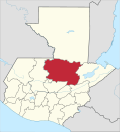
Cobán
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

César et les Romains Allgemeine Informationen Herkunft Québec, Kanada Genre(s) Yéyé Gründung 1965 Auflösung 1968 Letzte Besetzung Gesang Dino L’Espérance Gitarre Daniel Lachance Bass Pierre Sidor (ab 1966) Keyboard Donald Seward Schlagzeug Jacques Moisan Ehemalige Mitglieder Bass Maurice Bélanger (bis 1966) César et les Romains waren in den 1960er Jahren eine Yéyé-Band aus Québec. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Geschichte 2 Diskografie 3 Weblinks 4 Einzelnachweise Geschichte Die Band form...

1991 video by Celine DionUnisonVideo by Celine DionReleased2 July 1991 (1991-07-02)Recorded1990–91GenrePopLength45:00LabelSony Music VideoCeline Dion chronology Unison(1991) The Colour of My Love Concert(1995) Unison is the first home video by Canadian singer Celine Dion, released on VHS on 2 July 1991.[1] It includes the music videos from her English debut album, Unison (1990). Background This collection features never before used version of Calling You, prev...

У Вікіпедії є статті про інші значення цього терміна: Комарів. село Комарів Країна Україна Область Волинська область Район Ковельський район Громада Луківська селищна громада Код КАТОТТГ UA07060230070096054 Основні дані Засноване 1577 Населення 349 Площа 1,522 км² Густота населе

Virgil Misidjan Pemain sepak bola profesional Virgil Misidjan dari 1. FC Nürnberg pada pertandingan kandang melawan Werder Bremen pada 02.02.2019.Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Virgil MisidjanTanggal lahir 24 Juli 1993 (umur 30)Tempat lahir Goirle, BelandaTinggi 1,73 m (5 ft 8 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Willem IINomor 11Karier junior Willem IIKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2012– Willem II 29 (8) * Penampilan dan gol di klub senior hanya d...

Wappen Deutschlandkarte 49.9126388888898.4783333333333Koordinaten: 49° 55′ N, 8° 29′ O Basisdaten Bundesland: Hessen Regierungsbezirk: Darmstadt Verwaltungssitz: Groß-Gerau Fläche: 453,03 km2 Einwohner: 280.308 (31. Dez. 2022)[1] Bevölkerungsdichte: 619 Einwohner je km2 Kfz-Kennzeichen: GG Kreisschlüssel: 06 4 33 NUTS: DE717 Kreisgliederung: 14 Gemeinden Adresse der Kreisverwaltung: Wilhelm-Seipp-Straße 464521 Groß-Gera...

Turkish emergency response vessel ERV Nene Hatun ERV Nene Hatun at Istanbul in 2018. History Turkey NameNene Hatun NamesakeNene Hatun (1857–1955) OwnerDirectorate General of Coastal Safety OperatorDirectorate General of Coastal Safety BuilderSefine Shipyard Cost€31.140 million Launched24 October 2014 In service27 May 2015; 8 years ago (2015-05-27) Identification IMO number: 9675004 MMSI number: 271044031[1] Callsign: TCA3371 General characteristics Class and...

Media art gallery in Tokyo, Japan The entrance to the NTT ICC NTT InterCommunication Center (ICC) is a media art gallery in Tokyo Opera City Tower in Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan. It was established by NTT to commemorate the 100th anniversary of telephone service in Japan and opened in 1997. In addition to permanent and temporary exhibitions featuring international and Japanese artists, ICC holds workshops, performances, symposia, and produces publications with the goal of advancing communication b...

Arseniy YatsenyukАрсеній ЯценюкPerdana Menteri Ukraina ke-15Masa jabatan27 Februari 2014 – 14 April 2016PresidenOleksandr Turchynov (Pjs.)WakilVitaly YaremaPendahuluSerhiy Arbuzov (Pjs.)PenggantiVolodymyr GroysmanKetua Verkhovna RadaMasa jabatan4 Desember 2007 – 12 November 2008PresidenViktor YushchenkoPendahuluOleksandr MorozPenggantiOleksandr Lavrynovych (Pjs.)Menteri Luar Negeri UkrainaMasa jabatan21 Maret 2007 – 4 Desember 2007Perdana MenteriV...

For the advertising agency, see UWG Inc. Uniworld Boutique River Cruise CollectionTypePrivateIndustryCruise lineFoundedLos Angeles, California, 1976 (1976)HeadquartersLos Angeles, California, California, United StatesArea servedWorldwideKey peopleEllen Bettridge, President & CEOProductsRiver cruisesNumber of employees115ParentThe Travel CorporationWebsitewww.uniworld.com River Countess ship at Passau Uniworld Boutique River Cruises is a luxury river cruise line located in Los Angeles...

Genus of gastropods Planorbella Planorbella trivolvis Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Mollusca Class: Gastropoda Subclass: Heterobranchia Superorder: Hygrophila Family: Planorbidae Subfamily: Planorbinae Tribe: Helisomatini Genus: PlanorbellaHaldeman, 1843[1] Planorbella is a genus of freshwater air-breathing snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails, or planorbids, which all have sinistral, or l...

1933 film Hell BelowDirected byJack ConwayScreenplay byLaird DoyleRaymond L. SchrockJohn Lee MahinJohn MeehanBased onPigboats1931 novelby Edward EllsbergProduced byJack ConwayStarringRobert MontgomeryWalter HustonMadge EvansCinematographyHarold RossonEdited byHal C. KernMusic byWilliam AxtDistributed byMetro-Goldwyn-MayerRelease date June 9, 1933 (1933-06-09) Running time101 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishBudget$895,000[1]Box office$1,389,000[1] Hell ...

Sharp increase in measles cases between 2010 and 2019 Young boy with measles in 1968 Measles was declared eliminated from the United States in 2000 by the World Health Organization due to the success of vaccination efforts.[1] However, it continues to be reintroduced by international travelers,[1] and in recent years, anti-vaccination sentiment has allowed for the reemergence of measles outbreaks.[2][3] In 2018, 371 cases of measles were confirmed in the United...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. You can help. The talk page may contain suggestions. (September 2020) This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (Septe...
Drapeau de Jersey drapeau de Jersey Utilisation Caractéristiques Proportions 3:5 Adoption 7 juin 1979 Éléments Croix rouge en diagonale sur fond blanc surmonté d'un blason couronnée modifier Le drapeau de Jersey, dépendance de la Couronne britannique, n’est pas sans rappeler la Croix de saint Patrick, croix rouge sur fond blanc, tel qu’on le retrouve sur le drapeau du Royaume-Uni. Pourtant, l’origine du drapeau remonte bien avant la fondation de l’ordre de Saint-Patrick e...

EZ Aquarii A Datos de observación(Época J2000)Constelación AcuarioAscensión recta (α) 22h 38m 33,4sDeclinación (δ) -15° 18' 07Mag. aparente (V) 12,87Color RojaCaracterísticas físicasClasificación estelar Enana rojaTipo M5VMagnitud absoluta 14.68Variabilidad Flare starSistemaN.º de componentes 2Acompañantes EZ Aquarii BOtras designacionesLuyten 789-6, GCTP 5475.00, LHS 68, GJ 866 A, G 156-031.[editar datos en Wikidata] EZ Aquarii es un sistema triple que dista de la Tier...

性书大亨The People vs. Larry Flynt电影海报基本资料导演米洛斯·福尔曼监制奥利弗·斯通简尼特·杨(Janet Yang)迈克尔·豪斯曼(英语:Michael Hausman)编剧斯科特·亚历山大拉里·卡拉久斯基主演伍迪·哈里森科特妮·洛芙爱德华·诺顿理查德·保罗(英语:Richard Paul)詹姆斯·克伦威尔唐娜·汉诺瓦(英语:Donna Hanover)克利斯丁·格拉夫文森特·斯卡维利(英语:Vincent Schiavelli)配�...

Yermak TimofeyevichIlustrasi abad ke-17 yang menggambarkan Yermak, pemimpin Rusia pertama dalam penjelajahan dan penaklukan SiberiaLahirantara tahun 1532 dan 1542Sepanjang Sungai Chusovaya, Sungai Dvina, Sungai Kama atau Sungai Don, RusiaMeninggal5 atau 6 Agustus, 1585 (Umur 43–53 tahun)Sibiryak, Qashliq, Kekhanan Sibir, RusiaPekerjaanTentara, penjelajah, portir, pelaut, dan bajak laut sungaiDikenal atasSeorang Kazaki yang memimpin penjelajahan dan penaklukan Rusia atas Siberia, pada masa ...
Paghimo ni bot Lsjbot. Alang sa ubang mga dapit sa mao gihapon nga ngalan, tan-awa ang Pigeon Hill. 41°24′57″N 72°14′07″W / 41.41593°N 72.23536°W / 41.41593; -72.23536 Pigeon Hill Bukid Nasod Tinipong Bansa Estado Connecticut Kondado New London County Gitas-on 100 m (328 ft) Tiganos 41°24′57″N 72°14′07″W / 41.41593°N 72.23536°W / 41.41593; -72.23536 Timezone EST (UTC-5) - summer (DST) EDT (UTC-4) ...

Tramlijn Drieschouwen - Kloosterzande Spoorwijdtemeterspoor 1000 mmAangelegd doorZVTMGeopend1916Gesloten1949Huidige statusopgebrokenGeëlektrificeerdneeAantal sporen1 Traject tramlijn van Moerbeke opgebroken tramlijn van IJzendijke opgebroken Drieschouwen remise Brug Axel Kerkdreef Axel lijn van Terneuzen opgebroken Axel lijn naar Y Heike opgebroken Hoek Neuzenscheweg Rondeputten Zaamslag Dorp Zaamslag tramlijn van Philippine opgebroken Zaamslag tramlijn naar Grote Huissenspolder opgebroken ...

No debe confundirse con el T-1 SeaStar, avión de entrenamiento a reacción de la Lockheed. Beechcraft T-1 Jayhawk / T-400 Beechcraft T-1A Jayhawk. Tipo Avión de entrenamiento.Fabricante Raytheon Hawker BeechcraftIntroducido 1992.Estado En servicio activo.Usuario principal Fuerza Aérea de los Estados Unidos.Producción 1992-1997.N.º construidos 180.Coste unitario 4,1 millones de dólares (2005)[1]Desarrollo del Beechjet/Hawker 400A[editar datos en Wikidata] El Raytheon T-1...