Mobile Bay
|
Read other articles:

Riau dapat mengacu pada beberapa hal berikut: Peta Riau dan Kepulauan Riau Provinsi Riau, provinsi di daratan pulau Sumatra Kepulauan Riau (kepulauan), kepulauan di selatan Singapura Provinsi Kepulauan Riau, provinsi yang antara lain mencakup Kepulauan Riau, Kepulauan Lingga, Kepulauan Natuna dan Kepulauan Anambas Kesultanan Riau-Lingga, kerajaan yang beribu kota di pulau Lingga Riau (daerah pemilihan), bekas daerah pemilihan di Riau Riau TV, stasiun televisi di Kota Pekanbaru, Riau Sungai Ri...

Hjerm Parochie van Denemarken Situering Bisdom Bisdom Viborg Gemeente Struer Coördinaten 56°25'24NB, 8°38'35OL Algemeen Inwoners (2007) 1815 Leden Volkskerk (2007) 1712 Overig Kerken Hjerm Vestre Kirke Proosdij Struer Provsti Pastoraat Hjerm Foto's Portaal Denemarken Hjerm is een parochie van de Deense Volkskerk in de Deense gemeente Struer. De parochie maakt deel uit van het bisdom Viborg en telt 1712 kerkleden op een bevolking van 1815 (2007). Tot 1970 was de parochie deel v...

British espionage television series created in 1961 For other uses, see Avenger. The AvengersPatrick Macnee and Diana Rigg in the episode The Hour That Never Was, first aired in 1965Genre Action[1] Spy-fi[1] Comedy Mystery Created bySydney NewmanStarring Patrick Macnee Ian Hendry Honor Blackman Julie Stevens Diana Rigg Linda Thorson Patrick Newell Country of originUnited KingdomOriginal languageEnglishNo. of series6No. of episodes161 (list of episodes)ProductionProduction loca...

Brazilian footballer In this Portuguese name, the first or maternal family name is de Araújo and the second or paternal family name is Soares. Araújo Personal informationFull name Clemerson de Araújo SoaresDate of birth (1977-08-08) 8 August 1977 (age 46)Place of birth Caruaru, BrazilHeight 1.72 m (5 ft 7+1⁄2 in)Position(s) Second strikerTeam informationCurrent team Sete de SetembroYouth career1996 Porto-PESenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1997–2003 Goiás ...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع تقاطع (توضيح). الظهور الخاطف لإيفان تساريفيتش والشخصيتين الرئيسيتين لمسلسل الرسوم المتحركة بيبر وكاروت ضمن أحداث الحلقة الرابعة من مسلسل الرسوم المتحركة موريفنا نموذج على التقاطع في القصة. التقاطع في الأدب هو وضع شخصيتين أو أكثر من الشخصيات الخيا�...

Жоффруа Гішар Повна назва Stade Geoffroy-Guichard Країна Франція[1][2] Розташування Сент-Етьєн, Франція Координати 45°27′39″ пн. ш. 4°23′25″ сх. д. / 45.46083° пн. ш. 4.39028° сх. д. / 45.46083; 4.39028 Побудовано 1930 Відкрито 13 вересня, 1931 Власник «Сент-Етьєн» По�...

For other uses, see Colne (disambiguation). Human settlement in EnglandColneColne, with its town hall on the horizonColneShown within Pendle BoroughShow map of the Borough of PendleColneLocation within LancashireShow map of LancashirePopulation17,855 (2011 Census)[1]OS grid referenceSD884399Civil parishColneDistrictPendleShire countyLancashireRegionNorth WestCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townCOLNEPostcode districtBB8Dialling code012...

US legal case A&M Records, Inc. v. Napster, Inc.CourtUnited States Court of Appeals for the Ninth CircuitFull case nameA&M Records, Inc. v. Napster, Inc.ArguedOctober 2 2000DecidedFebruary 12 2001Citation(s)239 F.3d 1004HoldingNapster could be held liable for contributory and vicarious copyright infringement, affirming the District Court holding.Court membershipJudge(s) sittingMary M. Schroeder, Richard Paez, Robert BeezerCase opinionsMajorityRobert BeezerLaws applied17 U.S.C. § 501,...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Music of Austin, Texas – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2010) (Learn how and when to...

Governorate of Egypt Governorate in EgyptAswan GovernorateGovernorateView of Aswan in lake Nasser FlagAswan Governorate on the map of EgyptCoordinates: 23°35′N 32°49′E / 23.59°N 32.82°E / 23.59; 32.82Country EgyptSeatAswan (capital)Government • GovernorAhmed Ibrahim Mohamed Ibrahim[1]Area[2] • Total62,726 km2 (24,219 sq mi)Population (January 2023)[3] • Total1,643,211 •&...

Suffering experienced by animals living outside direct human control Juvenile red-tailed hawk eating a California vole Part of a series onAnimal rights Overview Animal welfare Around the world History Timeline Animal cruelty Veganism Vegetarianism Primate rights in research Movement Advocates Vegans Vegetarians Groups Animal abuse Animal–industrial complex Killing Mutilation Wild animals Consumption Dogs Horses Cats Cattle Bloodsports Bullfighting Hunting Fishing Animal testing Cosmetic Cap...

Imperial Japanese Navy's Kawachi-class battleship Settsu at anchor History Japan NameSettsu NamesakeSettsu Province Ordered22 June 1907 BuilderKure Naval Arsenal Laid down18 January 1909 Launched30 March 1911 Completed1 July 1912 Recommissioned1924 ReclassifiedConverted to target ship, 1924 Stricken 1 October 1923 20 November 1945 FateScrapped, 1946–1947 General characteristics Class and typeKawachi-class battleship Displacement21,443 long tons (21,787 t) (normal) Length533 ft (16...

Service for short-term scooter rentals Motorized scooters parked for use in Columbus, Ohio Bolt scooters parked at Bema Square, Wroclaw, 2021Rules printed on the deck of a Bird scooter A scooter-sharing system is a shared transport service in which electric motorized scooters (also referred to as e-scooters) are made available to use for short-term rentals. E-scooters are typically dockless, meaning that they do not have a fixed home location and are dropped off and picked up from certain loc...

SnowbombingSnowbombing Arctic Disco, MayrhofenGenreElectronic Dance MusicDates10 - 15 April 2023Location(s)Austrian ski resort of MayrhofenYears active2000-presentCapacity7000WebsiteSnowbombing Official Website Snowbombing is a ski resort festival, held annually in the spring at the Austrian ski resort of Mayrhofen. History Mayrhofen Bilder Snowbombing3 08 The event has been run since 2000 when it was first held at the French resort of Risoul as an après-ski nightclub promotional exercise st...

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Krakatau (disambiguasi). Anak KrakatauErupsi pada tahun 2008Titik tertinggiPuncak157 m (515 ft)Koordinat6°06′07″S 105°25′23″E / 6.102°S 105.423°E / -6.102; 105.423Koordinat: 6°06′07″S 105°25′23″E / 6.102°S 105.423°E / -6.102; 105.423 GeografiAnak KrakatauLokasiLetakLampung Selatan, Lampung, IndonesiaGeologiUsia batuanHolosen – kiniJenis gunungKalderaLetusan terakhir22 April - s...
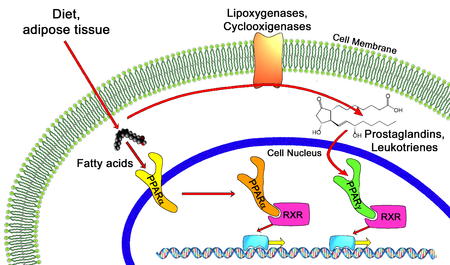
Drug PPAR-alpha and -gamma pathways PPAR agonists are drugs which act upon the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. They are used for the treatment of symptoms of the metabolic syndrome, mainly for lowering triglycerides and blood sugar. Classification PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma are the molecular targets of a number of marketed drugs. The main classes of PPAR agonists are: PPAR-alpha agonists An endogenous compound, 7(S)-Hydroxydocosahexaenoic Acid (7(S)-HDHA), which is a Docosanoid der...
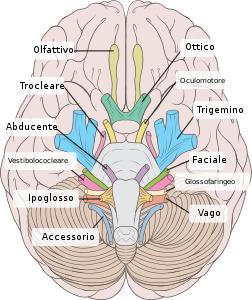
Nervi craniciL'emergenza dei nervi cranici dalla base dell'encefaloNervi cranici e il loro passaggio attraverso la base cranica IdentificatoriTAA14.2.01.001 e A14.2.00.038 FMA5865 Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale I nervi cranici o nervi encefalici sono un gruppo di fasci nervosi che originano direttamente dall'encefalo, più precisamente dal tronco encefalico. Fanno parte del sistema nervoso periferico. Nell'uomo adulto fisiologicamente sono presenti 12 paia di nervi cranici (24 nerv...

Thailand Open 2019Singolare Sport Tennis Vincitore Dayana Yastremska Finalista Ajla Tomljanović Punteggio 6–2, 2–6, 7–6(3) Tornei Singolare Singolare (q) Doppio Doppio 2017 2023 Voce principale: Thailand Open 2019. Belinda Bencic era la detentrice dell'ultima edizione del torneo disputatasi nel 2017, ma ha preso parte al concomitante torneo di San Pietroburgo. In finale Dayana Yastremska ha battuto Ajla Tomljanović con il punteggio di 6–2, 2–6, 7–6(3). Indice 1 Teste di s...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Grafiti ACAB di Barriera di Milano, Torino, Italia A.C.A.B. adalah sebuah akronim dari bahasa Inggris yang memiliki kepanjangan All Cops Are Bastards[1] (Indonesia: Semua Polisi Adalah Bajingan). Akronim ini digunakan sebagai slogan dalam grafi...

XXVI Supercopa de la UEFAMónaco 2001 El Estadio Luis II, sede de la final. Sede Mónaco Mónaco Espectadores 13 824[1] Fecha 24 de agosto de 2001 Cantidad de equipos 2 Podio • Campeón• Subcampeón Liverpool Bayern Múnich Partidos 1 Goles anotados 5 Mejor jugador Michael Owen Liverpool[2] La Supercopa de la UEFA 2001 fue un partido de fútbol disputado entre el Bayern Múnich alemán y el Liverpool inglés, el 24 de agosto de 2001 en el Estadio Luis II de ...



