Regnier de Graaf
| |||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Circunscripción de MadridCortes Generales* Congreso: 37 diputados (de 350)* Senado: 4 senadores (de 266)Asamblea de Madrid* 135 diputados (de 135) Madrid es una de las 52 circunscripciones electorales utilizadas como distritos electorales para la Cámara Baja de las Cortes Generales de España, el Congreso de los Diputados, y una de las 59 de la cámara alta, el Senado. Es la circunscripción que elige más diputados al Congreso. La provincia de Madrid como circunscripción electoral no divi...

Cố Văn Căn顾文根Phó Tư lệnh Hải quân Quân Giải phóng Nhân dân Trung QuốcNhiệm kỳTháng 1 năm 2008 – Tháng 12 năm 2009Tư lệnhNgô Thắng LợiKế nhiệmTừ Hồng MãnhTư lệnh Hạm đội Nam HảiNhiệm kỳTháng 7 năm 2004 – Tháng 1 năm 2008Tiền nhiệmNgô Thắng LợiKế nhiệmTô Sĩ Lượng Thông tin cá nhânSinhtháng 11, 1946 (76–77 tuổi)Nam Hối, thành phố Thượng HảiĐảng chính trị
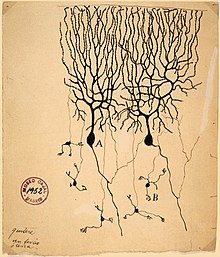
Клетки Пуркинье (А) и гранулярные клетки (B) в срезе мозгового вещества голубя. Рисунок Сантьяго Рамон-и-Кахаля Гранулярные клетки — несколько разновидностей мелких нейронов мозга. Название «гранулярная клетка» («зернистая клетка», «клетка-зерно») используется анатома

Dan Issel Issel en 1970.Datos personalesNombre completo Daniel Paul IsselApodo(s) Dan, HorseNacimiento Batavia, Illinois Estados Unidos25 de octubre de 1948 (75 años)Nacionalidad(es) EstadounidenseAltura 2,06 m (6′ 9″)Peso 109 kg (240 lb)Carrera deportivaDeporte BaloncestoEquipo universitario Kentucky (1967–1970)Club profesionalDraft de la NBA 8.ª ronda (puesto 122) 1970 por Detroit PistonsClub RetiradoLiga ABA, NBAPosición Ala-pívotDorsal(es) 44 - 25Trayec...

Гавриловопосадський район рос. Гаврилово-Посадский район Герб Гавриловопосадського району Прапор Гавриловопосадського району Основні дані Суб'єкт Російської Федерації: Івановська область Утворений: 1929 рік Населення (2021): ▼ 15 328 осіб Площа: 945.27 км² Поштові індекси:...

Leitões Plaats in Portugal Situering Gemeente Guimarães Coördinaten 41° 29′ NB, 8° 24′ WL Algemeen Oppervlakte 3,31 km² Inwoners (2001) 588[1] (177,6 inw./km²) Portaal Portugal Leitões is een plaats (freguesia) in de Portugese gemeente Guimarães en telt 588 inwoners (2001). Bevolkingsontwikkeling tussen 1864 en 2011 Bronnen, noten en/of referenties ↑ Instituto Nacional de Estatistica, Volkstelling 2001 · · Freguesias van Guimarães Aldão · Arosa...

Sporting event delegationJapan at the2010 Winter ParalympicsIPC codeJPNNPCJapan Paralympic CommitteeWebsitewww.jsad.or.jp (in Japanese)in VancouverCompetitors42 in 5 sportsFlag bearer Takayuki Endo[1]MedalsRanked 8th Gold 3 Silver 3 Bronze 5 Total 11 Winter Paralympics appearances (overview)1976198019841988199219941998200220062010201420182022 Japan sent 42 competitors to compete in all five disciplines at the 2010 Winter Paralympics[2] in Vancouver. Medalists Further...

O Parque Quase-Nacional Yatsugatake-Chushin Kogen é um parque quase-nacional localizado nas prefeituras japonesas de Yamanashi e Nagano. Estabelecido em 1 de junho de 1964, tem uma área de 39 857 hectares.[1] Este artigo sobre o Japão é um esboço. Você pode ajudar a Wikipédia expandindo-o.vde Referências ↑ «List of National and Quasi-national Parks» (em inglês). Ministério do Meio Ambiente do Japão. Consultado em 14 de junho de 2021 vdeParques nacionais do JapãoParques n...

1966 film of Raj Kapoor Teesri KasamTheatrical PosterDirected byBasu BhattacharyaScreenplay byNabendu GhoshPhanishwar Nath Renu (Dialogue)Story byPhanishwar Nath Renu[1]Based on Maare Gaye Gulfamby Phanishwar Nath RenuProduced byShailendraStarringRaj KapoorWaheeda RehmanRehanaCinematographySubrata Mitra[1]Edited byIqbalMusic byShankar-JaikishenShailendra (Lyrics)Hasrat Jaipuri (Lyrics)ProductioncompanyImage MakersRelease date1966Running time159 minCountryIndiaLanguageHindi Tee...

此條目或其章節极大或完全地依赖于某个单一的来源。 (2018年12月26日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:寶雅 — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引) 寶雅國際股份有限公司Poya International Co., Ltd.商业名称POYA寶雅公司類型上櫃公司股票代號櫃買中心:5904統�...

American discount department store chain owned by TJX Companies This article is about the international brand owned by TJX. For the American brand owned by TJX, see TJ Maxx. TK MaxxTypeSubsidiaryIndustryRetailFounded1994; 29 years ago (1994)FounderBernard CammarataHeadquartersWatford, United Kingdom[1]Number of locationsEurope: 596 (2 May 2020)[2]Australia: 56 (2 May 2020)[2]Total: 652 (2 May 2020)Area servedUnited KingdomAustraliaIrelandGermanyPoland...

Jamaican street subculture since 1960s For other uses, see Rude boy (disambiguation). Rudebwoy redirects here. For the song by Kardinal Offishall, see Everyday (Rudebwoy). Prince Buster performing at the Cardiff Festival, Cardiff, UK Rude boy is a subculture that originated from 1960s Jamaican street culture.[1] In the late 1970s, there was a revival in England of the terms rude boy and rude girl, among other variations like rudeboy and rudebwoy, being used to describe fans of two-ton...
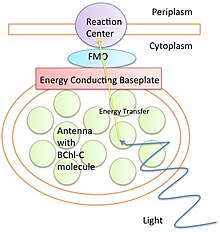
Ця стаття є сирим перекладом з іншої мови. Можливо, вона створена за допомогою машинного перекладу або перекладачем, який недостатньо володіє обома мовами. Будь ласка, допоможіть поліпшити переклад. Квантова біологія відноситься до застосування квантової механіки та те...

This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Springtime Tallahassee logo Springtime Tallahassee is an annual event held on either the last Saturday in March or the first Saturday in April in Tallahassee, Florida, United States celebrating Tallahassee's ...

Village in Podlaskie Voivodeship, PolandPrudziszkiVillagePrimary school in PrudziszkiPrudziszkiCoordinates: 54°10′N 22°55′E / 54.167°N 22.917°E / 54.167; 22.917Country PolandVoivodeshipPodlaskieCountySuwałkiGminaJeleniewoTime zoneUTC+1 (CET) • Summer (DST)UTC+2 (CEST) Prudziszki [pruˈd͡ʑiʂki] is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Jeleniewo, within Suwałki County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland.[1] It...

Annual German film and television award Not to be confused with Caméra d'Or. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Goldene Kamera – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) AwardGoldene KameraAwarded forFilm and televisionDate1...

تركسات 5 إيه البلد تركيا المصنع الشركة التركية لصناعات الفضاء تاريخ الإطلاق 8 يناير 2021[1] المكوك الحامل فالكون 9[1] تعديل مصدري - تعديل تركسات 5 إيه، هو قمر صناعي تركي للاتصالات. [2] التاريخ وفقًا لاتفاقية تم توقيعها في سبتمبر 2011، سيتم تطوير ا�...

Richmond Landon Medallista olímpico Datos personalesNacimiento Salisbury (Estados Unidos)20 de noviembre de 1898Nacionalidad(es) EstadounidenseFallecimiento Lynbrook (Estados Unidos)13 de junio de 1971Carrera deportivaDeporte Atletismo Medallero Atletismo Estados Unidos Juegos Olímpicos OroAmberes 1920Salto de altura [editar datos en Wikidata] Richmond Landon (Estados Unidos, 20 de noviembre ...

Questa voce sull'argomento nuotatori australiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Dyana Calub Nazionalità Australia Altezza 175 cm Peso 69 kg Nuoto Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Giochi olimpici 0 1 0 Mondiali 1 0 0 Giochi PanPacifici 2 2 0 Giochi del Commonwealth 2 1 0 Per maggiori dettagli vedi qui Statistiche aggiornate al 6 aprile 2008 Modifica dati su Wikidata&#...

Fallen Título OscurosFicha técnicaDirección Scott HicksProducción Mark Ciardi[1]Gordon Gray[1]Bill Johnson[1]Guion Michael Ross[1]Kathryn Price[1]Nichole Millard[1]Basada en Oscuros de Lauren KateMúsica Mark IshamFotografía Alar KiviloMontaje Scott GrayProtagonistas Addison TimlinJeremy IrvineHarrison GilbertsonJoely RichardsonLola KirkeDaisy Head Ver todos los créditos (IMDb)Datos y cifrasPaís Estados UnidosHungríaAño 2016Estreno 10 de novi...





