Mutual exclusion
|
Read other articles:

Valentine Kommun Vapen Land Frankrike Region Occitanien Departement Haute-Garonne Arrondissement Saint-Gaudens Kanton Saint-Gaudens Koordinater 43°6′N 0°43′Ö / 43.100°N 0.717°Ö / 43.100; 0.717 Yta 8,03 km²[1] Folkmängd 878 (2020-01-01)[2] Befolkningstäthet 109 invånare/km² Postnummer 31800 INSEE 31565 Geonames 6431867 OSM-karta 1457035 Kommunens läge i regionen Occitanien i Frankrike Kommunens läge i regionen Occitanien i Frankrike...

José Andrëa Información personalNombre de nacimiento José Mario Martínez ArroyoNacimiento 2 de junio de 1971 (52 años)La Paz, BoliviaNacionalidad BolivianaInformación profesionalOcupación Músico, compositor, cantanteAños activo 1994 - actualidadSeudónimo José Andrëa Género Power BalladPower Metal Hard rockHeavy metalBlues rockFolk rockFolk metalMetal sinfónicoMetal góticoMetal IndustrialÓpera rockInstrumentos Voz, teclados, batería y GuitarraTipo de voz Tenor lírico li...

الجبهة الإعلامية الإسلامية العالميةالإطارالنوع منظمة التنظيمالانتماء تنظيم القاعدة الدين سلفية جهادية تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات رسم بياني من إنتاج مكتب التحقيقات الفيدرالي يوضح عملية الإنتاج والنشر المعروفة لمقاطع الفيديو. الجبهة الإعلامية الإسلامية العال

Para migran berhenti di perbatasan Yunani-Macedonia di Gevgelija dan dijaga ketat oleh polisi Macedonia, 24 Agustus 2015 Krisis pengungsi di Eropa (atau Krisis migran Eropa) muncul seiring meningkatnya jumlah pengungsi (dan juga migran ekonomi)—ke Uni Eropa (UE) lewat Laut Mediterania dan Balkan dari Afrika, Timur Tengah, dan Asia Selatan. Istilah ini sudah digunakan sejak April 2015 ketika sedikitnya lima kapal yang mengangkut kurang lebih dua ribu migran tenggelam di Laut Mediterania. Jum...

National tennis team for Fed Cup BelgiumCaptainJohan Van HerckITF ranking6 3 (23 April 2018)Colorsred & blackFirst year1963Years played54Ties played (W–L)151 (80–71)Years inWorld Group42 (21–41)Titles1 (2001)Runners-up1 (2006)Most total winsSabine Appelmans (32–22)Most singles winsSabine Appelmans (25–13)Most doubles winsEls Callens (17–6)Best doubles teamMichèle Gurdal /Monique Van Haver (11–9)Most ties playedSabine Appelmans (33)Most years playedKirsten Flipkens (15) The ...

Dieser Artikel behandelt die heute Region Hochstift Paderborn; zum historischen Territorium siehe Hochstift Paderborn. Lage in Deutschland Fürstbischof Franz Egon änderte die ursprünglichen Farben des Wappens des Hochstifts Paderborn 1789 von silber-rot in rot-gold. Es gilt heute als Wappen der Region Hochstift Paderborn.[1] Das Hochstift Paderborn, oft auch nur Hochstift, gelegentlich auch Südostwestfalen genannt, ist eine etwa 440.000 Einwohner umfassende Region im Osten des deu...

Центральний госпіталь Міністерства внутрішніх справ України Тип Лікувально-реабілітаційний медичний закладГоловний лікар Начальник центру Коробка Василь Іванович[1]Країна УкраїнаАдреса вул. Бердичівська, 1, м. Київ, 04116.Координати 50°27′32″ пн. ш. 30°28′46″ �...

Carla J. ShatzAlmamaterKolese Radcliffe, Universitas Kolese London, Universitas HarvardDikenal atasPeran aktivitas neuron dalam maturasi rangkaian otakPenghargaan Penghargaan Peneliti Muda Perhimpunan Neurosains (1985) Akademi Seni dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Amerika Serikat (1992) Akademi Sains Nasional Amerika Serikat (1995) Perhimpunan Filsafat Amerika Serikat (1997) Akademi Kedokteran Nasional (1999) Penghargaan Gerard Perhimpunan Neurosains (2011) Anggota Royal Society (2011) Penghargaan Gruber...

2003 live album by Vince NeilLive at the Whisky: One Night OnlyLive album by Vince NeilReleasedMay 27, 2003[1]GenreHeavy metalLabelImage EntertainmentVince Neil chronology Carved in Stone(1995) Live at the Whisky: One Night Only(2003) Tattoos & Tequila(2010) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingAllmusic[2] Live at the Whisky: One Night Only is a live album by Vince Neil, lead vocalist of heavy metal band Mötley Crüe, recorded at the Whisky a Go Go. Conten...
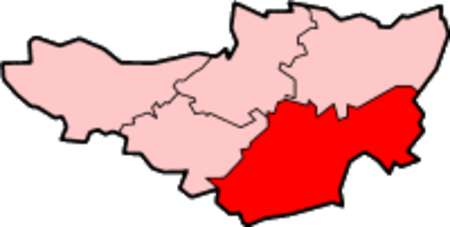
Civil parish in Somerset, England Yeovil Without is a civil parish in the South Somerset district of Somerset, England. It lies on the northern edge of Yeovil. It includes both suburbs of Yeovil, including the Bucklers Mead development, and rural areas including the hamlets of Yeovil Marsh and Longcroft. The parish includes Johnson Park and Bucklers Mead Community School. In 2011 the parish had a population of 6,834.[1] The parish was created in 1894 from part of the large ancient par...

Political party in India Indian political party Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam AbbreviationDMKPresidentM. K. StalinGeneral SecretaryDuraimuruganParliamentary ChairpersonT. R. BaaluLok Sabha LeaderT. R. BaaluRajya Sabha LeaderTiruchi SivaTreasurerT. R. BaaluFounderC. N. AnnaduraiFounded17 September 1949 (74 years ago) (1949-09-17)Split fromDravidar KazhagamPreceded byJustice Party (1917–1944)Dravidar Kazhagam(1944–1949)HeadquartersAnna Arivalayam,367�...

City in California, United States City in California, United StatesOceansideCity Clockwise: Mission San Luis Rey de Francia; Oceanside City Hall; Oceanside Strand; Mount Ecclesia; Roberts Cottages FlagSealLocation of Oceanside within San Diego County, CaliforniaOceansideLocation in the United StatesShow map of the United StatesOceansideOceanside (California)Show map of CaliforniaCoordinates: 33°12′42″N 117°19′33″W / 33.21167°N 117.32583°W / 33.21167; -117.3...

Desmond Connell Cardeal da Santa Igreja Romana Arcebispo-emérito de Dublin Atividade eclesiástica Diocese Arquidiocese de Dublin Nomeação 21 de janeiro de 1988 Predecessor Dom Kevin McNamara Sucessor Dom Diarmuid Martin Mandato 1988 — 2004 Ordenação e nomeação Ordenação presbiteral 19 de maio de 1951por Dom John Charles McQuaid, C.S.Sp. Nomeação episcopal 21 de janeiro de 1988 Ordenação episcopal 6 de março de 1988por Dom Gaetano Alibrandi Nomeado arcebispo 21 de janeiro de 1...

Japanese anime anthology series This article is about the 1993 series. For the 1975 series, see World Famous Fairy Tale Series. World Fairy Tale SeriesGenre Adventure Fantasy Romance Directed byHiroshi ShidaraComposer Seiji Yokoyama Country of originJapanOriginal languageJapaneseNo. of seasons1No. of episodes26ProductionProducersYoshifumi HatanoShinji ShimizuRunning time24 minutesProduction companies Toei Animation Fuji Eight Reteitalia Original releaseNetworkFuji TVRelease7 April (1995-...

British civil defence programme Recruitment poster for Air Raid Wardens ARP poster Air Raid Precautions (ARP) refers to a number of organisations and guidelines in the United Kingdom dedicated to the protection of civilians from the danger of air raids. Government consideration for air raid precautions increased in the 1920s and 30s, with the Raid Wardens' Service set up in 1937 to report on bombing incidents.[1] Every local council was responsible for organising ARP wardens, messenge...

Amusement park in Milson's Point, New South Wales, Australia For other amusement parks of the same name, see Luna Park. Luna Park SydneyPreviously known as Sydney's Luna Park, Luna Park Milsons Point, Harbourside Amusement ParkThe Luna Park FaceLocation1 Olympic Drive, Milsons Point, New South Wales, AustraliaCoordinates33°50′51″S 151°12′36″E / 33.8476°S 151.2100°E / -33.8476; 151.2100StatusOperatingOpened4 October 1935; 88 years ago (1935...

American actress (born 1948) Adrienne La RussaLa Russa in 1975BornNew York City, U.S.EducationCold Spring Harbor High SchoolOccupationActressYears active1968–1991 (as actress)Known forDays of Our LivesBeatrice CenciThe Man Who Fell to EarthCentennialThe Amazing Spider-ManLogan's RunSpouses Steven Seagal (m. 1984; ann. 1984) Robert French (m. 1987) Adrienne La Russa is an American actress kno...

محتوى هذه المقالة بحاجة للتحديث. فضلًا، ساعد بتحديثه ليعكس الأحداث الأخيرة وليشمل المعلومات الموثوقة المتاحة حديثاً. (أغسطس 2021) القاعدة في بلاد المغرب الإسلامي راية تنظيم القاعدة والحركات المتحالفة معها البلد الجزائر مالي التأسيس تاريخ التأسيس 2007 الجماعة السلفية ...

Canadian actress and model (1935–2023) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Sharon Acker – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Sharon AckerBornSharon Eileen Acker[1](1935-04-02)April 2, 1935Toronto, Ontario, Canada...

Demonstrasi Hong Kong 2014Polisi menembakkan gas air mata ke arah demonstranTanggal26 September 2014 (26 September 2014) – 15 Desember 2014 (15 Desember 2014)Lokasi Hong KongSebabKeputusan Kongres Komite Pembangunan Rakyat Nasional pada Reformasi Pemilu tentang Pemilihan Kepala Eksekutif dan Dewan Legislatif Hong Kong masa depanTujuan Hak pilih universal asli Pengunduran diri Kepala Eksekutif CY Leung Penghapusan konstituen fungsional DPRD Hong Kong HasilKemenangan Pe...


