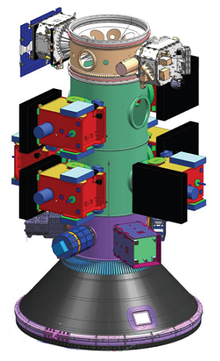
Space Test Program
|
Read other articles:

Prisciano, o el Gramático, panel de mármol que data del 1437-1439 desde el campanario de Florencia, Italia, por Luca della Robbia. La escena es una alegoría del gramático. La gramática de la lengua latina (en latín: Grammatica linguae latinae), al igual que la de otras lenguas indoeuropeas antiguas, es muy flexiva en el sentido estructural y orgánico, lo que significa que permite una gran flexibilidad para la elección del orden de palabras.[1] Por ejemplo, femina togam texuit, ...

Karoline Henriette von Hessen-Darmstadt mit ihrem Mohren, Porträt von Antoine Pesne (um 1750), Schlossmuseum Darmstadt Karoline Henriette von Hessen-Darmstadt Karoline Henriette Christine Philippine Luise von Pfalz-Zweibrücken (* 9. März 1721 in Straßburg; † 30. März 1774 in Darmstadt) war durch Heirat Landgräfin von Hessen-Darmstadt und wird auch als Große Landgräfin bezeichnet. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Leben 1.1 Herkunft und Familie 1.2 Landgräfin von Hessen-Darmstadt 1.3 Die Große ...

Koordinat: 37°45′04″N 97°17′15″W / 37.7511°N 97.2874°W / 37.7511; -97.2874 Koch Industries, Inc.JenisSwastaIndustriKonglomeratDidirikan8 Februari 1940; 83 tahun lalu (1940-02-08)PendiriFred C. KochKantorpusatWichita, Kansas, Amerika SerikatWilayah operasiSeluruh duniaTokohkunciCharles Koch(Ketua & CEO)ProdukAspal, zat kimia, perdagangan komoditas, energi, serat, pupuk, keuangan, mineral, gas alam, plastik, minyak bumi, pulp dan kertas, peternakan&#...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Marcadet et Poissonnier (homonymie). « Poissonniers (métro de Paris) » redirige ici. Ne pas confondre avec Poissonnière (métro de Paris). Marcadet - Poissonniers Quai de la ligne 12 en 2019 après le décarrossage Localisation Pays France Ville Paris Arrondissement 18e Coordonnéesgéographiques 48° 53′ 25″ nord, 2° 21′ 00″ est Caractéristiques Position parrapport au sol Souterraine Voies 4 Quais 4 Nombr...

For other people named Matiur Rahman, see Matiur Rahman (disambiguation). This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Matiur Rahman journalist – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JS...

ريبنيك (بالبولندية: Rybnik) ريبنيك ريبنيك الموقع الجغرافي تاريخ التأسيس 1327 تقسيم إداري البلد بولندا[1][2] التقسيم الأعلى محافظة سيليزيا خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 50°05′00″N 18°30′00″E / 50.083333333333°N 18.5°E / 50.083333333333; 18.5 المساحة 148 كيلومتر مربع �...
«Te voy a esperar»Sencillo de Juan Magán y Belindadel álbum Catarsis y Las aventuras de Tadeo JonesPublicación 7 de agosto de 2012[1]Formato Descarga digitalGénero(s) Dance, popDuración 3:35Discográfica Sony Music EspañaAutor(es) Juan Manuel Magán González, Carlos Andrés Alcaraz Gómez, David López Cendros, Diego Alejandro Vanegas Londono[2][3]Productor(es) Juan MagánCertificación ESP: [4]Juan Magán «Se vuelve loca» (2012) «Te voy a esperar» (20...

South African cement conglomerate PPC LtdTypePublic (JSE: PPC)Founded1892 (126 years ago)ProductsCement, lime (material), construction aggregate, ReadyMix, fly ashNet income ZAR 10,271 billion (2018)ZAR 9,641 billion (2017)Total assets ZAR 16,206 billion (2018)ZAR 18,035 billion (2017)Number of employees3,500+ (2018)Websitehttps://www.ppc.co.za/ PPC Ltd, a supplier of cement, lime (material) and related products in southern Africa. It has 11 cement factories and a lime manufacturing facility ...

The list of shipwrecks in 1899 includes ships sunk, foundered, grounded, or otherwise lost during 1899. This is a dynamic list and may never be able to satisfy particular standards for completeness. You can help by adding missing items with reliable sources. table of contents ← 1898 1899 1900 → Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Unknown date References January 1 January List of shipwrecks: 1 January 1899 Ship Country Description Harry United States The...

Attignat Attignat (Frankreich) Staat Frankreich Region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Département (Nr.) Ain (01) Arrondissement Bourg-en-Bresse Kanton Attignat Gemeindeverband Bassin de Bourg-en-Bresse Koordinaten 46° 17′ N, 5° 9′ O46.2891666666675.1583333333333Koordinaten: 46° 17′ N, 5° 9′ O Höhe 199–233 m Fläche 18,69 km² Einwohner 3.299 (1. Januar 2020) Bevölkerungsdichte 177 Einw./km² Postleitzahl 01340 INSEE-Code 01024 Web...

1988 San Marino general election ← 1983 29 May 1988 1993 → All 60 seats in the Grand and General Council31 seats needed for a majorityTurnout81.12% (1.40pp) Party % Seats +/– PDCS 44.13 27 +1 PCS 28.69 18 +3 PSU–IS 13.64 8 0 PSS 11.11 7 −2 This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below.Politics of San Marino Constitution Captains Regent Filippo Tamagnini Gaetano Troina Congress of State Grand and General Council Political parties Elections in San...

Author of Madeline books (1939-1999) Ludwig BemelmansBorn(1898-04-27)April 27, 1898Meran, South Tyrol, Austria-Hungary (now Italy)DiedOctober 1, 1962(1962-10-01) (aged 64)New York City, United StatesResting placeArlington National CemeteryOccupationWriter, illustratorNationalityAustrianCitizenshipAustria-Hungary United States (from 1918)GenreChildren's picture booksNotable worksMadeline series (1939–1999)Notable awardsCaldecott Medal 1954 SpouseMadeleine BemelmansChildrenBarbara Bemelm...

Kristiansand Prison (Norwegian: Kristiansand fengsel) was a prison in Kristiansand, Norway. It was the southernmost prison in the country. It belonged to the Norwegian Correctional Service. It had a capacity of 44 inmates and was located to the top two floors of the police house in the city.[1] The prison was closed in June 2020, at the same time as Agder Prison in Mandal, with a capacity of 100 inmates, was opened. Kristiansand Jailhouse in 1960. Photo: National Archival Services of ...

Facultad de Ciencias Sociales Acrónimo FACSOForma parte de Universidad de ChileFundación 1989LocalizaciónDirección Av. Capitán Ignacio Carrera Pinto 1045, Ñuñoa, Santiago, Chile[1]Campus Campus Juan Gómez MillasCoordenadas 33°28′01″S 70°35′38″O / -33.46697222, -70.59380556AdministraciónDecana Teresa Matus SepúlvedaVicedecano Cristian MirandaAcademiaDocentes 130 (2021)Estudiantes 1.650 (2021)Sitio web www.facso.uchile.cl[editar datos en Wikidata&...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с такой фамилией, см. Михайлов; Михайлов, Александр. Александр Валерьевич Михайлов Дата рождения 17 июня 1971(1971-06-17) Место рождения Тверь Дата смерти 18 октября 1993(1993-10-18) (22 года) Место смерти Москва Принадлежность СССР Россия �...

Human settlement in WalesMeifodThe King's Head InnMeifodLocation within PowysPopulation1,322 (2011)[1]OS grid referenceSJ154133CommunityMeifodPrincipal areaPowysPreserved countyPowysCountryWalesSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townLLANFYLLINPostcode districtSY22Post townMEIFODPostcode districtSY22Dialling code01938PoliceDyfed-PowysFireMid and West WalesAmbulanceWelsh UK ParliamentMontgomeryshireSenedd Cymru – Welsh ParliamentMo...

ParceTypeRumCountry of origin ColombiaIntroduced2014WebsiteParce Rum website Parce (pronounced par-say) is a brand of rum from Colombia. History Parce was founded by Jim Powers and his two brothers Patrick and Brian in 2012.[1] Previously all from Chicago, Jim was living in New York City and working in A&R while Brian was living in Vail, Colorado.[1][2] Patrick had been in Colombia since the 1990s to expand the family's water, oil and gas pipeline business. Th...

River in Gorj County, RomaniaAmaradiaAmaradia PietroasăLocationCountryRomaniaCountiesGorj CountyVillagesMușetești, Bălăneşti, Iași-GorjPhysical characteristicsMouthJiu • locationTârgu Jiu • coordinates44°58′57″N 23°13′47″E / 44.9824°N 23.2298°E / 44.9824; 23.2298Length41 km (25 mi)Basin size247 km2 (95 sq mi)Basin featuresProgressionJiu→ Danube→ Black SeaTributaries &#...

The vimpae may be seen here, though out of use, as the Anglican Bishop shown is wearing his mitre and holding his crozier. 'Pockets' may clearly be seen in the vimpae, for the servers to insert their hands when holding the pontificalia. A vimpa (plural: vimpae) is a veil or shawl worn over the shoulders of servers who carry the mitre and crosier during liturgical functions when they are not being used by the bishop, in the Roman Catholic, Anglican, and some other western churches.[1]&...

2003 studio album by John ZornMasada Anniversary Edition Vol. 1: Masada GuitarsStudio album by John ZornReleasedJanuary 2003 (2003-01)GenreJazz, klezmerLength74:39LabelTzadik TZ 7171ProducerJohn ZornJohn Zorn chronology Talisman: Live in Nagoya(2002) Masada Anniversary Edition Vol. 1: Masada Guitars(2003) Voices in the Wilderness(2003) Masada Anniversary chronology Masada Guitars(2003) Voices in the Wilderness(2003) Masada Anniversary Edition Vol. 1: Masada Guitars is the fi...