New York Railways Company
|
Read other articles:

American reality television series Party Down SouthAlso known asThe Dirty SouthDirty SouthGenreRealityCreated bySallyAnn SalsanoCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons7No. of episodes86ProductionExecutive producers SallyAnn Salsano Joel Zimmer Kyle Simpson Jayson Dinsmore Melanie Moreau Camera setupMultipleRunning time42 minutesProduction company495 ProductionsOriginal releaseNetworkCMTReleaseJanuary 16, 2014 (2014-01-16) –April 14, 2016 ...
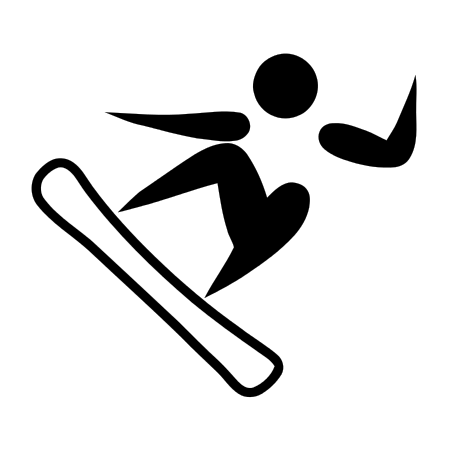
Faye Gulini Nazionalità Stati Uniti Altezza 163 cm Peso 57 kg Snowboard Specialità Snowboard cross Palmarès Competizione Ori Argenti Bronzi Mondiali 0 0 1 Mondiali juniores 0 1 0 Per maggiori dettagli vedi qui Statistiche aggiornate al 4 febbraio 2023 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Faye Gulini (Salt Lake City, 24 marzo 1992) è una snowboarder statunitense specializzata nello snowboard cross. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Palmarès 2.1 Mondiali 2.2 Mondiali juniores 2.3 Coppa d...

For people from the U.S. state, see List of people from Georgia (U.S. state). 1st row: Pharnavaz I, Pharasmanes I, Rhadamistus, Pharasmanes the Valiant, Peter the Iberian2nd row: Vakhtang I, Hilarion the Iberian, Tornike Eristavi, David III the Great, George of Athos3rd row: Maria of Alania, David IV the Builder, Shota Rustaveli, Tamar the Great, Simon I of Kartli 4th row: Ketevan the Martyr, Giorgi Saakadze, Anthim the Iberian, Archil of Imereti, David Guramishvili 5th row: Erekle II, Solomo...

2019 American sitcom created by Abby McEnany Work in ProgressOfficial release posterGenreComedyCreated by Abby McEnany Tim Mason Starring Abby McEnany Karin Anglin Celeste Pechous Julia Sweeney Theo Germaine ComposerEthan StollerCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons2No. of episodes18 (list of episodes)ProductionExecutive producers Abby McEnany Tim Mason Lisa Masseur (pilot) Lilly Wachowski Lawrence Mattis Josh Adler Ashley Berns Julia Sweeney Tony Hernandez Prod...

Mesa de tantawawas en Tacna (Perú), armada para el día de los muertos. Las guaguas de pan, muñecas de pan, wawas de pan o tantawawas, son dulces que consisten en panes grandes usualmente de trigo, moldeados y adornados con forma de niño pequeño o bebé, y decorados con pasta de azúcar o caritas hechas de yeso.[1][2] A veces rellenas de dulce, se elaboran y consumen junto a la colada morada y se usan como parte de ritos ancestrales en regiones andinas de Argentina, Bolivia,...

Dalam Kemah suci dan Camp (Abad ke-19 gambar) Tzav, Tsav, Zav, Sav, atau dalam bahasa Ibrani Alkitab Ṣaw (צַו – Bahasa Ibrani untuk perintah, kata keenam, dan kata khas pertama, dalam parsyah ini) adalah Bacaan Taurat Mingguan (פָּרָשָׁה, parashah) ke-25 dalam siklus tahunan Pembacaan Taurat dan yang kedua dari Kitab Imamat. Parsyah tersebut mengajarkan bagaimana imam melakukan persembahan korban dan menjelaskan tentang pentahbisan Harun dan anak-anaknya. Parsyah tersebut meli...

Al-Wehdat SCNama lengkapAl-Wehdat Sports Club of AmmanJulukanالمارد الأخضرAl-Mared Al-Akhdar(The Green Giant)Berdiri1956; 66 tahun lalu (1956)StadionStadion Raja Abdullah II, Amman(Kapasitas: 18.000)KetuaTareq KhouriManajerAdnan HamadLigaLiga Yordania2022-23ke-2Situs webSitus web resmi klub Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Musim ini Al-Wehdat SC (Arab: نادي الوحدات) adalah klub olahraga yang didirikan tahun 1956 dan bermarkas di Amman New Camp (Sebuah kamp pe...

First privately funded human spaceflight (2004) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: SpaceShipOne flight 15P – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) SpaceShipOne flight 15PPilot Mike Melvill moments after exiting SpaceShipOne a...

UNESCO World Heritage Site in Sichuan, People's Republic of China Sichuan Giant Panda SanctuariesUNESCO World Heritage SiteOfficial nameSichuan Giant Panda Sanctuaries - Wolong, Mt Siguniang and Jiajin MountainsLocationSichuan, People's Republic of ChinaCriteriaNatural: (x)Reference1213Inscription2006 (30th Session)Area924,500 ha (3,570 sq mi)Buffer zone527,100 ha (2,035 sq mi)Coordinates30°50′N 103°0′E / 30.833°N 103.000°E&...

En este artículo se detectaron varios problemas. Por favor, edítalo y/o discute los problemas en la discusión para mejorarlo: Necesita ser wikificado conforme a las convenciones de estilo de Wikipedia. Carece de fuentes o referencias que aparezcan en una fuente acreditada. Este aviso fue puesto el 25 de agosto de 2012. Imagen de revista semanal masónico (holandés), volumen 1, 1852, N ° 1 19 de enero de 1852. La historia de la francmasonería abarca los orígenes, la evolución y lo...

Deep neural network-based chess engine This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Original author(s)Gian-Carlo Pascutto, Gary ...

Student Residence in Ohio, United StatesQuaker SquareGeneral informationTypeStudent ResidenceLocation135 South Broadway Street, University of Akron, Akron, Ohio, United StatesCompleted1932Opening1975Closed2022Quaker Oats Cereal FactoryU.S. National Register of Historic Places Show map of OhioShow map of the United StatesLocation135 South Broadway Street, Akron, OhioCoordinates41°4′52″N 81°30′54″W / 41.08111°N 81.51500°W / 41.08111; -81.51500Area4 acres (2&#...

1950 film by Henry Levin Girl of the Year redirects here. For the FM Static song, see Critically Ashamed. For the Beach House song, see 7 (Beach House album). The Petty GirlDirected byHenry LevinScreenplay byNat PerrinBased onUnpublished story by Mary McCarthy[1]Produced byNat PerrinStarringRobert CummingsJoan CaulfieldElsa LanchesterCinematographyWilliam E. SnyderEdited byAl ClarkMusic byGeorge DuningWerner R. HeymannProductioncompanyColumbia PicturesDistributed byColumbia PicturesRe...

American TV reality series The Celebrity ApprenticeGenreReality competitionCreated byMark BurnettStarringDonald TrumpIvanka TrumpDonald Trump Jr.Eric TrumpArnold SchwarzeneggerTheme music composerKenneth GambleLeon HuffAnthony JacksonOpening themeFor the Love of Money Performed by The O'JaysCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons8No. of episodes90ProductionProducersMark BurnettDonald TrumpArnold Schwarzenegger(2017)Production locationsNew York City, New York (2008...

Fictional character from Jujutsu Kaisen Fictional character Ryomen SukunaJujutsu Kaisen characterRyomen Sukuna on the cover of Jujutsu Kaisen volume 14First appearanceJujutsu Kaisen #1, Ryomen Sukuna (2018)Created byGege AkutamiVoiced by Japanese: Junichi Suwabe English: Ray Chase In-universe informationAliasKing of CursesNationalityReincarnated Cursed Object Ryomen Sukuna (Japanese: 両面 宿儺, Hepburn: Ryōmen Sukuna) is a fictional character and one of the central antagonists of the man...

Iranian filmElevatorآسانسورDirected byHossein ShahabiWritten byHossein ShahabiProduced byHossein ShahabiStarringNasim ShahedRasool AbdiHossein AlamiKoroshe DavoodiAzar VakilCinematographyHossein ShahabiEdited byHossein ShahabiMusic byHossein ShahabiProductioncompanyBaran film houseDistributed byBaran Film HouseCountryIranLanguagePersian Elevator (Persian: آسانسور) is a 1995 Iranian film written and directed by Hossein Shahabi (Persian: حسین شهابی).[1][2]...

Запрос «Равно» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. Символы со сходным начертанием: 二 · ニ · ═ · ꞊ Знак равенства = Изображение ◄ 9 : ; < = > ? @ A ► Характеристики Название equals sign Юникод U+003D HTML-код = или = UTF-16 0x3D URL-код %3D И...

Illuminated manuscript gospel book Folio 27r from the Lindisfarne Gospels contains the incipit from the Gospel of Matthew. The Lindisfarne Gospels (London, British Library Cotton MS Nero D.IV) is an illuminated manuscript gospel book probably produced around the years 715–720 in the monastery at Lindisfarne, off the coast of Northumberland, which is now in the British Library in London.[1] The manuscript is one of the finest works in the unique style of Hiberno-Saxon or Insular art,...

American television sitcom (1983–1990) Mama's FamilyGenreSitcomCreated byDick ClairJenna McMahonDirected byRoger BeattyHarvey KormanDick MartinDave PowersStarringVicki LawrenceKen BerryDorothy LymanRue McClanahanEric BrownKarin ArgoudBetty WhiteBeverly ArcherAllan KayserTheme music composerMusic: Peter MatzLyrics: Vicki LawrenceOpening themeBless My Happy HomeCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons6No. of episodes130 (list of episodes)ProductionExecutive produce...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目已列出參考文獻,但文內引註不足,部分內容的來源仍然不明。 (2023年5月11日)请加上合适的文內引註来改善此条目。 此條目可能包含原创研究。 (2023年5月11日)请协助補充参考资料、添加相关内联标签和删除原创研究内容以改善这篇条目。详细情况请参见讨论页。 高雄捷運紅線Red Line高雄捷運高�...





