadjiPenggantiAnton CharliyanGubernur Akademi KepolisianMasa jabatan27 Agustus 2014 – 3 September 2015PendahuluEko Hadi SutedjoPenggantiAnas YusufKepala Korps Lalu LintasMasa j...

Sultan Abul Nashar Muhammad Ishaq Zainulmutaqin merupakan seorang sultan pada Kesultanan Banten. Ia juga dikenal dengan nama Sultan Ishaq dan berkuasa di Banten dalam rentang waktu 1803 - 1808. Biografi Sultan Ishaq naik tahta menggantikan Sultan Muhammad Muhyiddin Zainussalihin.[1] Pada masa pemerintahannya terjadi pertikaian dengan Herman Willem Daendels, Gubernur Jenderal Hindia Belanda 1808-1810, dan ia ditangkap kemudian diasingkan ke Batavia. Selanjutnya pada 22 November 1808, D...

Lokasi Kabupaten Maluku Barat Daya di Provinsi Maluku Berikut ini adalah daftar kecamatan, kelurahan, dan desa di Kabupaten Maluku Barat Daya, Provinsi Maluku, Indonesia. Kabupaten Maluku Barat Daya terdiri atas 17 kecamatan, 1 kelurahan, dan 117 desa dengan luas wilayah 4.581,06 km² dan jumlah penduduk 66.805 jiwa (2017). Kode Wilayah Kabupaten Maluku Barat Daya adalah 81.07.[1][2][3][4] Kode Wilayah Nama Kecamatan Ibu kota Jumlah Daftar Kelurahan dan Desa Ke...

Elemen 21 beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk perusahaan golf, lihat Element 21 (perusahaan). Skandium, 21ScSkandium tersublimasi dendritis dan kubus skandium 1 cm3 Garis spektrum skandiumSifat umumNama, lambangskandium, ScPengucapan/skandium/[1] Penampilanputih keperakanSkandium dalam tabel periodik Hidrogen Helium Lithium Berilium Boron Karbon Nitrogen Oksigen Fluor Neon Natrium Magnesium Aluminium Silikon Fosfor Sulfur Clor Argon Potasium Kalsium Skandium Titanium Vanadiu...

American/German engagement December 1944 Siege of BastognePart of the Battle of the Bulge (World War II)101st Airborne Division troops watch as C-47s drop supplies over Bastogne, 26 December 1944Date20–26 December 1944LocationBastogne, Wallonia, Belgium50°00′00″N 5°43′17″E / 50.0°N 5.7214°E / 50.0; 5.7214Result American victoryBelligerents United States GermanyCommanders and leaders Anthony McAuliffe (101st Airborne) William L. Roberts (Combat...

Russian theatre director (1874–1940) In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming conventions, the patronymic is Emilyevich and the family name is Meyerhold. Vsevolod MeyerholdBornKarl Kasimir Theodor Meyerhold9 February [O.S. 28 January] 1874Penza Oblast, Russian EmpireDied2 February 1940(1940-02-02) (aged 65)Moscow, Russian SFSR, Soviet UnionEducationMoscow Art TheatreKnown forTheatre directorMovementSymbolism, futurism, constructivistmSpouse(s)Olga Munt...

Жеребцов Володимир Володимирович Солдат Загальна інформаціяНародження 30 грудня 1976(1976-12-30)Бєлово, Кемеровська областьСмерть 5 грудня 2014(2014-12-05) (37 років)ПіскиВійськова службаРоки служби 2014Приналежність УкраїнаВид ЗС Сухопутні військаРід військ Механізовані ві...

Indonesian comedian and actor This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Sule comedian – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this ...