109th Infantry Regiment (United States)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Tarakan TimurKecamatanKantor kecamatan Tarakan TimurPeta lokasi Kecamatan Tarakan TimurNegara IndonesiaProvinsiKalimantan UtaraKotaTarakanPemerintahan • Camat...Populasi • Total... jiwa jiwaKode Kemendagri65.71.03 Kode BPS6571010 Luas... km²Desa/kelurahan-/7 Tarakan Timur adalah salah satu kecamatan di Kota Tarakan, Provinsi Kalimantan Utara, Indonesia. Kelurahan di Kecamatan Tarakan Timur Kelurahan Lingkas Ujung Kelurahan Gunung Lingkas Kelurahan Kampung Empat Kelu…

Límites Mapa de la ubicación y límites de Honduras Honduras tiene límites con otros tres países centroamericanos y dos líneas de costas bañadas por mares diferentes. Al norte, el territorio hondureño limita con el mar Caribe, en el Océano Atlántico, hasta el cabo Gracias a Dios, en una extensión de litoral de 671 km aproximadamente. En el Atlántico, Honduras comparte límites marítimos con Belice, Guatemala, Cuba, Jamaica, Gran Caimán, México, Nicaragua, y Colombia. Al Oeste y Nor…

Zoetermeer Entidad subnacional BanderaEscudo Coordenadas 52°03′40″N 4°29′36″E / 52.061111111111, 4.4933333333333Entidad Municipio de los Países Bajos, Ciudad y Lugar poblado cadastral en los Países Bajos • País Países Bajos • Provincia Holanda MeridionalDirigentes • Alcalde Michel Bezuijen (VVD) desde 2020Eventos históricos • Fundación ca. siglo XSuperficie • Total 37,06 km²Altitud
Сайджьо — термін, який має кілька значень. Ця сторінка значень містить посилання на статті про кожне з них.Якщо ви потрапили сюди за внутрішнім посиланням, будь ласка, поверніться та виправте його так, щоб воно вказувало безпосередньо на потрібну статтю.@ пошук посилань са

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Los Angeles (disambiguasi). Los AngelesKotaCity of Los AngelesDowntown Los Angeles, Venice, Griffith Observatory, Hollywood Sign BenderaLambangJulukan: L.A., the City of Angels,[1] Angeltown,[2] La-La Land[3]Lokasi di Los Angeles County di negara bagian CaliforniaLos AngelesLokasi di CaliforniaTampilkan peta CaliforniaLos AngelesLokasi di Amerika SerikatTampilkan peta Amerika SerikatLos AngelesLokasi di Amerika UtaraTampilkan peta Amerika U…

Frederico Castello Branco Clark Embaixador do Brasil no Japão Período 1939-1942 Ministro Osvaldo Aranha Antecessor(a) Pedro Leão Veloso Sucessor(a) Gastão Paranhos do Rio Branco Embaixador do Brasil na França Período 1944-1948 Ministro Pedro Leão Veloso Antecessor(a) Luiz Martins de Souza Dantas Sucessor(a) Hugo Gouthier de Oliveira Gondim Embaixador do Brasil no Vaticano Período 1948-1952 Ministro Raul Fernandes Antecessor(a) Mauricio Nabuco Sucessor(a) Aluysio Guedes Regis Bittencourt …

Die Bauernbefreiung bezeichnet die mehr als hundert Jahre dauernde Ablösung der persönlichen Verpflichtungen der Bauern gegenüber ihren Grund- und Leibherren vorwiegend im 18. und 19. Jahrhundert. Der Begriff wurde 1887 vom Straßburger Volkswirt Georg Friedrich Knapp (1842–1926) eingeführt.[1] Dieser kritisierte auch die Landabtretungen und das sich verschlechternde wirtschaftliche Schicksal der landlosen Schichten in Preußen. Meist werden unter dem Begriff die Abschaffung der pe…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Anna. Grotte AnnaEntrée de la grotte AnnaLocalisationCoordonnées 48° 06′ 18″ N, 20° 37′ 29″ EPays HongrieComitat (Hongrie)|Comitat Borsod-Abaúj-ZemplénDistrict (járás) MiskolcLocalité voisine Lillafüred (Miskolc)Aire protégée Parc national de BükkCaractéristiquesType CalcaireLocalisation sur la carte de HongrieLocalisation sur la carte d’Europemodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata La gro…

Hypericum laricifolium Photo from Cayambe-Coca Park of Ecuador Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Rosids Order: Malpighiales Family: Hypericaceae Genus: Hypericum Section: H. sect. Brathys Species: H. laricifolium Binomial name Hypericum laricifoliumJuss. Hypericum laricifolium is a shrub plant in the family Hypericaceae which is native to Venezuela and Peru.[1] References ^ Hypericum laricifolium Juss. | Plants …

2015 Total Nonstop Action Wrestling pay-per-view event Bound for Glory (2015)Promotional poster featuring various TNA wrestlersPromotionTotal Nonstop Action WrestlingDateOctober 4, 2015CityConcord, North CarolinaVenueCabarrus ArenaAttendance1,800[1]Pay-per-view chronology ← PreviousSlammiversary Next →Slammiversary Bound for Glory chronology ← Previous2014 Next →2016 The 2015 Bound for Glory was a professional wrestling pay-per-view (PPV) event produced by Tot…

إبراهيم عبد السيد معلومات شخصية مواطنة مصر الحياة العملية المهنة طبيب اللغة الأم اللهجة المصرية اللغات العربية، واللهجة المصرية تعديل مصدري - تعديل هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها…

Overview of sports traditions and activities in Iran Iranian champion Kimia Alizadeh Many sports in Iran are both traditional and modern. Tehran, for example, was the first city in West Asia to host the Asian Games in 1974, and continues to host and participate in major international sporting events to this day. Freestyle wrestling has been traditionally regarded as Iran's national sport, however today, football is the most popular sport in Iran. Because of economic sanctions, the annual governm…

3-й Колективний провулок УкраїнаНаселений пункт ЖитомирМісцевість РудняРайон БогунськийІсторичні відомостіКолишні назви Провулок СавицькогоЗагальні відомостіПротяжність 300 мПоштові індекси 10003ТранспортРух двостороннійІнфраструктураЗабудова садибна житловаЗовн…

2001 West Bengal Legislative Assembly election ← 1996 10 May 2001 2006 → All 294 seats in the West Bengal Legislative Assembly148 seats needed for a majorityTurnout75.29% First party Second party Third party Leader Buddhadeb Bhattacharya Mamata Banerjee Pranab Mukherjee Party CPI(M) TMC INC Alliance LF INC+TMC INC+TMC Leader's seat Jadavpur Did not contest[a] Did not contest Seats won 143 60 26 Seat change 10 New 56 Popular vote 13,…

Railway station in Leicestershire, England CroftCroft railway station in 1988General informationLocationNarborough, BlabyEnglandCoordinates52°33′26″N 1°14′44″W / 52.5572°N 1.2455°W / 52.5572; -1.2455Grid referenceSP512957Platforms2HistoryOriginal companySouth Leicestershire RailwayPre-groupingLondon and North Western RailwayPost-groupingLondon, Midland and Scottish RailwayKey dates1 December 1877Opened4 March 1968 (1968-03-04)Closed Croft railwa…

This article is about the Silver Age incarnation of Superman. For the graphic novel, see Superman: Earth One. Comics character SupermanThe Silver Age iteration of Superman, based on as he appeared during the 1960s, on a variant cover of Action Comics 1000Art by Michael Allred.Publication informationPublisherDC ComicsFirst appearanceMore Fun Comics #101 (January 1945)Created byJerry SiegelJoe ShusterIn-story informationAlter egoKal-El/Clark KentPlace of originKryptonTeam affiliationsThe Daily Pla…

Bay in QueenslandWide BayWide Bay at Rainbow Beach, 2016Wide BayLocationQueenslandGroupCoral SeaCoordinates25°54′02″S 153°08′26″E / 25.9006°S 153.1406°E / -25.9006; 153.1406 (Wide Bay)TypebaySettlementsRainbow Beach, Cooloola Wide Bay is a bay of the Coral Sea off the coast of the localities of Rainbow Beach and Cooloola, both in the Gympie Region, Queensland, Australia.[1][2] History Wide Bay was charted and named by Lieutenant James C…

1931 British drama film FascinationDirected byMiles ManderWritten byEliot Crawshay-Williams (play)Victor KendallProduced byClayton HuttonStarringMadeleine CarrollCarl HarbordDorothy BartlamCinematographyHorace WheddonWilly WintersteinEdited byLeslie NormanMusic byJohn ReyndersProductioncompanyBritish International PicturesDistributed byWardour FilmsRelease date15 July 1931Running time70 minutesCountryUnited KingdomLanguageEnglish Fascination is a 1931 British drama film directed by Miles Mander …

Species of flowering plant Hyacinthoides hispanica Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Monocots Order: Asparagales Family: Asparagaceae Subfamily: Scilloideae Genus: Hyacinthoides Species: H. hispanica Binomial name Hyacinthoides hispanica(Mill.) Chouard ex Rothm. Synonyms[1] List Agraphis campanulata (Aiton) Link Agraphis patula (Desf.) Rchb. Endymion campanulatus (Aiton) Parl. Endymion hispanicus (Mill.) Cho…

Reliekbuste van Sint-Amelberga tijdens de Heiligdomsvaart van Maastricht in 2018 Amelberga van Susteren, ook wel Amalberga genoemd, (Susteren, ca. 900) was een heilige abdis. Volgens de overlevering zou zij de drie dochters van koning Zwentibold van Lotharingen (Benedicta, Caecilia en Relindis) in het stiftsklooster in Susteren hebben opgevoed. Dan zou zij geleefd hebben rond 900. Algemeen wordt aangenomen dat zij de eerste abdis van het klooster was, dat een voortzetting was van het door Pepijn…

Ironclad ship The steam ram Dunderberg, Harper's Weekly, 1867 History United States NameDunderberg NamesakeSwedish: thunder(ing) mountain Ordered3 July 1862 BuilderWilliam H. Webb, New York City Laid downby 3 October 1862 Launched22 July 1865 FateNot accepted by U.S.N. Sold to France by 7 May 1867 France NameRochambeau NamesakeComte de Rochambeau Acquiredby 7 May 1867 Commissioned7 August 1867 Renamed7 August 1867 Stricken15 April 1872 FateScrapped, 1874 General characteristics (in French servic…

Advocacy group against racism and fascism, based in the United Kingdom Hope not HateFounded2004; 19 years ago (2004)FounderNick LowlesTypeCivil rights campaign groupAnti-hate organisationFocusHate groupsRacismCivil rightsLocationLondon, United KingdomArea served United KingdomProductCampaigning, lobbying, media, researchKey peopleNick Lowles (Chief Executive) Jenny Levene (Deputy Director) Ruth Smeeth (a director)Websitehopenothate.org.uk Hope not Hate (stylised as HOPE not hat…

Upazila in Chittagong, BangladeshDaudkandi দাউদকান্দিUpazilaCoordinates: 23°32′N 90°43′E / 23.533°N 90.717°E / 23.533; 90.717Country BangladeshDivisionChittagongDistrictComillaArea • Total314.99 km2 (121.62 sq mi)Population (2011) • Total349,910 • Density1,100/km2 (2,900/sq mi)Time zoneUTC+6 (BST)WebsiteOfficial Map of Daudkandi Daudkandi (Bengali: দাউদকান্দি)…

Pemilihan Umum Gubernur Sulawesi Selatan 2007200220135 November 2007Kandidat Calon Amin Sjam Aziz Qahhar Mudzakkar Syahrul Yasin Limpo Partai Golkar PPP PDI-P Pendamping Mansyur Ramli Mubyl Handaling Agus Arifin Nu'mang Suara rakyat 1.404.910 786.792 1.432.572 Persentase 38,76% 21,71% 39,53% Gubernur dan Wakil Gubernur petahanaAmin Sjam dan Syahrul Yasin Limpo Golkar Gubernur dan Wakil Gubernur terpilih Syahrul Yasin Limpo dan Agus Arifin Nu'mang PDI-P Sunting kotak info • L&#…

1982 Indian filmJustice ChowdaryTheatrical release posterDirected byK. Raghavendra RaoScreenplay byK. Raghavendra RaoStory bySatyanandProduced byT. Trivikrama RaoStarringN. T. Rama RaoSrideviCinematographyK. S. PrakashEdited byKotagiri Venkateswara RaoMusic byChakravarthyProductioncompanyVijayalakshmi Art PicturesRelease date 28 May 1982 (1982-05-28) Running time155 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageTelugu Justice Chowdary is a 1982 Indian Telugu-language action drama film, produced by T…

Mexican actress (born 1988) In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Boyer and the second or maternal family name is Rousseau. Angelique BoyerBoyer in 2014BornAngélique Monique-Paulette Boyer (1988-07-04) 4 July 1988 (age 35)Saint-Claude, Jura, FranceCitizenshipFranceMexicoOccupationActressYears active2004–presentPartnerSebastián Rulli (2014–present) Angelique Monique-Paulette Boyer Rousseau[1][2][3] (born 4 July 1988),[4] sim…

Filipino politician and diplomat This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Carlos P. Romulo – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) In this Philippine name, the middle name or maternal family name is Peña and the surname or p…

Chemical compound The correct title of this article is Benz[e]acephenanthrylene. The substitution of any brackets is due to technical restrictions. Benz[e]acephenanthrylene[1][2] Names Preferred IUPAC name Benzo[e]acephenanthrylene Other names Benzo[b]fluoranthene; Benzo[e]fluoranthene; 2,3-Benzofluoranthrene; B[b]F; 2,3-Benzofluoranthene; 4,5-Benzofluoranthene; 2,3-Benzfluoranthene; 3,4-Benzfluoranthene; 3,4-Benzofluoranthene; Benz[b]fluoranthene[1] Identifiers CAS Numbe…

Peta Alabama menunjukkan lokasi Huntsville Huntsville merupakan sebuah kota di Amerika Serikat. Kota ini letaknya di bagian selatan. Tepatnya di negara bagian Alabama. Pada tahun 2010, kota ini memiliki jumlah penduduk sebesar 180.105 jiwa dan memiliki luas wilayah 543,9 km². Kota ini memiliki angka kepadatan penduduk sebesar 857,6 jiwa/km². Pranala luar Situs web resmi. Artikel bertopik geografi atau tempat Amerika Serikat ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wikipedia dengan …
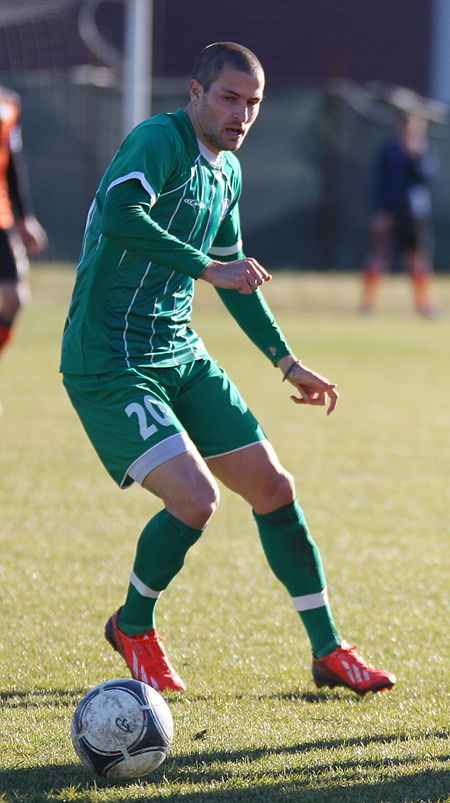

Bulgarian footballer Angel Madzhirov Personal informationFull name Angel Petkov MadzhirovDate of birth (1987-02-18) 18 February 1987 (age 37)Place of birth BulgariaHeight 1.80 m (5 ft 11 in)Position(s) Right backTeam informationCurrent team OborishteNumber 18Senior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2007–2008 Etar 1924 15 (1)2008 Sportist Svoge 2 (0)2009 Marek Dupnitsa 5 (0)2009–2011 Pirin Gotse Delchev 52 (0)2012 Kaliakra Kavarna 9 (0)2012–2013 Dobrudzha Dobrich 27 (1)2014–…


