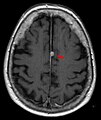
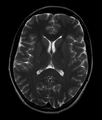
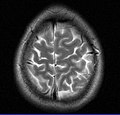
تصوير الدماغ بالرنين المغناطيسي
| |||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Mehdi Mostefa Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Mehdi Mostefa SbaaTanggal lahir 30 Agustus 1983 (umur 40)Tempat lahir Dijon, PrancisTinggi 1,81 m (5 ft 11+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini AC AjaccioNomor 14Karier junior1994–1997 Fontaine-les-Dijon FC1997–1998 Dijon1998–2003 MonacoKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2004–2005 Valence 37 (1)2005–2006 Montluçon - (-)2006–2007 Sète 31 (4)2007–2011 Nîmes 140 (7)2011– Ajaccio 36 (3)...

Bruno Paz Paz en 2018Datos personalesNacimiento Barreiro, Portugal23 de abril de 1998 (25 años)Nacionalidad(es) PortuguesaAngoleñaAltura 1,79 m (5′ 10″)Carrera deportivaDeporte FútbolClub profesionalDebut deportivo 2016(Sporting de Lisboa B)Club KonyasporLiga Superliga de TurquíaPosición CentrocampistaGoles en clubes 8Selección nacionalSelección ANG AngolaDebut 23 de marzo de 2023Part. (goles) 2 (0)Trayectoria Sporting de Lisboa B (2016-2022) → S. C. Farense (...
Fifth video game console generation, including the PlayStation This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Fifth generation of video game consoles – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Part of a series on theHistory of video game...

TempinoDesaNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJambiKabupatenMuaro JambiKecamatanMestongKode Kemendagri15.05.05.1009 Gapura di desa Tempino Tempino adalah sebuah desa dengan bentuk kelurahan di Kecamatan Mestong, Kabupaten Muaro Jambi, Jambi. Tempino dilintasi oleh Jalan Raya Lintas Sumatra dan merupakan pintu gerbang Jambi ditinjau dari Sumatera Selatan. Berjarak 28 Km. dari pusat kota Jambi, merupakan salah satu lumbung minyak bagi provinsi Jambi semenjak zaman Kolonial belanda. Oleh karena itu Be...

تعليم الصغية للإتش تي إم إل إبراز[1][2][3] أو إبانة[1] النحو[4][5] أو تعليم الصياغة أو إبراز الصياغة (بالإنجليزية: Syntax highlighting) هي ميزة في بعض محررات النصوص تقوم بعرض نص رماز المصدر بألوان وخطوط متعددة وفقا لفئة من الشروط.[6][7][8] تشتهر تعليم الصي

سِوِيسْرَا الاِتِّحَاد السُّوَيْسْرِيّ سويسراعلم سويسرا سويسراشعار سويسرا الشعار الوطني(باللاتينية: Unus pro omnibus, omnes pro uno)[1] النشيد: الأرض والسكان إحداثيات 46°47′55″N 8°13′55″E / 46.798562°N 8.231973°E / 46.798562; 8.231973[2] [3] أعلى قمة جبل مونتي روزا، ...

British rock band Matt Nicholls redirects here. For the Canadian football player, see Matt Nichols. Bring Me the HorizonBring Me the Horizon performing at Rock im Park in 2016Background informationOriginSheffield, West Yorkshire, EnglandGenres Metalcore alternative metal alternative rock pop rock electronic rock deathcore (early) DiscographyBring Me the Horizon discographyYears active2004–presentLabels BMG Sony RCA Columbia Visible Noise Epitaph Thirty Days of Night Earache Shock Members Ol...

В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилией Безгин. Игорь Дмитриевич Безгин Дата рождения 8 октября 1936(1936-10-08) Место рождения Харьков, Украинская ССР, СССР Дата смерти 29 сентября 2014(2014-09-29) (77 лет) Место смерти Киев, Украина Гражданство СССР Украина Профессия теат...
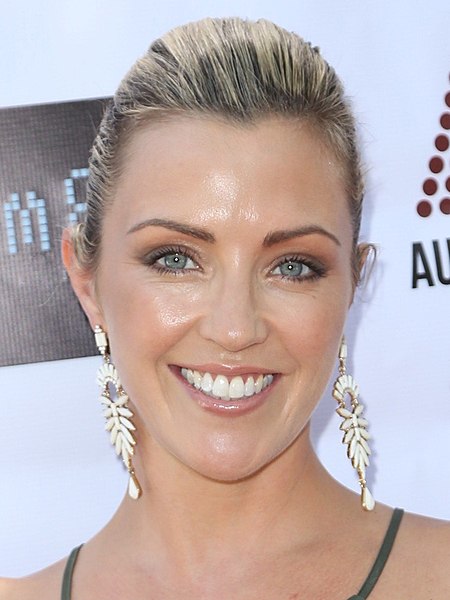

Australian actress (born 1979) This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about living persons that is unsourced or poorly sourced must be removed immediately from the article and its talk page, especially if potentially libelous.Find sources: Jacinta Stapleton – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this te...

Magic intended to turn away harm or evil influences Part of a series onAnthropology of religionTwo ancient anthropomorphic figures from Peru Basic concepts Afterlife Animism Augury Communitas Comparative religion Divination Divine language Evolutionary origin of religion Fetishism Great Spirit Henotheism Initiation Liminality Magic (supernatural) Mana Monotheism Nympholepsy Oracle Polytheism Rite of passage Ritual Sacred language Sacred–profane dichotomy Sacred site Shamanism Soul dualism S...

Areas with mostly commercial buildings This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Commercial area – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Aerial view of the Financial District in Downtown Toronto Main Street in Chesterton, India...

Sekelompok orang sedang menikmati makanan sambil berlesehan di Jalan Malioboro, Yogyakarta. Lesehan di Blok M, Jakarta Lesehan adalah suatu budaya dalam hal memperjualbelikan makanan atau sesuatu barang sembari duduk di tikar/lantai. Makanan atau barang yang diperjualbelikan turut digelar pada saat lesehan sehingga pengunjung bisa melihat dan memilihnya dengan santai. Budaya Lesehan yang sangat terkenal di Indonesia adalah di daerah Yogyakarta dan hal ini menjadi salah satu daya tarik tersend...

2004 Angolan filmThe HeroFrench theatrical poster.Directed byZézé GamboaWritten byCarla BaptistaPierre-Marie GouletFernando VendrellProduced byFernando VendrellStarringOumar Makena DiopMilton 'Santo' CoelhoMaria CeiçaCinematographyMario MasiniEdited byAnna RuizMusic byDavid LinxDiederik WisselsRelease dates May 18, 2004 (2004-05-18) (Cannes) December 7, 2005 (2005-12-07) (France) Running time97 minutesCountriesAngolaFrancePortugalLanguagePortuguese The...

Vietnamese television network For Virtual TV, Pakistan, see Virtual University of Pakistan § Distant teaching. For the ship, see Finnish patrol gunboat VTV-1. Television channel VTV1CountryVietnamBroadcast areaVietnamAsia-Pacific (via satellite)Worldwide (via satellite and Internet)HeadquartersVTV Tower, 43 Nguyen Chi Thanh Street, Ngoc Khanh, Ba Dinh District, HanoiProgrammingLanguage(s)VietnameseFrench (news program)Picture format1080i HDTVOwnershipOwnerVietnam TelevisionSister channe...

American aircraft remanufacturer Nextant AerospaceWebsitenextantaerospace.comvte Nextant Aerospace is a United States-based company specializing in the remanufacturing of business jets.[1] Founded in 2007, Nextant is the first company to introduce the concept of aircraft remanufacturing to the business jet market.[1] Nextant 400XT Nextant 400XT Exterior. The company's first product is the Nextant 400XT, a modified and modernized Beechjet 400A/XP that sells for approximately on...

James Clay James Clay (20 December 1804, London – 26 September 1873, Brighton)[1] was an English politician and a leading whist authority.[2] Early life and education Clay was born in Bloomsbury, London, son of merchant James Clay (1764–1828) and Mary (1766/7–1840). He was educated at Winchester College, then went up to Balliol College, Oxford, where he took a gentleman's third in classics.[3][4] Career Clay was MP for Kingston upon Hull from July 1847 un...
John C. StetsonUnited States Secretary of the Air ForceIn officeApril 6, 1977 – May 18, 1979PresidentJimmy CarterPreceded byJames W. PlummerSucceeded byHans Mark Personal detailsBornJohn Charles Stetson(1920-09-06)September 6, 1920Chicago, Illinois, U.S.DiedAugust 1, 2007(2007-08-01) (aged 86)Lake Forest, Illinois, U.S.EducationMassachusetts Institute of Technology (BS)Northwestern University John Charles Stetson (September 6, 1920 – August 1, 2007) was an American governmen...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Roland – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Frankish military leader under Charlemagne This article is about the legendary figure. For other uses, see Roland (disambiguation). RolandA s...

State Constitution Not to be confused with Constitution of India. The 1816 (superseded) and 1851 Constitutions of the State of Indiana, located in the Indiana Statehouse Rotunda. The Constitution of Indiana is the highest body of state law in the U.S. state of Indiana. It establishes the structure and function of the state and is based on the principles of federalism and Jacksonian democracy. Indiana's constitution is subordinate only to the U.S. Constitution and federal law. Prior to the ena...

P.P. Tomasi della Torretta, Datierung unbekannt Pietro Paolo Tomasi, Markgraf della Torretta (* 7. April 1873 in Palermo; † 4. Dezember 1962 in Rom) war ein italienischer Diplomat und Politiker. Vom 7. Juli 1921 bis zum 26. Februar 1922 war er im Kabinett Bonomi I Außenminister seines Landes. Leben und diplomatische Karriere Nach einem Studium der Rechtswissenschaften an der Universität Palermo trat Tomasi 1890 in den diplomatischen Dienst ein, in dem er bis zum Kabinettschef (heute etwa:...