Corps of Royal Artillery Drivers
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

معالي الشريف آرثر جيمس بلفور (بالإنجليزية: Arthur Balfour) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 25 يوليو 1848[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] ويتينغهام [لغات أخرى][8] الوفاة 19 مارس 1930 (81 سنة) [1][2][3][4][5][6] ووكينغ مواطنة المملكة ال

Forza di difesa nazionale etiopeየኢፌዲሪ መከላከያ ሠራዊትEmblema della Forza di difesa nazionale etiope Descrizione generaleNazione Etiopia ServizioForze armate Dimensione150.000 attivi (2022)[1] Guarnigione/QGMinistero della difesa (Etiopia) Battaglie/guerreGuerra Adal-etiopeSpedizione britannica in AbissiniaGuerra egiziano-etiopeGuerra mahdistaGuerra d'AbissiniaGuerra d'EtiopiaSeconda guerra mondialeGuerra di CoreaGuerra d'indipendenza dell'EritreaGuerra di c...

ЛодрефанLaudrefang Країна Франція Регіон Гранд-Ест Департамент Мозель Округ Форбак-Буле-Мозель Кантон Фолькемон Код INSEE 57386 Поштові індекси 57385 Координати 49°05′01″ пн. ш. 6°38′27″ сх. д.H G O Висота 305 - 394 м.н.р.м. Площа 4,7 км² Населення 346 (01-2020[1]) Густота 75,74...

Ampeg AMG1 Fabricant Ampeg Période 1998 - 2002 Fabrication Corps corps plein (solid body) Manche vissé Bois utilisés Corps Acajou, Érable Manche Érable Touche Palissandre Accastillage Chevalet combo cordier/chevalet Wilkinson wraparound Micros Seymour Duncan P-90 en position manche, Seymour Duncan P-90 en position chevalet Couleurs disponibles Amber Burst, Purple Burst, Black Cherry, Transparent Black modifier Guitare électrique en acrylique réalisée par Dan Armstrong et Ampeg e...

Jean Capelle Informações pessoais Data de nascimento 26 de outubro de 1913 Local de nascimento Nacionalidade Bélgica Data da morte 20 de fevereiro de 1977 (63 anos) Seleção nacional Bélgica Jean Capelle (26 de outubro de 1913 - 20 de fevereiro de 1977) foi um futebolista belga que competiu na Copa do Mundo FIFA de 1934[1] e 1938. Referências ↑ «Fifa.com - Seleção Belga na Copa do Mundo FIFA de 1934». Consultado em 13 de julho de 2010. Arquivado do ...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) موريس هالبرين معلومات شخصية الميلاد 3 مارس 1906 بوسطن الوفاة 9 فبراير 1995 (88 سنة) فانكوفر مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم جام

Potret di profil, 1470 (Museum Kunsthistorisches, Wina) Kota Ideal dikaitkan dengan Carnevale, dalam koleksi Museum Seni Walters Fra Carnevale OP (ca. 1420–25 – 1484) adalah seorang pelukis Italia dari Quattrocento, aktif terutama di Urbino. Secara luas dianggap sebagai salah satu seniman paling penuh teka-teki, hanya ada sembilan karya yang secara definitif dikaitkan dengan Carnevale yang dikenal saat ini.[1] Sebagian besar bahkan telah diperdebatkan sebagai asli Carnevale di...
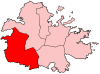
Peta Antigua menampilkan Paroki Saint Mary Saint Mary merupakan sebuah paroki di Antigua dan Barbuda di pulau Antigua. Ibu kotanya Bolans, kota-kota lainnya meliputi Ebenezer, Blubber Valley, Yorks, Seaforths, Sawcolts, Cedar Hall, Bishops, Cades Bay, Claremont, Glebe, Orange Valley Mill, New Division John Hughes dan Johnsons Point. lbsParoki dan dependensi di Antigua dan BarbudaParoki Saint George Saint John Saint Mary Saint Paul Saint Peter Saint Philip Dependensi Barbuda Redonda Artikel be...

البقالطة تقسيم إداري البلد تونس [1] التقسيم الأعلى ولاية المنستير إحداثيات 35°37′N 11°00′E / 35.62°N 11°E / 35.62; 11 السكان التعداد السكاني 17850 معلومات أخرى الرمز البريدي 5090 الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي الرمز الجغرافي 2473826 تعديل مصدري - تعديل &...

Fictional character created by author Tom Clancy This article is about the Tom Clancy character. For the franchise, see Jack Ryan (franchise). For other uses, see Jack Ryan. Fictional character Jack RyanRyanverse characterAlec Baldwin as Jack Ryan in The Hunt for Red October.First appearanceThe Hunt for Red October (1984)Created byTom ClancyPortrayed by Alec Baldwin (1990) Harrison Ford (1992–1994) Ben Affleck (2002) Chris Pine (2014) John Krasinski (2018–2023) In-universe informationOccu...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Богатирьов Георгій ОлексійовичНародився 1896(1896)Помер 1937(1937)місто КиївКраїна Російська імперія СРСРНаціональність росіянинДіяльність політикПартія ВКП(б) У Вікіпедії є статті про інших людей із прізвищем Богатирьов. Георгій Олексійович Богатирьов (нар. 1896(1896) —...

Aztec smallpox victims The history of smallpox in Mexico spans approximately 430 years from the arrival of the Spanish to the official eradication in 1951. It was brought to what is now Mexico by the Spanish, then spread to the center of Mexico, where it became a significant factor in the fall of Tenochtitlan. During the colonial period, there were major epidemic outbreaks which led to the implementation of sanitary and preventive policy. The introduction of smallpox vaccination in New Spain ...

Penumbral lunar eclipse took place on July 6, 1944 The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to be merged, redirected, or deleted.Find sources: July 1944 lunar eclipse – news · newspaper...

The Lion GuardGenrePetualanganDatang usiaDrama komediPengembangFord RileySutradaraHowy ParkinsTom DerosierPengisi suara Max Charles Joshua Rush Dusan Brown Diamond White Atticus Shaffer Bryana Salaz Lagu pembukaCall of the Guard dibuat oleh The Lion Guard ChorusLagu penutupHere Comes the Lion Guard (musim 1–2) dibuat oleh Beau BlackThe Power of the Roar (musim 3) ditulis oleh Ford Riley dan Beau Black diperankan oleh Michael LuwoyePenata musik Christopher Willis (nilai) Beau Black[...

The geology of Kosovo includes a variety of different tectonic and stratigraphic features.[1] Rock outcrop at Brod Geologic history, stratigraphy and tectonics Kacanik Flysch Vrska Cuka granite: An example of Carpatho-Balkan units. Early Paleozoic granites followed by a gap in the Aptian and pelagic clastic rocks from the Cretaceous. Novo Brdo area: Part of the Central Vardar zone. Situated south of a highly tectonized domain. Novo Brdo schist formed in the Triassic in a volcano-sedim...

1961 filmLeoni al soleDirected byVittorio CaprioliWritten byRaffaele La CapriaVittorio CaprioliCinematographyCarlo Di PalmaEdited byNino BaragliMusic byFiorenzo CarpiDistributed byVariety DistributionRelease date1961LanguageItalian Leoni al sole is a 1961 Italian comedy drama film. It is the directorial debut of Vittorio Caprioli.[1] In 2008, the film was included on the Italian Ministry of Cultural Heritage’s 100 Italian films to be saved, a list of 100 films that have changed the ...

German politician Christian LangeChristian Lange in 2016Member of the BundestagIn office1998–2021 Personal detailsBorn (1967-02-27) 27 February 1967 (age 56)Saarlouis, West Germany(now Germany)Political partySPD Christian Lange (born 27 February 1967) is a German lawyer and politician of the Social Democratic Party (SPD) who served as a member of the Bundestag from the state of Baden-Württemberg from 1998 until 2021.[1] Political career Born in Saarlouis, Saarland, Lange becam...

Artículo principal: Pandemia de COVID-19 en México Este artículo se refiere o está relacionado con un evento de salud pública reciente o actualmente en curso. La información de este artículo puede cambiar frecuentemente. Por favor, no agregues datos especulativos y recuerda colocar referencias a fuentes fiables para dar más detalles. Pandemia de COVID-19 en Durango Parte de la Pandemia de COVID-19 en México COVID-19 en DurangoAgente patógenoPatógeno SARS-CoV-2Tipo de patógeno...

1975 boardgame For other uses, see Dungeon (disambiguation). This article is about boardgame. For places of imprisonment, see Dungeon. Dungeon!Original 1975 box coverOther namesThe New Dungeon! (1989)Classic Dungeon! (1992)DesignersDavid R. Megarry[1]PublishersTSR, Inc. (1975—1999)Wizards of the Coast (2012—present)GenresAdventurePlayers1 to 8[2] or 12Setup time10 minutesPlaying time90 minutes[2]ChanceDice rollingWebsite[1] Dungeon! is an adventure board game desig...


