JosÃĐ PiÃąera
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
æåå―æéŦįđæĩ·æįŧåķįäļįå°åū åå―įļå ģ äļŧéĄåčĄĻ įīĒåž å―å į䚧æŧåž įģæēđåĻé å―éēéĒįŪ æĶčĢ éĻéïžåäšïž åŪæđčŊčĻ äššåĢįĩąčĻ äššåĢåŊåšĶ įčēį åšįį æŧ䚥į čŠæį č°æį åĪąäļį åĻčį čŊåį åšåĢéĒ čŋåĢéĒ į Ī䚧é åįĩé įįĶį æŧå å―åš åĪåš æŋä― éĶé― ååļ å°į éĒįĐ éļå°éĒįĐ æéŦįđ æä―įđ čĶåŊæ°é įģæēđæķčīđé ååēåæŋčŠįæģ åæŋčŠįæģ åĪååæēŧåģķåķž å ąå

ŲØ°Ų اŲŲ ŲاŲØĐ ŲØŠŲŲ ØĐ ØĨØ° ØŠØĩŲ ØĨŲŲŲا Ų ŲاŲا؊ ØĢØŪØąŲ ŲŲŲŲØĐ ØŽØŊŲا. ŲØķŲŲØ§Ø ØģاØđØŊ ØĻØĨØķاŲØĐ ŲØĩŲØĐ ØĨŲŲŲا ŲŲ Ų ŲاŲا؊ Ų ØŠØđŲŲØĐ ØĻŲا. (ŲŲŲŲŲ 2023) اŲØŠØŽØąØĻØĐ Ø§ŲØģØąŲØąŲØĐ ŲŲ اŲØģŲŲŲŲŲØ Ø§ŲŲ ØđØąŲŲØĐ ØĢŲØķŲا ØĻاØģŲ اŲØŠØŽØąØĻØĐ Ø§ŲØģØąŲØąŲØĐ Ø§ŲاŲØŠØąØ§ØķŲØĐØ ŲŲ Ų ØاŲاØĐ ØاØģŲØĻŲØĐ ŲØąØŊŲØĐ ØŠŲØģØŠØŪØŊŲ ŲŲ اŲ؊طŲŲØą ØĢŲ اŲØŠŲŲŲŲ اŲØŠŲØļŲŲ Ų ŲŲ ŲØŠØŽ ØĢŲ ØŽŲا...

įēæĶééãŪéŧčŧïžãããķãĶãĪãĐããŪã§ãããïž æūæŽéŧæ°ééããã1 æŽé ã§ãŊãįēæĶééïžįūåĻãŪæąæĨæŽæ åŪĒééäļåĪŪæŽį·ãŪäļéĻãŪåčšŦïžã1904åđīïžææēŧ37åđīïž8æãŪéĢŊį°įš - äļéééŧåãŦéããčĢ―é ããéŧčŧįūĪãŦãĪããĶčĻčŋ°ãããããããŪéŧčŧãŊã1906åđīïžææēŧ39åđīïž10æ1æĨãŪįēæĶééå―æåãŦãĻããŠãĢãĶãå―æééãŦåžãįķãããæĨæŽãŪå―æééãŦãããæåãŪéŧčŧãĻãŠãĢ

Cet article est une ÃĐbauche concernant lâItalie et lâhistoire. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en lâamÃĐliorant (comment ?) ; pour plus dâindications, visitez le projet Italie. La fonction de gouverneur gÃĐnÃĐral de la Libye italienne est une colonie de l'Empire colonial italien. Elle est crÃĐÃĐe en 1934 lors de l'unification de la Tripolitaine italienne et de la CyrÃĐnaÃŊque italienne jusqu'en 1943 lors de la victoire des AlliÃĐs en Afrique du Nord pendant la Second...
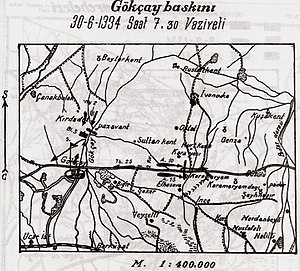
Battle in 1918 in the Caucasus that the OttomanâAzerbaijani forces won 40°39âē11âģN 47°44âē26âģE / 40.65306°N 47.74056°E / 40.65306; 47.74056 Battle of GoychayPart of the Armenian-Azerbaijani War during the Caucasus Campaign of World War I and Southern Front of the Russian Civil WarBattle plan written in Turkish.Date27 June â 1 July 1918 (4 days)LocationGoychay, Baku Governorate, Azerbaijan Democratic Republic40°39âē11âģN 47°44âē26âģE / &...

Artur Auernhammer (2020)Unterschrift von Artur Auernhammer Artur Auernhammer (* 9. MÃĪrz 1963 in Oberhochstatt) ist ein deutscher Politiker (CSU). Er war von 2004 bis 2005 bereits Mitglied des Deutschen Bundestages und ist seit 2013 erneut Mitglied. Zudem ist er seit 2015 Vorsitzender des Bundesverbandes Bioenergie.[1] Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Leben und Beruf 2 Politische TÃĪtigkeiten 3 Mitgliedschaft 4 Privates 5 Weblinks 6 Einzelnachweise Leben und Beruf Nach dem Besuch der Hauptschule ...

ŲØ°Ų اŲŲ ŲاŲØĐ ŲØŠŲŲ ØĐ ØĨØ° ØŠØĩŲ ØĨŲŲŲا Ų ŲاŲا؊ ØĢØŪØąŲ ŲŲŲŲØĐ ØŽØŊŲا. ŲØķŲŲØ§Ø ØģاØđØŊ ØĻØĨØķاŲØĐ ŲØĩŲØĐ ØĨŲŲŲا ŲŲ Ų ŲاŲا؊ Ų ØŠØđŲŲØĐ ØĻŲا. (ØĢØšØģØ·Øģ 2020) ØĨŲŲاØģ ŲØģØ·ŲØ·ŲŲ ØĻŲØąŲØąØ§ ŲŲŲŲŲ Ų ØđŲŲŲ ا؊ ØīØŪØĩŲØĐ Ø§ŲŲ ŲŲاØŊ 13 ŲØĻØąØ§ŲØą 1987 (36 ØģŲØĐ) ŲاŲ ØĻŲØģ ØŊŲØģ ØšŲŲ؊اŲاØēØģ اŲØ·ŲŲ 1.82 Ų (5 ŲØŊŲ 11 1⁄2 ØĻŲØĩØĐ) Ų ØąŲØē اŲŲØđØĻ Ų Ųا؎Ų اŲØŽŲØģ

ØŽØēØĄ Ų Ų ØģŲØģŲØĐ Ų ŲاŲا؊ ØŲŲØĢŲ Ų اŲŲ ØđŲŲŲ ا؊ Ų ŲاŲŲŲ ØąØĶŲØģØĐ ØĢŲ Ų اŲØĨŲØŠØąŲØŠ اŲØīØĻŲا؊ اŲØاØģŲØĻ اŲŲا؊Ų اŲŲ ØŲ ŲŲ اŲŲ ØđŲŲŲ ا؊ اŲŲ ØąŲØĻا؊ ØØąØĻ ØąŲŲ ŲØĐ ØđØĻØą اŲØĨŲØŠØąŲØŠ ØØąØĻ اŲŲ ØđŲŲŲ ا؊ ØŽØąŲŲ ØĐ ØąŲŲ ŲØĐ ØđØĻØą اŲØĨŲØŠØąŲØŠ ØŠØŽØ§ØąØĐ Ø§ŲØŽŲØģ اØØŠŲاŲ ØĻŲاØģØ·ØĐ Ø§ŲØاØģŲØĻ ØĨØąŲاØĻ ØąŲŲ Ų ØđØĻØą اŲØĨŲØŠØąŲØŠ ØĨØŊØ§ØąØĐ Ø§ŲØŲŲŲ اŲØąŲŲ ŲØĐ Ø§ŲØŠŲØŊŲØŊا؊ ØĻاØĻ Ø...

Muerte de Diana de Gales Flores a las puertas del Palacio de Kensington en homenaje a Diana de Gales (1 de septiembre de 1997).LocalizaciÃģnPaÃs FranciaLugar tÚnel del AlmaCoordenadas 48°51âē52âģN 2°18âē07âģE / 48.86436111, 2.30188889Datos generalesTipo accidente automovilÃsticoSede ParÃsHistÃģricoFecha 31 de agosto de 1997DesenlaceMuertos 3Heridos 1[editar datos en Wikidata] La muerte de Diana de Gales fue un acontecimiento que tuvo lugar en las primeras h...

Yves Claude VÄĐnh SanThÃīng tin chungSinh18 thÃĄng 4, 1934Saint-Denis, RÃĐunionMášĨt13 thÃĄng 7, 2016(2016-07-13) (82 tuáŧi)Saint-Denis, RÃĐunionHášu duáŧYves VÄĐnh San, Patrick VÄĐnh San, Johnny VÄĐnh San, Jerry VÄĐnh San, Thierry VÄĐnh San, Cyril VÄĐnh San, Didier VÄĐnh San, Marie Claude VÄĐnh San, Marilyn VÄĐnh San, Doris VÄĐnh San.[1]TÊn Äᚧy Äáŧ§Nguyáŧ n PhÚc BášĢo Và ng, Yves Claude VÄĐnh SanHoà ng táŧcNhà Nguyáŧ nThÃĒn pháŧĨDuy TÃĒnThÃĒn mášŦuFernande Antier Nguy...

vteLists of United Kingdom locations Aa-Ak Al Am-Ar As-Az Bab-Bal Bam-Bap Bar Bas-Baz Bea-Bem Ben-Bez Bi Bla-Blac Blad-Bly Boa-Bot Bou-Boz Bra Bre-Bri Bro-Bron Broo-Brt Bru-Bun Bur-Bz Ca-Cap Car-Cd Ce-Chap Char-Che Chi-Ck Cl-Cn Co-Col Com-Cor Cos-Cou Cov-Coy Cra Cre-Croc Croe-Cros Crot-Croz Cru-Cu Cw-Cz Da-Dam Dan-Ddu De-Dee Deo-Dn Do-Dor Dos-Doz Dr Ds-Dz Ea-Eass East A-D East E-L East M-Y Eat-Ee Ef-El Em-Ez Fa-Fe Ff-Fn Fo Fr-Fz Gab-Gan Gao-Gar Gas-Gaz Ge-Gl Gm-Gq Gr-Gred Gree-Gz Ha-Ham Han-H...

Album by Super Junior Sorry, SorryDigital and A version cover.Studio album by Super JuniorReleasedMarch 12, 2009 (2009-03-12)RecordedJuly 2008 â February 2009StudioSM Studios, SeoulGenreK-popR&BdanceelectronicaLanguageKoreanLabelSMProducerLee Soo-manSuper Junior chronology Don't Don(2007) Sorry, Sorry(2009) Bonamana(2010) Singles from Sorry, Sorry Sorry, SorryReleased: March 3, 2009 It's YouReleased: May 11, 2009 Music videoSorry, Sorry on YouTube It's You on YouTube ...

Regency in North Sumatra, IndonesiaToba Regency Kabupaten TobaRegencyKabupaten TobaOffice building of Toba Regency SealMotto(s): Tampakna do Rantosna, Rim ni Tahi do Gogona (If together in one spirit and purpose, then everything could be achieved.)Country IndonesiaProvinceNorth SumatraRegency seatBaligeGovernment âĒ RegentPoltak Sitorus âĒ Vice RegentTonny Simanjuntak âĒ Chairman of Council of RepresentativesEffendi S. Panangian Napitupulu (Golkar)&#...

Centre international Kofi Annan de formation au maintien de la paixHistoireFondation 1998CadreType Institut, terrain d'essaiPays GhanaCoordonnÃĐes 5° 34âē 31âģ N, 0° 06âē 47âģ OOrganisationSite web (en) www.kaiptc.orgmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata BasÃĐ au Ghana, le Centre international Kofi Annan de formation au maintien de la paix ou Kofi Annan International Peacekeeping Training Center (en l'honneur de l'un de ses fondateurs K...

ãŠãžãđããĢãģãŧãŊããžãļã§ãĒAustin Croshere 2007åđīãŪãŊããžãļã§ãĒåžéããļã·ã§ãģ PF/SFåšæŽæ å ąå―įą ãĒãĄãŠãŦåčĄå―įåđīææĨ (1975-05-01) 1975åđī5æ1æĨïž48æģïžåščšŦå° ãŦãŠããĐãŦããĒå·ããĩãģãžãŦãđčšŦé·(įūå―đæ) 208cm (6 ft 10 in)ä―é(įūå―đæ) 107kg (236 lb)ããĢãŠãĒæ å ąåščšŦ ãããããģãđåĪ§åĶããĐãã 1997åđīã12ä―éļæįĩæī1997-20062006-20072007-20082008-20092009 ãĪãģããĢãĒ...

Brunei Darussalam Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seri Politik dan KetatanegaraanBrunei Darussalam Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah Konstitusi Dewan Penasihat Perdana Menteri Hassanal Bolkiah Kabinet Dewan Suksesi Dewan Agama Islam Dewan Legislatif Yudikatif Pengadilan Sipil Pengadilan Syariah Pembagian administratif DistrikMukimDesaKota Hubungan luar negeri Menteri Luar Negeri Melayu Islam Beraja (Kerajaan Melayu Islam)(filsafat nasional) Negara lainnya Atlas lbs Distrik di Brunei Pembagian administra...

1995 film SharakuFilm posterDirected byMasahiro ShinodaWritten byMidori KatakuraHiroko MinagawaMasatoshi SakaiMasahiro ShinodaProduced byMasato HaraFrankie SakaiStarringHiroyuki SanadaCinematographyTatsuo SuzukiEdited byHirohide AbeMusic byTÅru TakemitsuRelease date 4 February 1995 (1995-02-04) Running time115 minutesCountryJapanLanguageJapanese Sharaku (Japanese: åæĨ―) is a 1995 Japanese drama film directed by Masahiro Shinoda.[1][2] It was entered into the ...

Ne pas confondre cette abbaye avec celle de la BÃĐnisson-Dieu de Boulogne-sur-Gesse, situÃĐe en Haute-Garonne. Abbaye de la BÃĐnisson-Dieu Vue de l'ancienne ÃĐglise abbatiale. DiocÃĻse ArchidiocÃĻse de Lyon Patronage Vierge Marie sainte MÃĻre de Dieu NumÃĐro d'ordre (selon Janauschek) CXXXI (131)[1] Fondation 29 septembre 1138 DÃĐbut construction XIIe siÃĻcle Dissolution 1791 Abbaye-mÃĻre Clairvaux LignÃĐe de Clairvaux Abbayes-filles Aucune CongrÃĐgation Ordre cistercien PÃĐriode ou styl...

Hindu Temple in Uttarakhand Some of this article's listed sources may not be reliable. Please help this article by looking for better, more reliable sources. Unreliable citations may be challenged or deleted. (May 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)Shidhpeeth[1] Mata Bhagwati Maa Mathiyana Devi Mandir[2][3] is a Hindu temple in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is located at Bhardhar Patti, north of Mathiyana Khal and is surrounded by green mou...

æéŪæŪæįķåšįūį§čĨŋæéŪæŪčŠįķåšįūį§ïžäļïž æąæéŪæŪčŠįķåšįūį§ïžäļïžæĻåŋį―įŦįąŧåįķēįĩĄįūį§å ĻæļčŊčĻæéŪæŪčŠææč įķåšåŠéŦåšéæį―åpa.wikipedia.orgpnb.wikipedia.orgåäļæ§čīĻéįåĐæģĻåéļææ§įĻæ·æą: 47,981 čĨŋ: 36,686æĻåšæķéī2008åđī10æ24æĨïž15åđīåïž2008-10-24ïž ïžčĨŋæéŪæŪčŠïž 2002åđī6æ3æĨïž21åđīåïž2002-06-03ïž ïžæąæéŪæŪčŠïžį°įķæīŧčšå §åŪđčĻąåŊįĨčå ąäšŦį...

