Mississippi Plan
|
Read other articles:

Генри Джордж — основоположник учения Джорджизм (англ. Georgism, также геоизм) — основанное Генри Джорджем экономико-философское учение, в основе которого лежит идея, что каждый владеет созданным им продуктом (англ. everyone owns what they create), однако все природные блага, и п�...

American politician James Edmund Burke18th, 20th, 22nd, and 27th Mayor of Burlington, VermontIn officeApril 3, 1933 – March 31, 1935Preceded byJohn Holmes JacksonSucceeded byLouis F. DowIn officeApril 7, 1913 – April 4, 1915Preceded byRobert RobertsSucceeded byAlbert S. DrewIn officeApril 5, 1909 – April 2, 1911Preceded byWalter J. BigelowSucceeded byRobert RobertsIn officeJune 1, 1903[1] – March 31, 1907Preceded byDonly C. HawleySucceeded b...

This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (October 2014) The Cultural Properties of Costa Rica (Patrimonio Cultural de Costa Rica) refer to those tangible and intangible cultural properties that by decree has been awarded the distinction of being part of the cultural heritage of Costa Rica.[1] The properties are overseen by the Centro de Conservación Patrimonio Cultura...
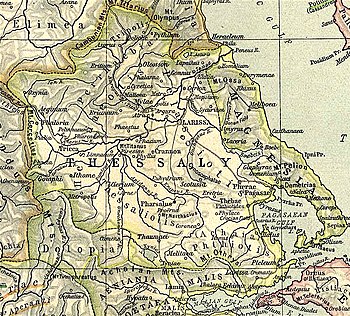
Карта, яка показує стародавню Фессалію. Трікка показана в центрі ліворуч. Трікка (з давньогрецької: ΤρίΚκη або ΤρίΚκα) — місто і поліс стародавньої Фессалії (один з традиційних районів Стародавньої Греції) в районі Гістіеотіс, що розташований на Лівому березі Пенея і �...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (سبتمبر 2018) أنطون تشيشولين معلومات شخصية الميلاد 27 نوفمبر 1984 (39 سنة) أستانا الطول 1.82 م (5 قدم 11 1⁄2 بوصة) مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية كازاخستان المسيرة ا�...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع خطاب (توضيح). هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (مايو 2019) خطاب خطاب اللفظ خَطَّابْ الجنس مذكر لغة الاسم العربية[1] أصل الاسم الأصل اللغوي العربية الاشتقاق خ ط ب النوع من حيث

Passport issued to the citizens of Uzbekistan International Uzbekistan passportFront cover of International Uzbekistan passportTypePassportIssued by UzbekistanFirst issued1 January 2019PurposeIdentificationEligibilityUzbekistan citizenship The Uzbekistan passport, being the property of the Republic of Uzbekistan, is issued to the citizens of Uzbekistan for international travels. An ordinary international passport can be issued to an infant at birth and must be renewed after 2 years,...

2014 video game 2014 video gameDivinity: Original SinDeveloper(s)Larian StudiosPublisher(s) Larian Studios (PC) Focus Home Interactive (PS4, XONE) Director(s)Swen VinckeProducer(s)David WalgraveDesigner(s)Farhang NamdarWriter(s) Jan Van Dosselaer Sarah Baylus Composer(s)Kirill PokrovskySeriesDivinityPlatform(s)Windows, OS X, Linux, PlayStation 4, Xbox OneReleaseWindows30 June 2014[1]PlayStation 4, Xbox One27 October 2015[2]Linux, OS X23 December 2015[3]Genre(s)Role-pla...

Purbalingga beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Purbalingga (disambiguasi). Kabupaten PurbalinggaKabupatenTranskripsi bahasa daerah • HanacarakaꦥꦸꦂꦧꦭꦶꦁꦒBaris ke-1: Alun-alun PurbalinggaBaris ke-2: Bukit Siregol, Stadion Goentoer DarjonoBaris ke-3: Bendungan Slinga, Masjid Agung Purbalingga, Patung KnalpotBaris ke-4: Bandar Udara Jenderal Besar Soedirman, Patung Jenderal Soedirman Purbalingga LambangJulukan: Kota PerwiraKota KnalpotKota Ramb...

Russian actress (born 1974) In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming conventions, the patronymic is Aleksandrovna and the family name is Rappoport. Kseniya RappoportRappoport at 2009 Venice Film Festival.Born (1974-03-25) 25 March 1974 (age 49)Leningrad, RSFSR, USSROccupationActressYears active1991–presentTitlePeople's Artist of Russia (2015)PartnerYuri Kolokolnikov (until 2014)ChildrenAglaya Tarasova Kseniya Aleksandrovna Rappoport (Russian: Ксе́ния Алекса...

Entrada do Colégio Militar de Belo Horizonte. O Sistema Colégio Militar do Brasil (SCMB)[1] é formado por 15 colégios militares.[2][3][4] Encontra-se sob o controle da Diretoria de Educação Preparatória e Assistencial (DEPA), por sua vez subordinada ao Departamento de Educação e Cultura do Exército (DECEX), anteriormente Departamento de Ensino e Pesquisa (DEP).[5] O SCMB é um subsistema de ensino do Exército Brasileiro. Seu objetivo é promover grande parte da Educação Básica (...
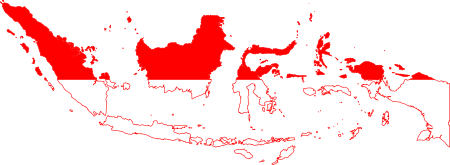
Teluk Banten adalah sebuah teluk di Provinsi Banten, dekat ujung barat laut Pulau Jawa, Indonesia. Merupakan bagian dari Laut Jawa dan luas wilayah permukaan totalnya 150 km² dan kedalaman rata-rata 7 m, yang termasuk ekosistem bawah laut seperti ladang rumput laut, terumbu karang, dan cagar alam burung internasional utama.[1] Diarsipkan 2006-02-22 di Wayback Machine. Daerah pesisirnya, termasuk Kota Serang di dekatnya dan Pelabuhan Merak sedang mengalami industrialisasi yang cepat. Tel...

Dengan olesan gula merah kental Setelah matang Kue rangi, atau juga disebut sagu rangi, adalah salah satu kue tradisional Betawi. Kue ini terbuat dari campuran tepung kanji (orang Betawi biasa menyebutnya tepung sagu) dengan kelapa parut yang dipanggang dengan cetakan khusus di atas tungku kecil dan ditutup agar cepat matang.[1] Kue rangi disajikan dengan olesan gula merah yang dikentalkan dengan sedikit tepung kanji. Untuk menambah selera dan wangi, gula merah dicampur dengan potonga...

Soviet-Russian wrestling coach (1962–2020) In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming conventions, the patronymic is Magomedovich and the family name is Nurmagomedov. Abdulmanap NurmagomedovАбдулманап НурмагомедовNurmagomedov in 2016BornAbdulmanap Magomedovich Nurmagomedov(1962-12-10)10 December 1962Sildi, Dagestan ASSR, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union(now Sildi, Dagestan, Russia)Died3 July 2020(2020-07-03) (aged 57)Moscow, RussiaNationalitySoviet (1962–1991...

1962 studio album by Sonny StittFeelin'sStudio album by Sonny StittReleased1962RecordedFebruary–April 1962 New York CityGenreJazzLabelRoostRLP 2247ProducerTeddy ReigSonny Stitt chronology Soul Summit(1962) Feelin's(1962) Low Flame(1962) Professional ratingsReview scoresSourceRatingDown Beat[1]Allmusic[2] Feelin's is an album by saxophonist Sonny Stitt recorded in 1962 and originally released on the Roost label.[3] Reception The Allmusic site awarded the album...

Constitutional officer in the executive branch of the government of the U.S. state of Wisconsin Secretary of State of WisconsinGreat Seal of the State of WisconsinIncumbentSarah Godlewskisince March 17, 2023StyleMister or Madam Secretary(informal)The Honorable(formal)Member ofBoard of Commissioners of Public LandsSeatWisconsin State CapitolMadison, WisconsinAppointerGeneral electionTerm lengthFour years, no term limitsConstituting instrumentWisconsin Constitution of 1848, Article VIInaug...

British BMX rider (born 1999) Beth ShrieverMBEPersonal informationFull nameBethany Kate ShrieverBorn (1999-04-19) 19 April 1999 (age 24)Leytonstone, England Medal record Women's BMX Representing Great Britain Olympic Games 2020 Tokyo Women's BMX racing World Championships 2021 Arnhem Women's Elite Race 2023 Glasgow Women's Elite Race World Junior Championships 2017 Rock Hill Women's BMX 2016 Medellín Women's Time Trial European Championships 2022 Dessel Women's Elite Race 201...

Stephen Douglas Kerr (lahir 27 September 1965 di Beirut, Lebanon) adalah seorang mantan pemain bola basket profesional Amerika Serikat. Ia adalah pemain dengan tembakan tiga-angka yang paling akurat dalam sejarah NBA (National Basketball Association) dan menjadi anggota dari lima tim bola basket yang memenangi kompetisi NBA. Pada tanggal 2 Juni 2007, Phoenix Suns, salah satu tim NBA, mengangkat Steve Kerr sebagai President of Basketball Operations dan General Manager organisasi tersebut. Seba...

この記事には参考文献や外部リンクの一覧が含まれていますが、脚注による参照が不十分であるため、情報源が依然不明確です。適切な位置に脚注を追加して、記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(2017年8月) ペルシア戦争 戦争:ペルシア戦争 年月日:紀元前499年-紀元前449年 場所:ギリシア、小アジア他 結果:ギリシア連合軍の勝利 交戦勢力 アテナイ、スパルタ�...

此條目之中立性有争议。其內容、語調可能帶有明顯的個人觀點或地方色彩。 (2019年1月4日)加上此模板的編輯者需在討論頁說明此文中立性有爭議的原因,以便讓各編輯者討論和改善。在編輯之前請務必察看讨论页。 2018年高雄市長選舉風波及爭議事件日期2018年 (2018)(民國107年)地点 中華民國参与者韓國瑜VS.陳其邁、雙方候選人及其競選團隊、支持者 2018年高雄市長...