Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor |
Read other articles:

Cover page of the thesis In 1969, Hillary Rodham wrote a 92-page senior thesis for Wellesley College about the views advocated by community organizer Saul Alinsky, titled There Is Only the Fight . . . : An Analysis of the Alinsky Model.[1] While the work by Rodham as a college student was the subject of much speculation in articles and biographies of Hillary Rodham Clinton in the 1990s, access to the thesis was limited by the college, at the request of the Clinton ...

Jalur kereta api Batuceper–Bandara Soekarno-HattaIkhtisarJenisJalur kereta api lintas cabangSistemJalur kereta api ekspresStatusBeroperasiTerminusBatuceperBandara Soekarno-HattaStasiun2OperasiDibangun olehPT Kereta Api IndonesiaDibuka2017[1]PemilikDirektorat Jenderal PerkeretaapianBadan Pengelola Transportasi JabodetabekOperatorKAI CommuterData teknisLebar sepur1.067 mmElektrifikasi1.500 V DC listrik aliran atasKecepatan operasi60 s.d. 85 km/jam Jalur kereta api Batuceper–Bandara ...
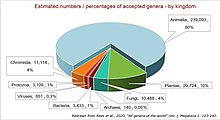
Taxonomic rank directly above species For other uses, see Genus (disambiguation). Genera redirects here. For the operating system, see Genera (operating system). The hierarchy of biological classification's eight major taxonomic ranks. A family contains one or more genera. Intermediate minor rankings are not shown. Genus (/ˈdʒiːnəs/ pl.: genera /ˈdʒɛnərə/) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses.[1] In the hi...

Dieser Artikel behandelt den Popsänger, zum Schriftsteller siehe Alex Jahnke. Alexander Jahnke (2019) ChartplatzierungenErklärung der Daten Singles[1] Halt alle Uhren an DE 34 12.05.2017 (1 Wo.) AT 33 19.05.2017 (1 Wo.) CH 20 14.05.2017 (1 Wo.) Alexander Jahnke (* 29. April 1987 in Lehrte) ist ein deutscher Popsänger, der durch seine Teilnahme an der Casting-Show Deutschland sucht den Superstar Bekanntheit erlangte. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Leben 1.1...

Suburb of Sydney, New South Wales, AustraliaBotanySydney, New South WalesBotany School of Arts (1867), Botany RoadMapPopulation12,960 (2021 census)[1] • Density1,066.6/km2 (2,762/sq mi)Postcode(s)2019Elevation6 m (20 ft)Area7 km2 (2.7 sq mi)Location11 km (7 mi) south of Sydney CBDLGA(s)Bayside CouncilState electorate(s)MaroubraFederal division(s)Kingsford Smith Suburbs around Botany: Sydney Airport Mascot Pagewood Sydney Ai...

For the men's team, see Brazil national rugby sevens team. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Brazil women's national rugby sevens team – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Rugby teamBrazilUnionBrazilian Rugby Confederati...

ديريك ستيفن برينس معلومات شخصية الميلاد 5 فبراير 1969 (العمر 54 سنة)إنغليووود، لوس أنجليس، كاليفورنيا مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم جامعة كارنيغي ميلون المهنة مؤدي أصوات اللغة الأم الإنجليزية اللغات الإنجليزية المواقع IMDB صفحته على IMDB تع

Павел Кра́ловец Народився 16 серпня 1977(1977-08-16) (46 років)ЧехословаччинаГромадянство ЧехіяНаціональність чехДіяльність футбольний арбітрЗнання мов чеська Медіафайли у Вікісховищі Павел Кра́ловец (англ. Pavel Královec; нар. 16 серпня 1977) — чеський футбольний арбітр катег...

Academic journalJournal of Legal Pluralism and Unofficial LawDisciplineLawLanguageEnglishEdited byDik RothPublication detailsFormer name(s)African Law StudiesHistory1969-presentPublisherTaylor & FrancisFrequencyTriannuallyOpen accessDelayed, after 2 yearsStandard abbreviationsISO 4 (alt) · Bluebook (alt1 · alt2)NLM (alt) · MathSciNet (alt )ISO 4J. Leg. Plur. Unoff. LawIndexingCODEN (alt · alt2) · JSTOR (alt) &...

Santhanam at Vallavanukku Pullum Aayudham Thanksgiving Meet Santhanam is an Indian actor who has predominantly appeared in Tamil films as a comedian and also has appeared in films in a lead role.[1] He began his career on television shows including Vijay TV's Lollu Sabha enacting the lead role in spoofs of Tamil films. He was subsequently given a chance by actor Silambarasan in a supporting role in Manmadhan (2004) and then was signed on to appear in films including Sachien (2005) and...

This is a dynamic list and may never be able to satisfy particular standards for completeness. You can help by adding missing items with reliable sources. Map all coordinates using: OpenStreetMap Download coordinates as: KML GPX (all coordinates) GPX (primary coordinates) GPX (secondary coordinates) This list of tallest statues includes completed statues that are at least 50 m (160 ft) tall. The height values in this list are measured to the highest part of the human (or animal) fig...

2018 studio album by ShoppingThe Official BodyStudio album by ShoppingReleased19 January 2018 (2018-01-19)Genre Post-punk[1] funk rock[1] new wave[2] post-rock[2] surf rock[3] Length40:54LabelFatCatProducerEdwyn CollinsShopping chronology Why Choose(2015) The Official Body(2018) All or Nothing(2020) Singles from The Official Body The HypeReleased: 25 September 2017[4][5] The Official Body is the third studio album ...

German World War II submarine Rendering of a Type XXIII submarine History Nazi Germany NameU-2326 Ordered20 September 1943 BuilderDeutsche Werft, Hamburg Yard number480 Laid down8 May 1944 Launched17 July 1944 Commissioned10 August 1944 Fate Surrendered on 14 May 1945 Sunk on 6 December 1946 General characteristics Class and typeType XXIII submarine Displacement 234 t (230 long tons) (surfaced) 258 t (254 long tons) (submerged) Length 34.68 m (113 ft 9 in) (o/a) 26.00...

Statue in Central Park, Manhattan, New York, U.S. Statue of BaltoThe statue in 2010ArtistFrederick RothYear1925 (1925)SubjectBaltoLocationNew York City, New York, U.S.Coordinates40°46′11.9″N 73°58′15.7″W / 40.769972°N 73.971028°W / 40.769972; -73.971028 A bronze statue of Balto by Frederick Roth is installed in Central Park, Manhattan, New York. Balto (1919 – March 14, 1933) was an Alaskan husky and sled dog belonging to musher and breeder Leonhard S...

Rumah baris batu cokelat di Bedford-Stuyvesant, Brooklyn Batu cokelat adalah sebuah batu pasir zaman Trias atau Jura yang dulunya merupakan bahan bangunan yang populer. Istilah batu cokelat atau brownstone ini juga digunakan di Amerika Serikat untuk menyebut sebuah rumah teras (rumah baris) yang dibangun dengan material ini. Ada banyak rumah batu cokelat di beberapa permukiman New York City, khususnya di Brooklyn (Park Slope, Fort Greene, Cobble Hill, Prospect Heights, Brooklyn Heights, dan B...

New Zealand rower (1922–1997) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Edwin Smith rower – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Edwin SmithPersonal informationBorn(1922-09-17)17 September 1922Auckland, New ZealandDied15...

1963 film The Wheeler DealersTheatrical release posterDirected byArthur HillerScreenplay byGeorge GoodmanIra WallachBased onThe Wheeler Dealers1959 novelby George GoodmanProduced byMartin RansohoffStarringJames GarnerLee RemickCinematographyCharles LangEdited byTom McAdooMusic byFrank De VolProductioncompanyFilmwaysDistributed byMetro-Goldwyn-MayerRelease date November 14, 1963 (1963-11-14) Running time107 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishBox office$3,200,000 (US/ Cana...

Komponis Rumania George Enescu (1881-1955) George Enescu (19 Agustus 1881 – 4 Mei 1955), seorang komponis, pianis, pemain biola, dirigen dan guru berkebangsaan Rumania, adalah musikus Rumania yang paling menonjol pada abad ke-20, dan salah satu pemain sandiwara terbesar di waktu yang lalu. Referensi Sumber Axente, Colette, and Ileana Ratiu. 1998. George Enescu: Biografie documentara, tineretea si afirmarea: 1901–1920. Bucharest: Editura muzicala a U.C.M.R. Bentoiu, Pascal. 2...

Election for the governorship of the U.S. state of Ohio 1903 Ohio gubernatorial election ← 1901 November 2, 1903 1905 → Nominee Myron T. Herrick Tom L. Johnson Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 475,560 361,748 Percentage 54.89% 41.76% Governor before election George K. Nash Republican Elected Governor Myron T. Herrick Republican Elections in Ohio Federal government U.S. President 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 186...

Voce principale: Piacenza Calcio 1919. Piacenza Football ClubStagione 1965-1966Sport calcio Squadra Piacenza Allenatore Enrico Radio Presidente Vincenzo Romagnoli Serie C6º posto nel girone A. Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Favari (33) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Mentani (8) StadioBarriera Genova 1964-1965 1966-1967 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti il Piacenza Football Club nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1965-1966. Indi...
