Guillaume Groen van Prinsterer
|
Read other articles:

GAM-87 Skybolt Tipo misil bal├ŁsticoHistoria de servicioEn servicio 1962Dise├▒ada 1958Fabricante Douglas[editar datos en Wikidata] El Douglas GAM-87 Skybolt (Rayo celeste, AGM-48 bajo el sistema Tri-service de 1962 ) fue un misil bal├Łstico hipers├│nico lanzado desde el aire (ALBM) desarrollado por los Estados Unidos a finales de la d├®cada de 1950. El concepto b├Īsico era permitir que los bombarderos estrat├®gicos estadounidenses lanzaran sus armas desde muy fuera del alcance de la...

┘Ŗ┘üž¬┘éž▒ ┘ģžŁž¬┘ł┘ē ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® žź┘ä┘ē ž¦┘䞦ž│ž¬ž┤┘枦ž» ž©┘ģžĄž¦ž»ž▒. ┘üžČ┘䞦┘ŗžī ž│ž¦┘ć┘ģ ┘ü┘Ŗ ž¬žĘ┘ł┘Ŗž▒ ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® ┘ģ┘å ž«┘䞦┘ä žźžČž¦┘üž® ┘ģžĄž¦ž»ž▒ ┘ģ┘łž½┘ł┘é ž©┘枦. žŻ┘Ŗ ┘ģž╣┘ä┘ł┘ģž¦ž¬ ž║┘Ŗž▒ ┘ģ┘łž½┘éž® ┘Ŗ┘ģ┘ā┘å ž¦┘䞬ž┤┘ā┘Ŗ┘ā ž©┘枦 ┘łžźž▓ž¦┘䞬┘枦. (ž»┘Ŗž│┘ģž©ž▒ 2018) ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® ž╣┘å ┘ģ┘垬ž«ž© ž¦┘äž¼ž▓ž¦ž”ž▒ ┘ä┘āž▒ž® ž¦┘äžĘž¦ž”ž▒ž® ┘ä┘äž│┘Ŗž»ž¦ž¬. ┘ä┘ģž╣ž¦┘å┘Ź žŻž«ž▒┘ēžī žĘž¦┘äž╣ ┘ģ┘垬ž«ž© ž¦┘äž¼ž▓ž¦ž”ž▒ ┘ä┘āž▒ž® ž¦┘äžĘž¦ž”ž▒ž®. ┘ģ┘å

┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘鞦┘äž® ┘Ŗž¬┘Ŗ┘ģž® žźž░ ž¬žĄ┘ä žź┘ä┘Ŗ┘枦 ┘ģ┘鞦┘䞦ž¬ žŻž«ž▒┘ē ┘é┘ä┘Ŗ┘äž® ž¼ž»┘ŗž¦. ┘üžČ┘ä┘ŗž¦žī ž│ž¦ž╣ž» ž©žźžČž¦┘üž® ┘łžĄ┘äž® žź┘ä┘Ŗ┘枦 ┘ü┘Ŗ ┘ģ┘鞦┘䞦ž¬ ┘ģž¬ž╣┘ä┘éž® ž©┘枦. (┘å┘ł┘ü┘ģž©ž▒ 2019) ž│ž¦┘ģž¦┘åž½ž¦ ┘ā┘Ŗž▒ ┘ģž╣┘ä┘ł┘ģž¦ž¬ ž┤ž«žĄ┘Ŗž® ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘Ŗ┘䞦ž» 17 žŻž©ž▒┘Ŗ┘ä 1999 (24 ž│┘åž®) ┘ü┘ä┘āž▒┘ā ┘ģž▒┘āž▓ ž¦┘ä┘äž╣ž© ┘łž│žĘ ž¦┘äž¼┘åž│┘Ŗž® ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘ģ┘ä┘āž® ž¦┘ä┘ģž¬žŁž»ž® ┘ģž╣┘ä┘ł┘ģž¦ž¬ ž¦┘ä┘垦ž»┘Ŗ ž¦┘ä┘垦ž»┘Ŗ ž¦┘䞣ž¦┘ä┘Ŗ Rangers W.F.C. [ž¦┘äžź┘åž¼┘ä┘Ŗž▓

US television series GMA3: What You Need to KnowAlso known asGMA Day (2018ŌĆō19)GMA3: Strahan & Sara (2019)GMA3: Strahan, Sara & Keke (2019ŌĆō20)Pandemic: What You Need to Know (2020)GMA3: What You Need to Know (2020ŌĆōpresent)GenreNews and talkCreated byJames GoldstonCatherine McKenzieDirected byLily OlszewskiPresented byJennifer AshtonDeMarco MorganEva PilgrimNarrated byRandy ThomasCountry of originUnited StatesOriginal languageEnglishNo. of seasons4ProductionExecutive producersJust...

ž▒ž╣┘Ŗž®┘ģž╣┘ä┘ł┘ģž¦ž¬ ž╣ž¦┘ģž®žĄ┘å┘ü ┘üž▒ž╣┘Ŗ ┘ģ┘å ž¦┘ä┘ā┘Ŗž¦┘å ž¦┘äžźž»ž¦ž▒┘Ŗ ž¦┘äž»┘Ŗ┘å┘Ŗ ž¦┘äžź┘é┘ä┘Ŗ┘ģ┘Ŗ┘ā┘Ŗž¦┘å žźž»ž¦ž▒┘Ŗ ž»┘Ŗ┘å┘Ŗ ž¼ž▓žĪ ┘ģ┘å žŻž©ž▒ž┤┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž»┘É┘æ┘Ŗ┘å ž¦┘ä┘ģž│┘ŖžŁ┘Ŗž®[1] ┘ģ┘åžĄž© ž▒ž”┘Ŗž│ ┘ćž░┘ć ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘åžĖ┘ģž® ┘āž¦┘ć┘åpastoral care (en) ┘äž»┘Ŗ┘ć ž¼ž▓žĪ žŻ┘ł žŻž¼ž▓ž¦žĪ parish church (en) filial church (en) parishioner (en) ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä - ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä ┘ģžĄž»ž▒┘Ŗ - ž¬ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ä ┘ł┘Ŗ┘ā┘Ŗ ž©┘Ŗž¦┘垦ž¬ ┘ā┘å┘Ŗž│ž® ž▒ž╣┘Ŗž® ž¦┘ä┘éž»┘Ŗž│ž® ┘ģž¦ž▒ž║ž▒┘Ŗž¬žī ž©┘Ŗž▒┘åž»┘łž▒┘...

ą¦ąŠą╗ąŠą▓č¢čćąĖą╣ ą║ąŠą╝ą░ąĮą┤ąĮąĖą╣ čüą┐čĆąĖąĮčé čā ą╗ąĖąČąĮąĖčģ ą┐ąĄčĆąĄą│ąŠąĮą░čģąĮą░ XXII ąŚąĖą╝ąŠą▓ąĖčģ ą×ą╗č¢ą╝ą┐č¢ą╣čüčīą║ąĖčģ č¢ą│čĆą░čģ ą£č¢čüčåąĄ ą┐čĆąŠą▓ąĄą┤ąĄąĮąĮčÅą╗ąĖąČąĮąŠ-ą▒č¢ą░čéą╗ąŠąĮąĮąĖą╣ ą║ąŠą╝ą┐ą╗ąĄą║čü ┬½ąøą░čāčĆą░┬╗ąöą░čéąĖ19 ą╗čÄč鹊ą│ąŠ 2014ąŻčćą░čüąĮąĖą║č¢ą▓46 ąĘ 23 ą║čĆą░茹Įą¤čĆąĖąĘąĄčĆąĖ ąåą╣ą▓ąŠ ąØč¢čüą║ą░ąĮąĄąĮ ąĪą░ą╝č¢ ą»čāčģąŠčÅčĆą▓č¢ ążč¢ąĮą╗čÅąĮą┤č¢čÅ ą£ą░ą║čüąĖą╝ ąÆąĖą╗ąĄą│ąČą░ąĮąĖąĮ ą£ąĖą║ąĖčéą░ ąÜčĆčÄą║ąŠą▓ ...

Permalink Logo Permalink atau permanen link, adalah URL yang mengarah pada suatu catatan blog atau forum tertentu setelah melewati halaman depan ke arsip. Karena Permalink bersifat permanen tanpa ada batas waktu, maka permalink lebih tahan terhadap kerusakan. Kebanyakan weblogging modern dan sistem perangkat lunak yang mengindikasikan konten memiliki jenis link ini. Jenis website lain menggunakan istilah link permanen, tetapi istilah permalink paling umum digunakan dalam blogosphere. Permalin...

International Sporting Event The World Transplant Games (WTG) are an international multi-sport event, occurring every two years, organized by the World Transplant Games Federation (WTGF). The Games promote amateur sport amongst organ transplant recipients, living donors and donor families. Summer and winter sports alternate years and the event is open to anyone who has received a solid organ transplant including liver, heart, lung, kidney, pancreas or bone marrow. The idea is that people who ...
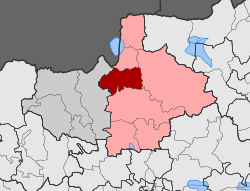
Place in GreeceKalindria ╬Ü╬▒╬╗╬»╬Į╬┤Žü╬╣╬▒The railway station photographed by the French Army in July 1916KalindriaLocation within the regional unit Coordinates: 41┬░06ŌĆ▓51.01ŌĆ│N 22┬░47ŌĆ▓23.79ŌĆ│E / 41.1141694┬░N 22.7899417┬░E / 41.1141694; 22.7899417CountryGreeceAdministrative regionCentral MacedoniaRegional unitKilkisMunicipalityKilkisMunicipal unitCherso ŌĆó Municipal unit157.9 km2 (61.0 sq mi)Elevation120 m (390 ft)Population&...

This article is about the area of Glasgow. For other places with the same name, see Parkhead (disambiguation). Human settlement in ScotlandParkheadScots: PairkheidParkhead Cross, the traditional heart of the districtParkheadLocation within GlasgowOS grid referenceNS625639Council areaGlasgow City CouncilLieutenancy areaGlasgowCountryScotlandSovereign stateUnited KingdomPost townGLASGOWPostcode districtG31Dialling code0141PoliceScotlandFireScottishAmbulanceSco...

Union Army officer. Hollon RichardsonPhotograph circa 1861District Attorney of Chippewa County, WisconsinIn officeJanuary 1, 1861 ŌĆō August 1861Preceded byA. K. GreggSucceeded byRodman Palmer Personal detailsBorn(1835-12-25)December 25, 1835Poland, Ohio, U.S.DiedDecember 24, 1916(1916-12-24) (aged 80)Keyport, Washington, U.S.Resting placeMount Pleasant Cemetery, Seattle, WashingtonPolitical partyRepublicanSpouse Leonora Colista Robinson (m. 1862 ...

Swedish warship Resande Man History Sweden FateSank on 26 November 1660 General characteristics Length27 m Armament22 guns Resande Man was a Swedish warship that sank on 26 November 1660 in the Stockholm archipelago. 25 people survived the sinking while 37 people died. The ship was 27 meters long and had 22 cannons.[1] The wreck was thought to have been found in 2009.[1] New reports that the wreck was found came in May 2012.[2][3] References ^ a b Porne, Lars; ...

Lykke Li Informa├¦├Żo geral Nome completo Li Lykke Timotej Zachrisson Tamb├®m conhecido(a) como Lili Nascimento 18 de mar├¦o de 1986 (37 anos) Origem Ystad, Esc├ónia Pa├Łs Su├®cia G├¬nero(s) Indie rockIndie popEletr├┤nicaAlternativoElectropopDream pop Ocupa├¦├Żo(├Ąes) CantoraCantautoraModeloAtriz Instrumento(s) Vocal, piano, percuss├Żo, auto-harpa, kazoo Per├Łodo em atividade 2007 ŌĆō presente Gravadora(s) Atlantic═Ą WMG═Ą LL Recordings═Ą EMI Afilia├¦├Żo(├Ąes) LIV P├Īgina oficial Ly...

Disputed submerged rock in the Yellow Sea For the island in the Indian Ocean, see Socotra. Ieodo redirects here. For the 1977 film by Kim Ki-young, see Iodo (film). 32┬░07ŌĆ▓22.63ŌĆ│N 125┬░10ŌĆ▓56.81ŌĆ│E / 32.1229528┬░N 125.1824472┬░E / 32.1229528; 125.1824472 Socotra RockSocotra Rock location mapSummit depth4.6 metresTranslation Ieodo (ņØ┤ņ¢┤ļÅä, ķøóµ¢╝Õ│Č) Parangdo (Ēīīļ×æļÅä, µ│󵥬Õ│Č)[1] Suyan Islet (ĶŗÅÕ▓®ńżü, S┼½y├Īn Ji─üo) LocationLocationYellow SeaCoor...

artikel ini perlu dirapikan agar memenuhi standar Wikipedia. Tidak ada alasan yang diberikan. Silakan kembangkan artikel ini semampu Anda. Merapikan artikel dapat dilakukan dengan wikifikasi atau membagi artikel ke paragraf-paragraf. Jika sudah dirapikan, silakan hapus templat ini. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menamba...

Bridge in Brooklyn, New York Squibb Park BridgeSquibb Park Bridge in 2013Coordinates40┬░42ŌĆ▓04ŌĆ│N 73┬░59ŌĆ▓47ŌĆ│W / 40.70111┬░N 73.99639┬░W / 40.70111; -73.99639CrossesFurman StreetLocaleBrooklyn Bridge Park/Brooklyn Heights, Brooklyn, New York CityCharacteristicsDesignUnderspanned suspension bridge (2013), Inverted truss bridge (2020)MaterialBlack locust wood, galvanized cableTotal length400 feet (120 m)Clearance below50 feet (15 m)HistoryArchitectTheodore...

The first movie theater in Korea, Ae Kwan Theater, still in operation in Incheon (2019)Movie theaters have existed in what is now South Korea for over a century now. The earliest theaters arrived in the peninsula beginning in the late Joseon period. The first known dedicated theater was Ae Kwan Theater, which was founded in 1895 and is still in operation as of 2023[update]. Other notable early theaters include the 1907 Dansungsa and the 1910 Umigwan. During the 1910ŌĆō1945 Japanese co...

American baseball player (1907-1997) Baseball player Dolph CamilliFirst basemanBorn: (1907-04-23)April 23, 1907San Francisco, California, U.S.Died: October 21, 1997(1997-10-21) (aged 90)San Mateo, California, U.S.Batted: LeftThrew: LeftMLB debutSeptember 9, 1933, for the Chicago CubsLast MLB appearanceSeptember 23, 1945, for the Boston Red SoxMLB statisticsBatting average.277Home runs239Runs batted in950 Teams Chicago Cubs (1933ŌĆō1934) Philadelphia Phillies...

ž¼ž▓žĪ ┘ģ┘å ž│┘äž│┘äž® ┘ģ┘鞦┘䞦ž¬ ž│┘Ŗž¦ž│ž® ž¦┘äž»┘å┘ģž¦ž▒┘āž¦┘äž»┘å┘ģž¦ž▒┘ā ž¦┘äž»ž│ž¬┘łž▒ ž¦┘äž»ž│ž¬┘łž▒ žŁ┘é┘ł┘é ž¦┘äžź┘åž│ž¦┘å ž¦┘䞬ž¦ž¼ ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘ä┘ā (ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘ä┘āž® ┘ģž¦ž▒ž║ž▒┘Ŗž¬ ž¦┘äž½ž¦┘å┘Ŗž®) ┘ł┘ä┘Ŗ ž¦┘äž╣┘ćž» (┘üž▒┘Ŗž»ž▒┘Ŗ┘ā) ž¦┘äž╣ž¦ž”┘äž® ž¦┘ä┘ģž¦┘ä┘āž® ž¦┘ä┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž¦┘äž«ž¦žĄ ž¦┘äž│┘äžĘž® ž¦┘䞬┘å┘ü┘Ŗž░┘Ŗž® ž▒ž”┘Ŗž│ ž¦┘ä┘łž▓ž▒ž¦žĪ ┘ģž¼┘äž│ ž¦┘ä┘łž▓ž▒ž¦žĪ ž¦┘äž│┘äžĘž® ž¦┘䞬ž┤ž▒┘Ŗž╣┘Ŗž® ž¦┘äž©ž▒┘ä┘ģž¦┘å ž¦┘äž│┘äžĘž® ž¦┘ä┘éžČž¦ž”┘Ŗž® ž¦┘ä┘éžČž¦žĪ ž¦┘ä┘ģžŁ┘ā┘ģž® ž¦┘äž╣┘ä┘Ŗž¦ ž¦┘䞬┘...

Brazil competed at the 2017 World Games[1] in Wroclaw, Poland, from July 20, 2017 to July 30, 2017. Sporting event delegationBrazil at the2017 World GamesIOC codeBRANOCBrazilian Olympic Committeein Wroclaw, Poland20 July 2017 ŌĆō 30 July 2017Competitors10 in 2 sportsWorld Games appearances19811985198919931997200120052009201320172022 Competitors Sports Men Women Mixed Total Events Fistball 9 0 0 9 1 Gymnastics - Aerobics 0 0 8 8 1 Gymnastics - Trampoline 0 1 0 1 1 Powerlifting 0 1...